Types of Circuit - Series, Parallel, Properties, Examples
Last Updated : 17 Apr, 2025
Circuits are pathways or networks that allow the flow of electrical current between different components or elements. Circuits are fundamental to the functioning of electronic devices and systems
This article talks about what are circuits, types of circuits, series circuits, parallel circuits, and various other types of circuit along with it's properties.
What are Circuits?
Circuits or Electrical Circuits are defined as a closed loop through which electricity can flow. These closed loops, or paths, are formed by a network of electrical components. Circuits are closed paths that have the same starting and ending points. The paths of the circuits are constructed with the help of electrical wires. The circuit contains electrical components like bulb, battery, electric wire, switch, etc. The point from which electrons start flowing is termed the source, while the point where electrons leave the circuit is termed the return.
Types of Circuits
Depending on the types of connection and power source used, circuits can be classified into various types. Based on the connection there are primarily two types of circuits:
- Series Circuits
- Parallel Circuits
Series Circuits
Series Circuits are defined as a type of circuits in which the electrical components or resources are arranged one after other. This type of connection is also termed as an end-to-end connection or cascade connection. In the series circuit there is only one path of the flow of current. In this circuits, the amount of current that flows the all the components is same.

Properties of Series circuit
- The amount of current that flows through each component in the circuit is same.
- The Voltage that is supplied in the circuit is sum total of all the individual voltage across each component.
V = V1 + V 2+ V3 + ... + Vn
- The total resistance across the circuit is the sum total of all the resistances offered by each component.
R = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... + Rn
- The equivalent electrical resistance is equivalent to the sum total of all individual resistances.
- The equivalent electrical resistance offered by the series circuit is greater than each individual resistance.
R > R1, R > R2, ... , R > Rn
Example: If 2 resistors of 3 ohm and 4 ohm are connected in series. What is the resistance of the circuit?
Solution:
Since the resistors are connected in series,
to calculate resistance of the circuit follow these steps
R = R1 + R2
R = 3 + 4
R = 7
R = 7 ohm
Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits are defined as a type of circuit in which various electrical components or resources are connected across one another in parallel. This circuit contains two or more paths for the flow of electric current. In this circuit the amount of voltage across each resource or components is constant or same. The amount of electric current through each component is variable.

Properties of Parallel Circuits
- The voltage or potential difference is same across each electrical components in the circuit.
- The total amount of current flowing through the circuit is sum total of all the individual electric current flowing through each components.
I = I1 + I2 + I3 + ... + In
- The equivalent electrical resistance of the circuit is calculated in following way
R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... + 1/Rn
- The equivalent electrical resistance is the minimum of all the individual resistance.
R < R1, R < R2, ..., R < Rn
Example: If 2 resistors of 3ohm and 4ohm are connected in parallel. What is the resistance of the circuit?
Solution:
Since the resistors are connected in parallel,
to calculate resistance of the circuit follow these steps
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2
1/R = 1/3 + 1/4
1/R = 4+3/12
1/R = 7/12
R = 12/7
R = 1.71 ohm
Difference between of Series and Parallel Circuits
The difference between series and parallel circuit is tabulated below:
Series Circuits | Parallel Circuits |
|---|
In series circuits, there will be one and only one path of the flow of current. | In parallel circuits, there will be two or more than two paths of the flow of current. |
In series circuits, the electrical components are arranged in a single path. | In parallel circuits, the electrical components are arranged in parallel to each other. |
The total voltage flowing across the circuit is sum total of all the individual voltages across each electrical components. | The voltage or potential difference across the parallel circuits is same or constant across the circuits. |
The equivalent electrical resistance is equal to the sum total of all the individual resistances. | The equivalent electrical resistance is calculated by taking sum of reciprocal of individual resistances. |
If there is any break in the circuit, the whole circuit breaks. | Failure of a single point did not break the whole circuit. |
Some Other Circuits
Apart from the above there are other circuits as well. These other types of circuits are mentioned below:
- AC Circuits
- DC Circuits
- Open Circuit
- Closed Circuit
- Series Parallel Circuit
- Linear Circuit
- Non-Linear Circuit
- Unilateral Circuit
- Bilateral Circuit
- Star-Delta Circuit
Let's discuss these circuits one by one.
AC Circuits
AC circuits are defined as a type of circuit in which electricity flow and it's magnitude changes from zero to its maximum value. Simply we can say, AC circuit uses alternating current power source. In AC circuits, the direction of flow of current changes alternatively. The voltage level in a AC circuit will vary in sinusoidal form. To perform long-distance power transmission we prefer the use of AC circuit. In AC circuit, there is a higher risk of electric shock.
AC voltage: V = V0sinωt
AC current: I = I0sinωt

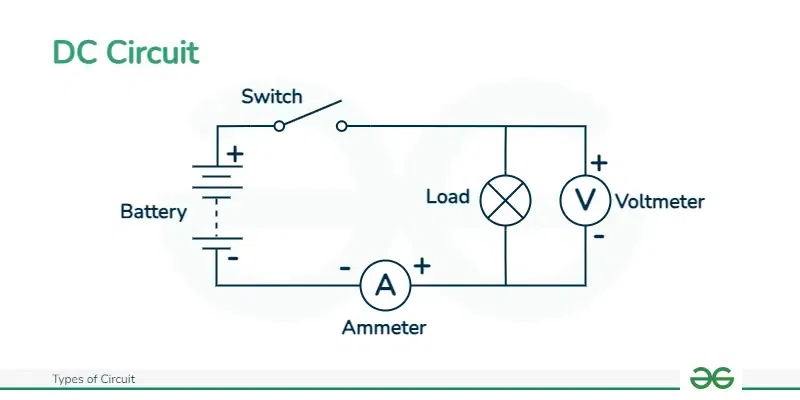
DC Circuits
DC circuits are defined as a type of circuit in which the current flow only in a single direction. It is generally used in solar cells, batteries, electronic devices, etc. To perform simple applications, we mostly prefer DC circuits. The voltage level in a DC circuit is constant. To perform short-distance power transmission we prefer the use of AC circuit. In DC circuit, there is a low risk of electric shock.
Open Circuits
Open circuit is defined as an electric circuit in which there is no flow of electric current through the circuit. In an open circuit, the terminals are not connected with each other. This type of circuit generally consists of path which are incomplete. It is generally used to represent the off state of the circuit. Example of open circuits include socket, flashlight etc.

Closed Circuits
Closed circuit is defined as an electric circuit in which there is flow of electric current through the circuit. In a closed circuit, the terminals are connected with each other. In a closed circuit, the path is complete. It is generally used to represent the on state of the circuit.

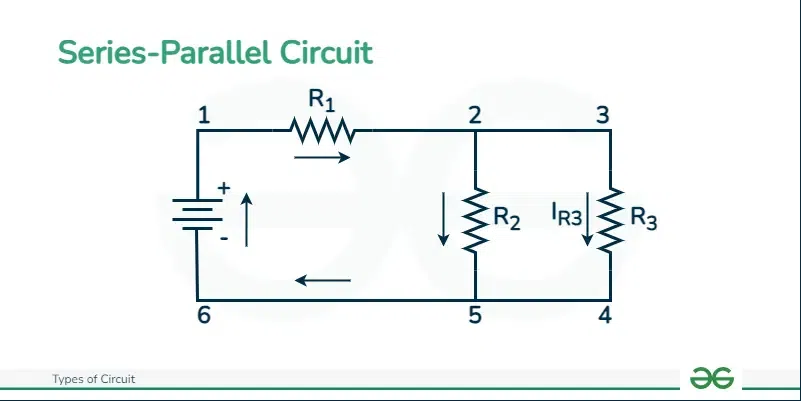
Series-Parallel Circuit
Series-Parallel Circuit are circuits in which there is use of both series and parallel type of circuits. This circuit includes the features of both the circuit and improves its efficiency.
Linear Circuit
Linear circuit is an electric circuit in which the present elements or characteristics, their values does not change. It remains constant and does not get affected by any change in voltage or current flowing in the circuit.

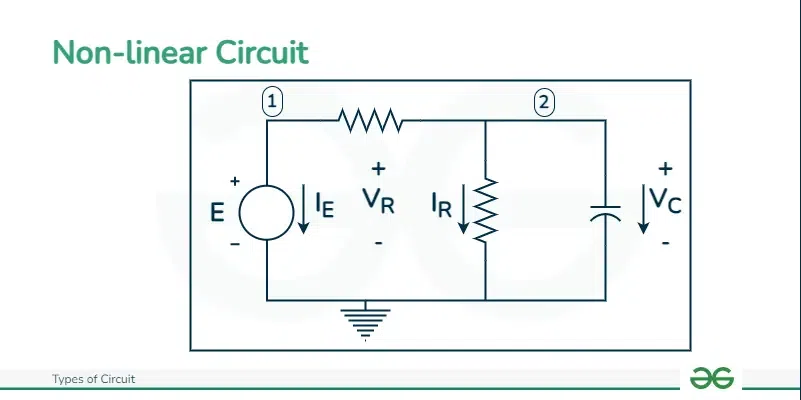
Non-linear Circuit
Non Linear circuit is an electric circuit in which the present elements or characteristics, their values does change. The properties or characteristics values are variable and does get affected by any change in voltage or current flowing in the circuit.
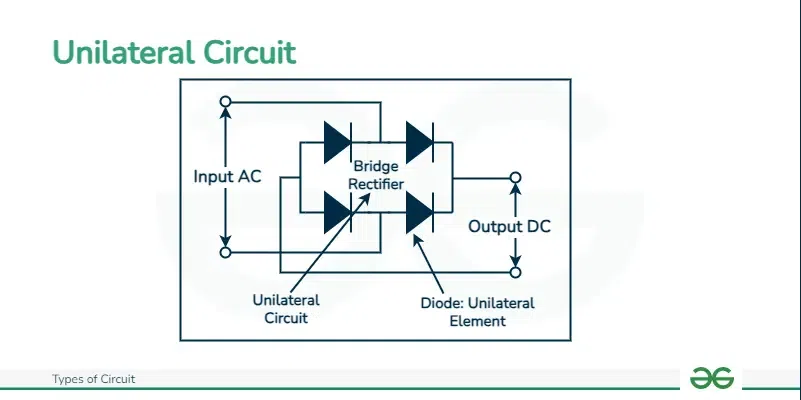
Unilateral Circuits
Unilateral circuit is defined as a circuit in the properties or characteristics of the circuit changes when either the current direction or voltage direction changes. This type of circuit allows the flow of current only in one direction. Example: Diode Rectifier
Bi-lateral Circuits
Bi-lateral circuit is defined as a circuit in the properties or characteristics of the circuit does not change when either the current direction or voltage direction changes. This type of circuit allows the flow of current in two direction without any change in the behaviour of circuit.

Star Delta Circuit
A star-delta circuit is also known as a star-delta starter. It is circuit present in the speed control system of three-phase induction motors. This technique involves connecting the motor windings in a star (Y) configuration during starting and then switching to a delta (Δ) configuration once the motor reaches a certain speed

Parts of Circuit
A circuit consists of following parts:
- Voltage Source
- Conductors
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Inductors
- Diodes
- Switches
Uses of Circuits
The different applications of circuits are tabulated below:
- Circuits act as a medium to transfer some resources.
- It is useful in transferring electrical energy.
- It is used to transfer signals.
- It is used to control the current and other property as per the need of the circuit.
Conclusion
Electrical Circuits are important concept in electrical field. This article discusses that circuit are a closed loop through which electric current flows. There are two types of circuits that is series and parallel circuits. Series circuit involve connection in which all the electrical components are arranged in a single path. While in parallel circuit, there are two or more paths for the flow of current. We have also learnt various other types of circuits in this article.
Related Articles
Similar Reads
Parallelogram | Properties, Formulas, Types, and Theorem A parallelogram is a two-dimensional geometrical shape whose opposite sides are equal in length and are parallel. The opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal in measure and the Sum of adjacent angles of a parallelogram is equal to 180 degrees.A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon (quadrilater
10 min read
How to Solve Parallel Circuit A parallel circuit is one of the important electric circuits. To solve parallel circuits, we use different formulas accordingly. We can calculate the total current, total resistance, voltage, and current through specific resistors accordingly to solve parallel circuits. The total current in a parall
8 min read
Total Resistance in a Parallel Circuit The opposition to the current flowing in a circuit is called resistance. In other words, resistance is the measurement of opposition of current in a circuit. The SI unit of resistance is Ohm (Ω). Commonly it is denoted as R. According to Ohm's law, resistance is ratio of voltage applied to current f
6 min read
What is the Difference Between Series and Parallel Circuits? To understand the difference between series and parallel circuits, let us first define what a circuit is. An electric circuit is defined as a closed loop of conducting elements through which current can flow. An electric circuit basically consists of the following components: Voltage or a Current so
6 min read
Resistors in Series and Parallel Combinations Resistors are devices that obstruct the flow of electric current in the circuit. They provide the hindrance to the path of the current which flows in the circuit. Resistors consume the current in any circuit and convert them to other forms of energy as required. Various resistors can be added to the
9 min read