URL class in Java is a part of java.net package that makes it easy to work with Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). URL is simply a string of text that identifies all the resources on the internet, telling us the address of the resource, how to communicate with it, and retrieve something from it. This article covers the key components, classes, constructors, methods, and examples of using the URL class in Java applications.
Components of a URL
A URL can have many forms. The most general however follows a three-component system as proposed below:
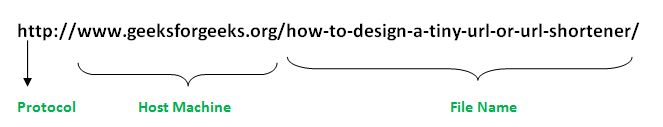
- Protocol: "http" is the protocol here.
- Host Machine: Name of the machine on which the resource lives (www.geeksforgeeks.org)
- File Name: The pathname to the file on the machine.
- Port Number: Port number to which to connect (typically optional).
URL Class
- The
URL class in Java is a fundamental component for accessing resources on the internet - The URL can point to various types of resources such as static files, dynamic content, API's.
- The
URL class provides constructors and methods to create URL objects and retrieve their components.
Constructors of URL class
1. URL(String address): It creates a URL object from the specified String.
Example:
try {
URL url = new URL("https://www.example.com");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
2. URL(String protocol, String host, String file): Creates a URL object from the specified protocol, host, and file name.
Example:
try {
URL url = new URL("http", "www.example.com", "/path/to/resource");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
3. URL(String protocol, String host, int port, String file): Creates a URL object from protocol, host, port, and file name.
Example:
try {
URL url = new URL("https", "www.example.com", 443, "/path/to/resource");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
4. URL(URL context, String spec): Creates a URL object by parsing the given spec in the given context.
Example:
try {
URL baseUrl = new URL("https://www.example.com");
URL relativeUrl = new URL(baseUrl, "/path/to/resource");
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
5. URL(String protocol, String host, int port, String file, URLStreamHandler handler): Creates a URL object from the specified protocol, host, port number, file, and handler.
Example:
try {
URL url = new URL("http", "www.example.com", 80, "/path/to/resource", new MyCustomHandler());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
6. URL(URL context, String spec, URLStreamHandler handler): Creates a URL by parsing the given spec with the specified handler within a specified context.
Example:
try {
URL baseUrl = new URL("https://www.example.com");
URL relativeUrl = new URL(baseUrl, "/path/to/resource", new MyCustomHandler());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Java URL Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|
| getAuthority() | Returns the authority part of URL or null if empty |
| getDefaultPort() | Returns the default port used |
| getFile() | Returns the file name. |
| getHost() | Return the hostname of the URL in IPv6 format |
| getPath() | Returns the path of the URL, or null if empty |
| getPort() | Returns the port associated with the protocol specified by the URL |
| getProtocol() | Returns the protocol used by the URL |
| getQuery() | Return the query part of the URL, which is the portion following the ? character, used to pass parameters to a web application. |
| getRef() | Return the reference part of the URL, which is the portion following the # character, typically used to navigate to a specific section within a web page. |
| toString() | As in any class, toString() returns the string representation of the given URL object. |
Example: The below Java program demonstrate the working of URL.
Java // Java program to demonstrate working of URL import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException { // Creating a URL with string representation URL u1 = new URL( "https://www.google.co.in/?gfe_rd=cr&ei=ptYq" + "WK26I4fT8gfth6CACg#q=geeks+for+geeks+java"); // Creating a URL with a protocol, hostname, and // path URL u2 = new URL("http", "www.geeksforgeeks.org", "/jvm-works-jvm-architecture/"); URL u3 = new URL( "https://www.google.co.in/search?" + "q=gnu&rlz=1C1CHZL_enIN714IN715&oq=gnu&aqs=chrome..69i57j69i60l5.653j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8#q=geeks+for+geeks+java"); // Printing the string representation of the URL System.out.println(u1.toString()); System.out.println(u2.toString()); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Different components of URL3:"); // Retrieving the protocol for the URL System.out.println("Protocol: " + u3.getProtocol()); // Retrieving the hostname of the URL System.out.println("Hostname: " + u3.getHost()); // Retrieving the default port System.out.println("Default port: " + u3.getDefaultPort()); // Retrieving the query part of the URL System.out.println("Query: " + u3.getQuery()); // Retrieving the path of the URL System.out.println("Path: " + u3.getPath()); // Retrieving the file name System.out.println("File: " + u3.getFile()); // Retrieving the reference System.out.println("Reference: " + u3.getRef()); } } Output:

Similar Reads
Java Reader Class Reader class in Java is an abstract class used for reading character streams. It serves as the base class for various subclasses like FileReader, BufferedReader, CharArrayReader, and others, which provide more efficient implementations of the read() method. To work with the Reader class, we must ext
6 min read
Java Class File A Java class file is a file containing Java bytecode and having .class extension that can be executed by JVM. A Java class file is created by a Java compiler from .java files as a result of successful compilation. As we know, a single Java programming language source file (or we can say .java file)
5 min read
Object Class in Java Object class in Java is present in java.lang package. Every class in Java is directly or indirectly derived from the Object class. If a class does not extend any other class then it is a direct child class of the Java Object class and if it extends another class then it is indirectly derived. The Ob
7 min read
Wrapper Classes in Java A Wrapper class in Java is one whose object wraps or contains primitive data types. When we create an object in a wrapper class, it contains a field, and in this field, we can store primitive data types. In other words, we can wrap a primitive value into a wrapper class object. Let's check on the wr
6 min read
Static class in Java Java allows a class to be defined within another class. These are called Nested Classes. Classes can be static which most developers are aware of, henceforth some classes can be made static in Java. Java supports Static Instance Variables, Static Methods, Static Block, and Static Classes. The class
3 min read