What is Load Balancer & How Load Balancing works?
Last Updated : 17 Apr, 2025
A load balancer is a crucial component in system design that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers. Its main purpose is to ensure that no single server is overburdened with too many requests, which helps improve the performance, reliability, and availability of applications.

What is a Load Balancer?
A load balancer is a networking device or software application that distributes and balances the incoming traffic among the servers to provide high availability, efficient utilization of servers, and high performance. A load balancer works as a “traffic cop” sitting in front of your server and routing client requests across all servers
- Load balancers are highly used in cloud computing domains, data centers, and large-scale web applications where traffic flow needs to be managed.
- It simply distributes the set of requested operations effectively across multiple servers and ensures that no single server bears too many requests.
What will happen if there is NO Load Balancer?
Before understanding how a load balancer works, let's understand what problem will occur without the load balancer through an example.
 Without Load Balancing
Without Load Balancing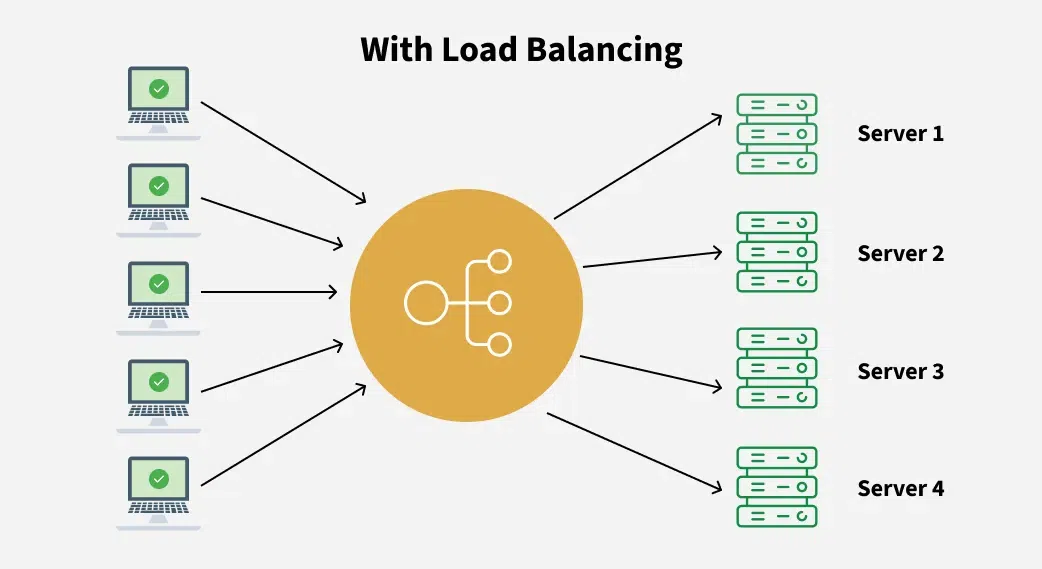 With Load Balancing
With Load BalancingThere are three main problems with this model:
- Single Point of Failure:
- If the server goes down or something happens to the server the whole application will be interrupted and it will become unavailable for the users for a certain period. It will create a bad experience for users which is unacceptable for service providers.
- Overloaded Servers:
- There will be a limitation on the number of requests that a web server can handle. If the business grows and the number of requests increases the server will be overloaded.
- Limited Scalability:
- Without a load balancer, adding more servers to share the traffic is complicated. All requests are stuck with one server, and adding new servers won’t automatically solve the load issue.
Key characteristics of Load Balancers
Below are some of the Key characteristics of Load Balancers:
- Traffic Distribution: To keep any one server from becoming overburdened, load balancers divide incoming requests evenly among several servers.
- High Availability: Applications' reliability and availability are improved by load balancers, which divide traffic among several servers. The load balancer reroutes traffic to servers that are in good condition in the event that one fails.
- Scalability: By making it simple to add servers or resources to meet growing traffic demands, load balancers enable horizontal scaling.
- Optimization: Load balancers optimize resource utilization, ensuring efficient use of server capacity and preventing bottlenecks.
- Health Monitoring: Load balancers often monitor the health of servers, directing traffic away from servers experiencing issues or downtime.
- SSL Termination: Some load balancers can handle SSL/TLS encryption and decryption, offloading this resource-intensive task from servers.
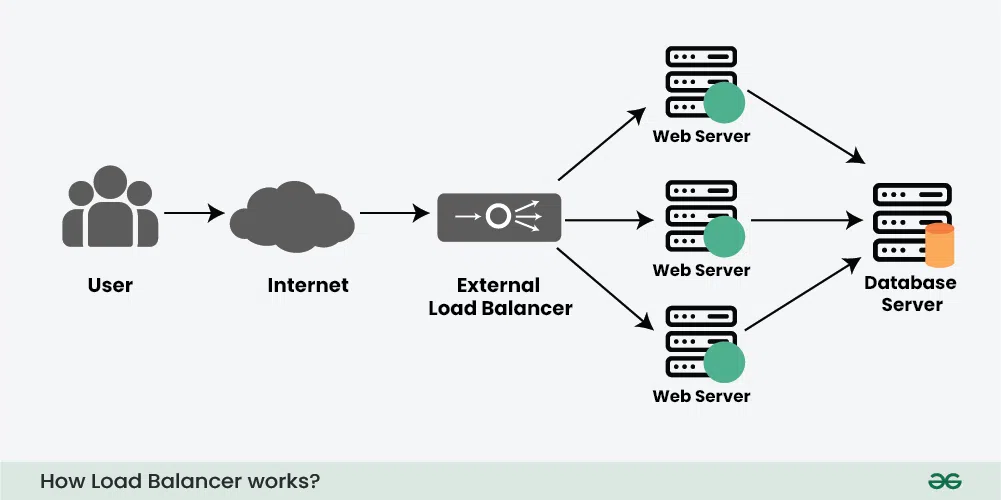
How Load Balancer Works?
Let us see how load balancer works in simple steps:
- Receives Incoming Requests: When users try to access a website or application, their requests first go to the load balancer instead of directly to a server.
- Checks Server Health: The load balancer continuously monitors the status of all servers. It checks which servers are healthy and ready to handle requests.
- Distributes Traffic: Based on factors like server load, response time, or proximity, the load balancer forwards each request to the most appropriate server. This helps avoid any server getting overloaded.
- Handles Server Failures: If a server goes down or becomes unresponsive, the load balancer automatically stops sending traffic to that server and redirects it to others that are still functioning properly.
- Optimizes Performance: By spreading traffic efficiently and using healthy servers, load balancers improve overall performance and reduce delays
Types of Load Balancers
1. Hardware Load Balancers
These are real devices that are set up within a data center to control how traffic is distributed among servers. They are highly reliable and work well since they are specialized devices, but they are costly to purchase, scale, and maintain. They're often used by large companies with consistent, high traffic volumes.
2. Software Load Balancers
These are software or programs that divide up traffic among servers. They operate on pre-existing infrastructure (on-premises or in the cloud), in contrast to hardware load balancers.
- Because software load balancers make it simple to modify resources as needed, they are more scalable and less expensive.
- They are adaptable and appropriate for a range of businesses, including ones that use the cloud.
Software vs. Hardware Load Balancers: Which one to choose?
The choice between software and hardware load balancers depends on various factors such as the scale of your application, budget constraints, and specific performance requirements.
3. Cloud Load Balancers
Cloud load balancers, which are offered as a service by cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, automatically distribute traffic without requiring physical hardware. Users just pay for the resources they use, and they are very scalable. They are perfect for dynamic workloads since they can readily interface with cloud-based apps and adjust to traffic spikes.
uses IP addresses and port numbers (TCP/UDP) to distribute traffic while operating at the OSI model's transport layer. Because Layer 4 load balancers do not examine the data being sent, they are quicker and better suited for easier routing jobs. They effectively manage high traffic volumes with little overhead.
These load balancers function at the OSI model's application layer, so they can route traffic according to specific application data, such as HTTP headers, URLs, cookies, or user sessions. They are able to make more complex routing choices, like sending traffic to various servers according on user preferences or the type of content. Web applications that need content-based routing frequently use them.
These distribute traffic across servers located in different geographical regions, improving user experience by routing requests to the closest or most responsive server. They help reduce latency and provide disaster recovery by ensuring service availability across multiple data centers in case of server or region failures.
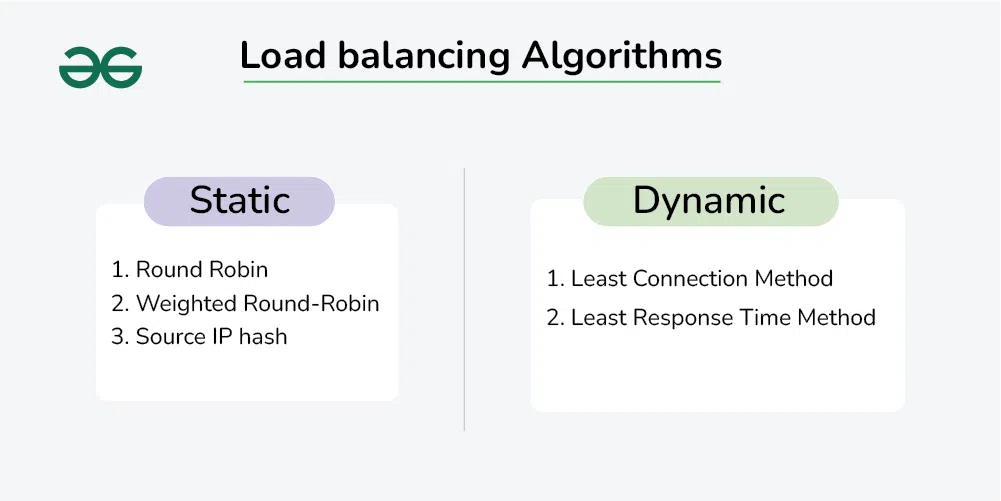
Load Balancing Algorithms
We need a load-balancing algorithm to decide which request should be redirected to which backend server. The different system uses different ways to select the servers from the load balancer. Companies use varieties of load-balancing algorithm techniques depending on the configuration. Load balancing algorithms can be broadly categorized into two types: Dynamic load balancing and Static load balancing.
Static load balancing involves predetermined assignment of tasks or resources without considering real-time variations in the system. This approach relies on a fixed allocation of workloads to servers or resources, and it doesn't adapt to changes during runtime.
Types of Static Load Balancing Algorithms
- Round Robin
- Weighted Round-Robin
- Source IP hash
Making judgments in real time regarding the distribution of incoming network traffic or computing burden among several servers or resources is known as dynamic load balancing. This method adjusts to the system's shifting circumstances, including changes in resource availability, network traffic, and server load.
Types of Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithms
- Least Connection Method
- Least Response Time Method
The system's properties, the type of workload, and the required degree of flexibility all influence the decision between dynamic and static load balancing. While static load balancing might work well in situations that are more predictable, dynamic load balancing is frequently preferred in dynamic, high-traffic environments.
Benefits of using a Load Balancer
- Increases performance: Any web server when given huge traffic may not perform well and can give down time to user and thereby degrading the performance. However, Load Balancer makes sure user experience no down time and gets better performance.
- Increase Scalability: Load balancer along with auto scaling will make sure that if your minimum number of servers are getting high traffic then more servers will be provisioned and load balancer will automatically accommodate in the server cluster.
- Efficiently manages failure: Load balancer makes sure that any server that is experiencing issue or is not healthy to serve user request are been kept away from the distribution.
- Prevent Traffic Bottleneck: A software load balancer anticipates when there will be a significant surge in traffic to the servers and alerts us to take the necessary precautions.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Load balancers distribute incoming requests or tasks across multiple servers, ensuring that each server handles an appropriate share of the workload.
- Maintaining User Sessions: Load balancers can be configured for session persistence, ensuring that user sessions are maintained even when requests are directed to different servers. This is essential for applications that require stateful communication.
Challenges of using Load Balancers
- Single Point of Failure: Load balancers might create a single point of failure even though they improve fault tolerance. Issues with the load balancer itself could cause traffic distribution to be disrupted.
- Complexity and Cost: High-quality load balancing solutions may be expensive, and load balancer implementation and management can be complicated. This covers load balancers for both software and hardware.
- Configuration Challenges: Configuring load balancers correctly can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex application architectures or diverse server environments.
- Potential for Overhead: Depending on the load balancing technique and configuration, there may be additional overhead in the form of delay and processing time, even though modern load balancers are designed to lessen this effect.
- SSL Inspection Challenges: When SSL termination is performed at the load balancer, it may introduce challenges related to SSL inspection and handling end-to-end encryption.
Roadmap to Understand Load Balancers
1. Basics of Load Balancer
2. Types of Load Balancers
3. Working and Deployment of Load Balancers
5. Advanced Features and Startegies
Conclusion
In conclusion, a load balancer serves as a pivotal component in modern computing architectures, providing numerous benefits for the efficient and reliable operation of applications and services. By distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, load balancers optimize resource utilization, enhance performance, and ensure high availability.
Similar Reads
What is Load Balancer & How Load Balancing works? A load balancer is a crucial component in system design that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers. Its main purpose is to ensure that no single server is overburdened with too many requests, which helps improve the performance, reliability, and availability of applications.Ta
9 min read
Load Balancer - System Design Interview Question When a website becomes extremely popular, the traffic on that website increases, and the load on a single server also increases. The concurrent traffic overloads the single server and the website becomes slower for the users. To meet the request of these high volumes of data and to return the correc
7 min read
Types of Load Balancer Load Balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource utilization, minimize response time, and prevent server overload. When it comes to load balancing, three primary types exist: software load balancers, hardware load balancers, and virtual load balan
4 min read
Load Balancing Algorithms To control traffic across servers in a network, load-balancing algorithms are important. By spreading requests evenly, load balancers make sure that no single server is overloaded when several people visit an application. Various techniques, such as IP hash, Least Connections, and Round Robin, are e
15+ min read
How does a Load Balancer Works? A load balancer is a crucial component in system design, ensuring that incoming network traffic is efficiently distributed across multiple servers or resources. The primary goal is to optimize resource utilization, enhance system performance, and ensure high availability and fault tolerance. The fun
3 min read
Load Balancing Approach in Distributed System A load balancer is a device that acts as a reverse proxy and distributes network or application traffic across a number of servers. Load adjusting is the approach to conveying load units (i.e., occupations/assignments) across the organization which is associated with the distributed system. Load adj
3 min read
How to Create a Load Balancer? Creating a load balancer typically involves using dedicated hardware or software solutions. Below are general steps for setting up a basic load balancer in a traditional, non-cloud environment: To create a Classic Load Balancer:Table of Content Step 1: Choose a Load Balancer SolutionStep 2: Design Y
3 min read
Reverse Proxy Vs. Load Balancer In the realm of system design, confusion often arises regarding the distinct roles of reverse proxies and load balancers. Despite their critical importance in managing and optimizing web traffic, these components serve unique purposes and possess different functionalities. In this article, we will d
4 min read
Layer 4 Load Balancing vs. Layer 7 Load Balancing Load balancing is the process of distributing incoming network traffic or computational workloads across multiple servers, resources, or processes in a network. The primary goal of load balancing is to optimize resource utilization, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and avoid overload on
5 min read
Load Balancing using AWS Load balancing is a critical component in ensuring the seamless functioning and high availability of web applications. As cloud computing continues to dominate the modern tech landscape, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has emerged as a leading cloud platform, offering an array of robust load-balancing ser
6 min read