Switch functions at layer 2
Last Updated : 09 Nov, 2021
Prerequisite - Switch
The switch is a layer 2 device that works on the basis of the MAC address (physical address) of a device. Switch mainly performs these functions:
- Learning - The switch learns the MAC address of the device on the switch port on which it receives the frame.
- Forwarding - The switch does 2 types of message forwarding:
(a) Unicast: The switch unicasts the frame to the destination only when it has an entry for destination MAC address in its MAC address table.
(b) Unknown Unicast: When a switch receives a unicast frame for a destination for which the switch has no entry in its MAC table then the switch simply broadcasts the frame through all ports. This is known as flooding. - Filtering - The frame will be forwarded through that switch port only for which the switch has already learned the MAC address in its MAC table.
- Loop avoidance - For redundancy, two switches are connected to each other through two links which can also result in layer 2 loops. These loops are avoided by switching by using the STP(Spanning tree protocol) protocol.
Note - An entry in the switch MAC table, also known as CAM (Content Addressable Memory), can remain up to 300 seconds. When a frame is received for a destination MAC address, the time limit of 300 seconds gets reset. MAC table has 4 entries:
- Port Number - The switch port is attached to the destination MAC.
- MAC Address - MAC address of that host which is attached to that switch port.
- Type - It tells us about how the switch has learned the MAC address of the host i.e static or dynamic. If the entry is added manually then it will be static otherwise it will be dynamic.
- VLAN -It tells about to which Vlan the host, attached to that switch port, belongs.
How does switch learn the Mac address?
The switch will update its MAC table only when it receives any frame from the host. If there is no entry for the destination host then switch will first learn the Mac address of the source host and then flood the frame through all its ports except the port on which the frame is received but if there is an entry for the destination host in Mac table of the switch then it will be unicast.
Let's see this by an example.
Example - Here is a small topology having host A (192.168.1.1/24), host B (192.168.1.2/24), host C (192.168.1.3/24), host D (192.168.1.4/24), and 2 switches in between. It will understand the switch MAC address learning process by ping from host A to Host C. Initially both switches MAC tables have an entry for another switch only.
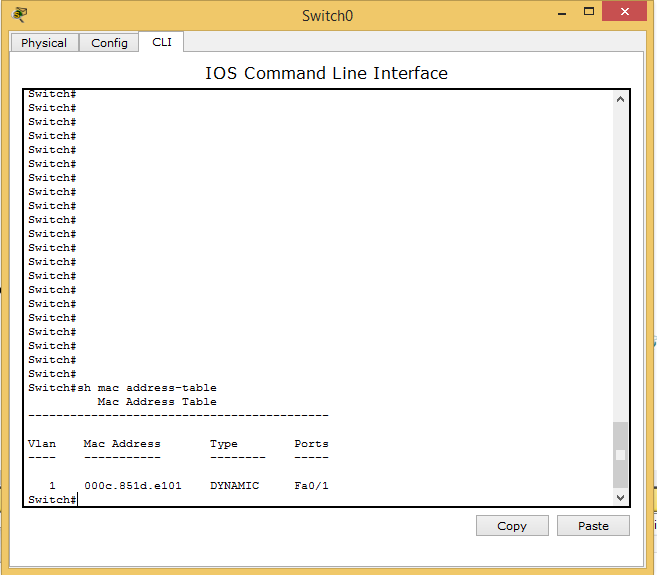

As soon as the user tries to ping host C, he sees that 2 packets are generated: one of ICMP and the other of ARP.

First, ARP will be resolved i.e ARP request is broadcast in the network by host A.

The switch0 receives the broadcast ARP request and will update its MAC table.

Note - The switch0 already has an entry for Switch1. The switch0 broadcasts the frame in return to switch1 and the PC. Host B will discard the frame as it is not destined for it.

Now, switch1 will receive the frame and will first update its MAC table.

Note - Here, switch1 has learned the different MAC addresses of switch0 and host A on the same port fa0/1 because host A is attached to switch0 on fa0/1, therefore, showing the same port fa0/1. Now, switch1 will broadcast the ARP frame to host C and host D as these are present in the same broadcast domain.

Host C will generate an ARP reply which is unicast to the switch. The switch1 will update its MAC table putting an entry for host C.

Both the switch(switch0 and switch1) will unicast this ARP reply to host A this time because this time switches have already learned the MAC address of host A.

The frame is successfully delivered to host A resolving the ARP.

Now the ICMP echo request is unicast to host C.



The ICMP echo reply is unicast to host A.



Remember -
When the switch will broadcast? If the host has broadcast a frame then the switch receiving it will broadcast it further through its ports anyway.
When the switch will do flooding (unknown unicast)? If the host has unicast a frame and the switch doesn't have a destination Mac address in its Mac table then the switch will flood through all its ports except the port on which the frame is received.
When the switch will unicast? If the switch has an entry for the destination host in its Mac table then the frame will be unicast.
Similar Reads
Layer 3 Switches in Cisco A layer 3 Switch is a special type of networking device which is able to perform/execute functions of 2 layers of the OSI Model i.e., the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) and the Network Layer (Layer 3). In simple words, a Layer 3 Switch is a networking device that can perform switching (functions of layer
3 min read
Difference between layer-2 and layer-3 switches A switch is a device that sends a data packet to a local network. What is the advantage of a hub? A hub floods the network with the packet and only the destination system receives that packet while others just drop due to which the traffic increases a lot. To solve this problem switch came into the
5 min read
Functions of Physical layer in OSI Model The physical layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model. The physical layer consists of various networking devices such as connectors, receivers, plugs, modems, repeaters, cables, Hubs, etc. The rules and procedures that are defined for interaction between the physical layers are known as physical l
5 min read
How States are Decided in a Switch? In the seven-layer OSI model, the hubs are broadcast devices that operate on layer-1 in half-duplex mode, so only one device can transfer data at a time. To overcome this issue, bridges were introduced. The bridge is used to segment a LAN connection into smaller sub-networks. The bridge stores the M
7 min read
Difference Between Router and Layer-3 Switch Routing traffic is a crucial part of network implementation and management, making it essential to choose the right device for the job. Routers and Layer-3 switches are both commonly used for this purpose. While they both handle routing, they differ in functionality, features, and ideal use cases. S
4 min read