Symmetric Tree (Mirror Image of itself)
Last Updated : 07 Jun, 2025
Given a binary tree, the task is to check whether it is a mirror of itself.
Example:
Input: root[] = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3]
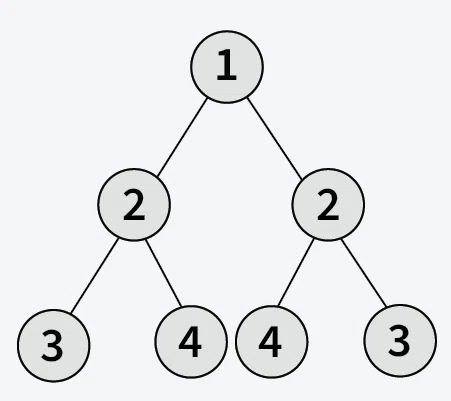 Output: True
Output: True
Explanation: Tree is mirror image of itself i.e. tree is symmetric.
Input: root[] = [1, 2, 2, N, 3, N, 3]
 Output: False
Output: False
Explanation: Tree is not mirror image of itself i.e. tree is not symmetric.
[Approach - 1] Using Recursion - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
The idea is to recursively compare the left and right subtrees of the root. For the tree to be symmetric, the root values of the left and right subtrees must match, and their corresponding children must also be mirrors.
C++ // C++ program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Recursive helper function to check if two subtrees are mirror images bool isMirror(Node* leftSub, Node* rightSub) { // Both are null, so they are mirror images if (leftSub == nullptr && rightSub == nullptr) return true; // One of them is null, so they aren't mirror images if (leftSub == nullptr || rightSub == nullptr || leftSub->data != rightSub->data) { return false; } // Check if the subtrees are mirrors return isMirror(leftSub->left, rightSub->right) && isMirror(leftSub->right, rightSub->left); } bool isSymmetric(Node* root) { // If tree is empty, it's symmetric if (root == nullptr) return true; // Check if the left and right subtrees are // mirrors of each other return isMirror(root->left, root->right); } int main() { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node* root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(2); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->left->right = new Node(4); root->right->left = new Node(4); root->right->right = new Node(3); if(isSymmetric(root)) cout << "true"; else cout << "false"; return 0; } // Java program to check if a given // Binary Tree is symmetric class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG{ // Recursive helper function to check if two subtrees are mirror images static boolean isMirror(Node leftSub, Node rightSub) { // Both are null, so they are mirror images if (leftSub == null && rightSub == null) return true; // One of them is null, so they aren't mirror images if (leftSub == null || rightSub == null || leftSub.data != rightSub.data) return false; // Check if the subtrees are mirrors return isMirror(leftSub.left, rightSub.right) && isMirror(leftSub.right, rightSub.left); } static boolean isSymmetric(Node root) { // If tree is empty, it's symmetric if (root == null) return true; // Check if the left and right subtrees are mirrors of each other return isMirror(root.left, root.right); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); if (isSymmetric(root)) System.out.println("true"); else System.out.println("false"); } } # Python program to check if a given # Binary Tree is symmetric class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # Recursive helper function to check if two subtrees are mirror images def isMirror(leftSub, rightSub): # Both are null, so they are mirror images if leftSub is None and rightSub is None: return True # One of them is null, so they aren't mirror images if leftSub is None or rightSub is None or leftSub.data != rightSub.data: return False # Check if the subtrees are mirrors return isMirror(leftSub.left, rightSub.right) and \ isMirror(leftSub.right, rightSub.left) def isSymmetric(root): # If tree is empty, it's symmetric if root is None: return True # Check if the left and right subtrees are mirrors of each other return isMirror(root.left, root.right) if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating a sample symmetric binary tree # 1 # / \ # 2 2 # / \ / \ # 3 4 4 3 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(3) root.left.right = Node(4) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(3) print("true" if isSymmetric(root) else "false") // C# program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Recursive helper function to check if two subtrees are mirror images static bool isMirror(Node leftSub, Node rightSub) { // Both are null, so they are mirror images if (leftSub == null && rightSub == null) return true; // One of them is null, so they aren't mirror images if (leftSub == null || rightSub == null || leftSub.data != rightSub.data) return false; // Check if the subtrees are mirrors return isMirror(leftSub.left, rightSub.right) && isMirror(leftSub.right, rightSub.left); } static bool isSymmetric(Node root) { // If tree is empty, it's symmetric if (root == null) return true; // Check if the left and right subtrees are mirrors of each other return isMirror(root.left, root.right); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); Console.WriteLine(isSymmetric(root) ? "true" : "false"); } } // JavaScript program to check if a given // Binary Tree is symmetric class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Recursive helper function to check if two subtrees are mirror images function isMirror(leftSub, rightSub) { // Both are null, so they are mirror images if (leftSub === null && rightSub === null) return true; // One of them is null, so they aren't mirror images if (leftSub === null || rightSub === null || leftSub.data !== rightSub.data) return false; // Check if the subtrees are mirrors return isMirror(leftSub.left, rightSub.right) && isMirror(leftSub.right, rightSub.left); } function isSymmetric(root) { // If tree is empty, it's symmetric if (root === null) return true; // Check if the left and right subtrees are mirrors of each other return isMirror(root.left, root.right); } // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); console.log(isSymmetric(root) ? "true" : "false"); [Approach - 2] Using Stack - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
The idea is to use two stack to check if a binary tree is symmetric. One stack is for the left side of the tree, and the other is for the right side. By comparing nodes from both stack at each level, we can check if the left and right sides are mirror images of each other.
Step-by-Step Implementation:
- Create a two stacks, say s1 and s2 and push the left child of the root node in s1 and right child of the root node into s2.
- While both the stack are not empty, repeat the following steps:
- Pop two nodes from the stack, say node1 and node2.
- If both node1 and node2 are null, continue to the next iteration.
- If one of the nodes is null and the other is not, return false as it is not a mirror.
- If both nodes are not null, compare their values. If they are not equal, return false.
- Push the left child of node1 and the right child of node2 onto the stack.
- Push the right child of node1 and the left child of node2 onto the stack.
- If the loop completes successfully without returning false, return true as it is a mirror.
C++ // C++ program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric bool isSymmetric(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return true; // Two stacks to store nodes for comparison stack<Node*> s1, s2; // Initialize the stacks with the left // and right subtrees s1.push(root->left); s2.push(root->right); while (!s1.empty() && !s2.empty()) { // Get the current pair of nodes Node* node1 = s1.top(); Node* node2 = s2.top(); s1.pop(); s2.pop(); // If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if (node1 == nullptr && node2 == nullptr) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 == nullptr || node2 == nullptr || node1->data != node2->data) { return false; } // Push children of node1 and node2 in opposite order // Push left child of node1 and right child of node2 s1.push(node1->left); s2.push(node2->right); // Push right child of node1 and left child of node2 s1.push(node1->right); s2.push(node2->left); } // If both stacks are empty, the tree is symmetric return s1.empty() && s2.empty(); } int main() { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node* root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(2); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->left->right = new Node(4); root->right->left = new Node(4); root->right->right = new Node(3); if(isSymmetric(root)) cout << "true"; else cout << "false"; return 0; } // Java program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric static boolean isSymmetric(Node root) { if (root == null) { return true; } // Two stacks to store nodes for comparison Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<>(); // Initialize the stacks with the left // and right subtrees s1.push(root.left); s2.push(root.right); while (!s1.isEmpty() && !s2.isEmpty()) { // Get the current pair of nodes Node node1 = s1.pop(); Node node2 = s2.pop(); // If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if (node1 == null && node2 == null) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 == null || node2 == null || node1.data != node2.data) { return false; } // Push children of node1 and node2 in opposite order // Push left child of node1 and right child of node2 s1.push(node1.left); s2.push(node2.right); // Push right child of node1 and left child of node2 s1.push(node1.right); s2.push(node2.left); } // If both stacks are empty, the tree is symmetric return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); System.out.println(isSymmetric(root)); } } # Python program to check if a given # Binary Tree is symmetric class Node: def __init__(self, val): self.data = val self.left = self.right = None # Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric def isSymmetric(root): if root is None: return True # Two stacks to store nodes for comparison s1 = [] s2 = [] # Initialize the stacks with the # left and right subtrees s1.append(root.left) s2.append(root.right) while s1 and s2: # Get the current pair of nodes node1 = s1.pop() node2 = s2.pop() # If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if node1 is None and node2 is None: continue # If one node is null and the other is not, # or the nodes' data do not match # then the tree is not symmetric if node1 is None or node2 is None or node1.data != node2.data: return False # Push children of node1 and node2 in opposite order # Push left child of node1 and right child of node2 s1.append(node1.left) s2.append(node2.right) # Push right child of node1 and left child of node2 s1.append(node1.right) s2.append(node2.left) # If both stacks are empty, the tree is symmetric return len(s1) == 0 and len(s2) == 0 if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating a sample symmetric binary tree # 1 # / \ # 2 2 # / \ / \ # 3 4 4 3 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(3) root.left.right = Node(4) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(3) print(isSymmetric(root))
// C# program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric static bool isSymmetric(Node root) { if (root == null) { return true; } // Two stacks to store nodes for comparison Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); // Initialize the stacks with the left // and right subtrees s1.Push(root.left); s2.Push(root.right); while (s1.Count > 0 && s2.Count > 0) { // Get the current pair of nodes Node node1 = s1.Pop(); Node node2 = s2.Pop(); // If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if (node1 == null && node2 == null) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 == null || node2 == null || node1.data != node2.data) { return false; } // Push children of node1 and node2 in opposite order // Push left child of node1 and right child of node2 s1.Push(node1.left); s2.Push(node2.right); // Push right child of node1 and left child of node2 s1.Push(node1.right); s2.Push(node2.left); } // If both stacks are empty, the tree is symmetric return s1.Count == 0 && s2.Count == 0; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); Console.WriteLine(isSymmetric(root)); } } // JavaScript program to check if a // given Binary Tree is symmetric class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = this.right = null; } } // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric function isSymmetric(root) { if (root === null) { return true; } // Two stacks to store nodes for comparison let s1 = []; let s2 = []; // Initialize the stacks with the // left and right subtrees s1.push(root.left); s2.push(root.right); while (s1.length > 0 && s2.length > 0) { // Get the current pair of nodes let node1 = s1.pop(); let node2 = s2.pop(); // If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if (node1 === null && node2 === null) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 === null || node2 === null || node1.data !== node2.data) { return false; } // Push children of node1 and node2 in opposite order // Push left child of node1 and right child of node2 s1.push(node1.left); s2.push(node2.right); // Push right child of node1 and left child of node2 s1.push(node1.right); s2.push(node2.left); } // If both stacks are empty, the tree is symmetric return s1.length === 0 && s2.length === 0; } // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 let root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); console.log(isSymmetric(root)); [Approach - 3] Using Queue - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The basic idea is to check if the left and right subtrees of the root node are mirror images of each other. To do this, we perform a level-order traversal of the binary tree using a queue. Initially, we push the root node into the queue twice. We dequeue two nodes at a time from the front of the queue and check if they are mirror images of each other.
Step-by-Step implementation:
- If the root node is NULL, return true as an empty binary tree is considered symmetric.
- Create a queue and push the left and right child of root node into the queue.
- While the queue is not empty, dequeue two nodes at a time, one for the left subtree and one for the right subtree.
- If both the left and right nodes are NULL, continue to the next iteration as the subtrees are considered mirror images of each other.
- If either the left or right node is NULL, or their data is not equal, return false as they are not mirror images of each other.
- Push the left and right nodes of the left subtree into the queue, followed by the right and left nodes of the right subtree into the queue.
- If the queue becomes empty and we have not returned false till now, return true as the binary tree is symmetric.
C++ // C++ program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric bool isSymmetric(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return true; } // Use a queue to store nodes for comparison queue<Node*> q; // Initialize the queue with the left // and right subtrees q.push(root->left); q.push(root->right); while (!q.empty()) { Node* node1 = q.front(); q.pop(); Node* node2 = q.front(); q.pop(); // If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if (node1 == nullptr && node2 == nullptr) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 == nullptr || node2 == nullptr || node1->data != node2->data) { return false; } // Enqueue children in opposite // order to compare them q.push(node1->left); q.push(node2->right); q.push(node1->right); q.push(node2->left); } // If the loop completes without // returning false, the tree is symmetric return true; } int main() { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node* root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(2); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->left->right = new Node(4); root->right->left = new Node(4); root->right->right = new Node(3); if(isSymmetric(root)) { cout << "true"; } else cout << "false"; return 0; } // Java program to check if a given // Binary Tree is symmetric import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric static boolean isSymmetric(Node root) { if (root == null) { return true; } // Use a queue to store nodes for comparison Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Initialize the queue with the left and right subtrees q.offer(root.left); q.offer(root.right); while (!q.isEmpty()) { Node node1 = q.poll(); Node node2 = q.poll(); // If both nodes are null, continue to the next pair if (node1 == null && node2 == null) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 == null || node2 == null || node1.data != node2.data) { return false; } // Enqueue children in opposite order to compare them q.offer(node1.left); q.offer(node2.right); q.offer(node1.right); q.offer(node2.left); } // If the loop completes without // returning false, the tree is symmetric return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); if (isSymmetric(root)) System.out.println("true"); else System.out.println("false"); } } from collections import deque # Definition for a binary tree node class TreeNode: def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): self.val = val self.left = left self.right = right # Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric def isSymmetric(root): if root is None: return True # Use a queue to store nodes for comparison q = deque() # Initialize the queue with the left and right subtrees q.append(root.left) q.append(root.right) while q: node1 = q.popleft() node2 = q.popleft() # If both nodes are None, continue if node1 is None and node2 is None: continue # If only one is None or values don't match, it's not symmetric if node1 is None or node2 is None or node1.val != node2.val: return False # Enqueue children in opposite order q.append(node1.left) q.append(node2.right) q.append(node1.right) q.append(node2.left) return True if __name__ == "__main__": # Example symmetric tree # 1 # / \ # 2 2 # / \ / \ # 3 4 4 3 root = TreeNode(1) root.left = TreeNode(2, TreeNode(3), TreeNode(4)) root.right = TreeNode(2, TreeNode(4), TreeNode(3)) print("true" if isSymmetric(root) else "false") // C# program to check if a given Binary // Tree is symmetric using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric static bool IsSymmetric(Node root) { if (root == null) { return true; } // Use a queue to store nodes for comparison Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Initialize the queue with the // left and right subtrees q.Enqueue(root.left); q.Enqueue(root.right); while (q.Count > 0) { Node node1 = q.Dequeue(); Node node2 = q.Dequeue(); // If both nodes are null, // continue to the next pair if (node1 == null && node2 == null) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 == null || node2 == null || node1.data != node2.data) { return false; } // Enqueue children in opposite // order to compare them q.Enqueue(node1.left); q.Enqueue(node2.right); q.Enqueue(node1.right); q.Enqueue(node2.left); } // If the loop completes without // returning false, the tree is symmetric return true; } static void Main() { // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); Console.WriteLine(isSymmetric(root) ? "true" : "false"); } } // JavaScript program to check if a given // Binary Tree is symmetric class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = this.right = null; } } // Function to check if the binary tree is symmetric function isSymmetric(root) { if (root === null) { return true; } // Use a queue to store nodes for comparison const q = []; // Initialize the queue with the left // and right subtrees q.push(root.left); q.push(root.right); while (q.length > 0) { const node1 = q.shift(); const node2 = q.shift(); // If both nodes are null, // continue to the next pair if (node1 === null && node2 === null) { continue; } // If one node is null and the other is not, // or the nodes' data do not match // then the tree is not symmetric if (node1 === null || node2 === null || node1.data !== node2.data) { return false; } // Enqueue children in opposite // order to compare them q.push(node1.left); q.push(node2.right); q.push(node1.right); q.push(node2.left); } // If the loop completes without // returning false, the tree is symmetric return true; } // Creating a sample symmetric binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 2 // / \ / \ // 3 4 4 3 let root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(4); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(3); console.log(isSymmetric(root) ? "true" : "false");
Similar Reads
Binary Tree Data Structure A Binary Tree Data Structure is a hierarchical data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the left child and the right child. It is commonly used in computer science for efficient storage and retrieval of data, with various operations such as insertion, deletion, and
3 min read
Introduction to Binary Tree Binary Tree is a non-linear and hierarchical data structure where each node has at most two children referred to as the left child and the right child. The topmost node in a binary tree is called the root, and the bottom-most nodes are called leaves. Introduction to Binary TreeRepresentation of Bina
15+ min read
Properties of Binary Tree This post explores the fundamental properties of a binary tree, covering its structure, characteristics, and key relationships between nodes, edges, height, and levelsBinary tree representationNote: Height of root node is considered as 0. Properties of Binary Trees1. Maximum Nodes at Level 'l'A bina
4 min read
Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages of Binary Tree A binary tree is a tree that has at most two children for any of its nodes. There are several types of binary trees. To learn more about them please refer to the article on "Types of binary tree" Applications:General ApplicationsDOM in HTML: Binary trees help manage the hierarchical structure of web
2 min read
Binary Tree (Array implementation) Given an array that represents a tree in such a way that array indexes are values in tree nodes and array values give the parent node of that particular index (or node). The value of the root node index would always be -1 as there is no parent for root. Construct the standard linked representation o
6 min read
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree Given a binary tree, the task is to find the maximum depth of the tree. The maximum depth or height of the tree is the number of edges in the tree from the root to the deepest node.Examples:Input: Output: 2Explanation: The longest path from the root (node 12) goes through node 8 to node 5, which has
11 min read
Insertion in a Binary Tree in level order Given a binary tree and a key, the task is to insert the key into the binary tree at the first position available in level order manner.Examples:Input: key = 12 Output: Explanation: Node with value 12 is inserted into the binary tree at the first position available in level order manner.Approach:The
8 min read
Deletion in a Binary Tree Given a binary tree, the task is to delete a given node from it by making sure that the tree shrinks from the bottom (i.e. the deleted node is replaced by the bottom-most and rightmost node). This is different from BST deletion. Here we do not have any order among elements, so we replace them with t
12 min read
Enumeration of Binary Trees A Binary Tree is labeled if every node is assigned a label and a Binary Tree is unlabelled if nodes are not assigned any label. Below two are considered same unlabelled trees o o / \ / \ o o o o Below two are considered different labelled trees A C / \ / \ B C A B How many different Unlabelled Binar
3 min read
Types of Binary Tree