SQL Logical Operators are essential tools used to test the truth of conditions in SQL queries. They return boolean values such as TRUE, FALSE, or UNKNOWN, making them invaluable for filtering, retrieving, or manipulating data. These operators allow developers to build complex queries by combining, negating, or comparing conditions effectively.
In this article, we will explore the various Logical Operators in SQL, their types, and examples. To ensure clarity, all examples will reference a defined sample table.
What Are Logical Operators in SQL?
Logical operators in SQL are used to combine multiple conditions in a query to control the flow of execution. They evaluate whether these conditions are TRUE, FALSE, or NULL, assisting in refining query results effectively. By using these operators, developers can retrieve highly specific data based on given conditions.
We will use the following employee table throughout the examples. This table represents employee details, including their unique ID, name, city, and country.
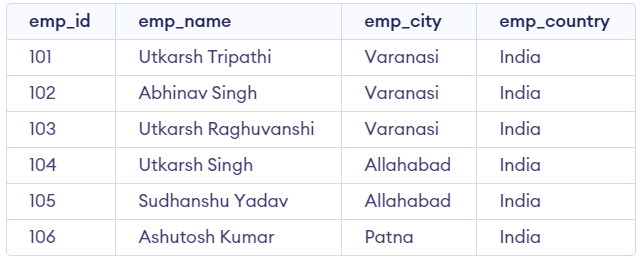 employee Table
employee TableBelow is the comprehensive list of SQL Logical Operators along with their meanings, detailed explanations, and practical examples:
1. AND Operator
The AND operator is used to combine two or more conditions in an SQL query. It returns records only when all conditions specified in the query are true. This operator is commonly used when filtering data that must satisfy multiple criteria simultaneously.
Let's explore an example to understand how the AND operator works in an SQL query.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employees table who are located in 'Allahabad' and belong to 'India', ensuring that both conditions are met.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_city = 'Allahabad' AND emp_country = 'India';
Output
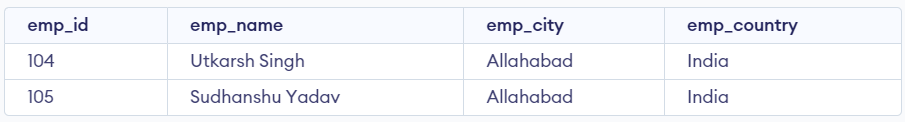 output
outputExplanation:
In the output, both conditions (emp_city = 'Allahabad' and emp_country = 'India') are satisfied for the listed employees, so these records are returned by the query.
2. IN Operator
The IN operator simplifies the process of checking if a value matches any value in a list, making it more efficient and readable compared to using multiple OR conditions. This operator is especially helpful when we need to filter results based on multiple possible values for a given column, reducing the complexity of the query.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employee table who are located in either 'Allahabad' or 'Patna'.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_city IN ('Allahabad', 'Patna');
Output
 output
outputExplanation:
In this query, the IN operator checks if the value of the emp_city column matches any value in the list ('Allahabad', 'Patna'). The query returns all employees who are located in either of these two cities.
3. NOT Operator
The NOT operator is used to reverse the result of a condition, returning TRUE when the condition is FALSE. It is typically used to exclude records that match a specific condition, making it useful for filtering out unwanted data.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employee table whose city names do not start with the letter 'A'.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_city NOT LIKE 'A%';
Output
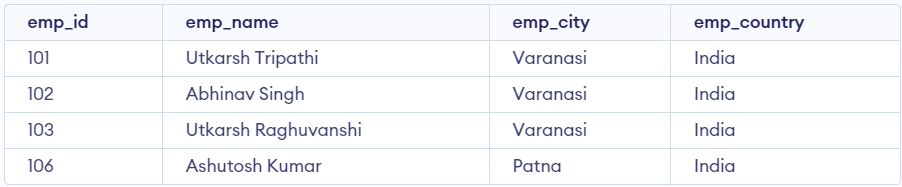 output
outputExplanation:
In this query, the NOT operator negates the LIKE condition. The LIKE operator is used to match patterns in string data, and the 'A%' pattern matches any city name that starts with the letter 'A'. By using the NOT operator, we exclude cities starting with 'A' from the result set.
4. OR Operator
The OR operator combines multiple conditions in a SQL query and returns TRUE if at least one of the conditions is satisfied. It is ideal for situations where you want to retrieve records that meet any of several possible conditions.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employee table who are either from 'Varanasi' or have 'India' as their country.
Query
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_city = 'Varanasi' OR emp_country = 'India';
Output
 output
outputExplanation:
In this case, the output includes employees from 'Varanasi' as well as those who have 'India' as their country, even if they are from different cities. The query returns all records where at least one of the conditions is true.
5. LIKE Operator
The LIKE operator in SQL is used in the WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column. It is particularly useful when we want to perform pattern matching on string data. The LIKE operator works with two main wildcards:
- %: Represents zero or more characters. It allows matching any sequence of characters in the string.
- _: Represents exactly one character. It is used when you want to match a specific number of characters at a given position.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employee table whose city names start with the letter 'P'.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_city LIKE 'P%';
Output
 output
outputExplanation:
In this case, the output includes only those employees whose emp_city starts with 'P'. The % wildcard ensures that the query matches any city name starting with the specified letter, regardless of how many additional characters follow it.
6. BETWEEN Operator
The BETWEEN operator in SQL allows us to test if a value or expression lies within a specified range. The BETWEEN condition is inclusive, meaning it includes both the lower and in the results. This operator is particularly useful when we need to filter records based on a range of values, such as numerical ranges, dates, or even text values.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employee table whose emp_id values fall within the range of 101 to 104 (inclusive).
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_id BETWEEN 101 AND 104;
Output
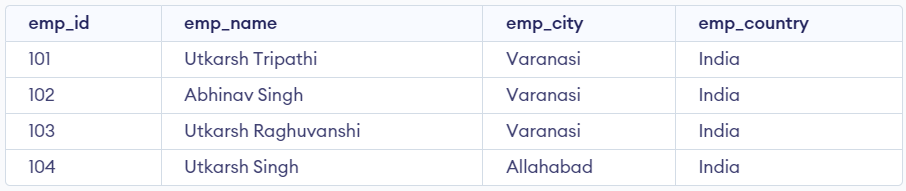 output
outputExplanation:
In this query, the BETWEEN operator is used to filter employees with emp_id values ranging from 101 to 104. Since the BETWEEN operator is inclusive, employees with emp_id values of 101, 102, 103, and 104 will be included in the result set.
7. ALL Operator
The ALL operator in SQL is used to compare a value to all values returned by a subquery. It returns TRUE if the condition specified is TRUE for all values retrieved by the subquery. The ALL operator is commonly used with SELECT, WHERE, and HAVING clauses to ensure that a value satisfies a condition when compared to a set of values.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees whose emp_id is equal to all emp_id values in the employees table where the emp_city is 'Varanasi'.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_id = ALL
(SELECT emp_id FROM employee WHERE emp_city = 'Varanasi');
Output
 output
outputExplanation:
The query checks whether emp_id in the outer query is equal to every emp_id from the subquery (which retrieves emp_id values from employees in 'Varanasi'). In this case, the output will include employees whose emp_id matches all the values in the subquery, i.e., employees with emp_id values 101, 102, and 103 who are in 'Varanasi'.
8. ANY Operator
The ANY operator in SQL is used to compare a value with the results of a subquery. It returns TRUE if the value satisfies the condition with any of the values returned by the subquery. This operator allows for greater flexibility when you want to check if a value matches at least one of the results in a set of values.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees whose emp_id matches any of the emp_id values in the employees table where the emp_city is 'Varanasi'.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_id = ANY
(SELECT emp_id FROM employee WHERE emp_city = 'Varanasi');
Output

Explanation:
The output includes employees whose emp_id matches any of the emp_id values from the subquery. In this case, the subquery selects emp_id values from employees in 'Varanasi'. The outer query then returns records where emp_id matches at least one of these values, which includes employees with emp_id 101, 102, and 106.
9. EXISTS Operator
The EXISTS operator in SQL is used to check whether a subquery returns any rows. It evaluates to TRUE if the subquery results in one or more rows. The EXISTS operator is typically used with SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE statements to determine if any rows exist that meet a specified condition. It is often used in correlated subqueries where the subquery references columns from the outer query.
Example
Retrieve the names of employees from the employee table if there are any employees in the employee table who are located in 'Patna'.
Query
SELECT emp_name FROM employee WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT emp_id FROM employee WHERE emp_city = 'Patna');
Output
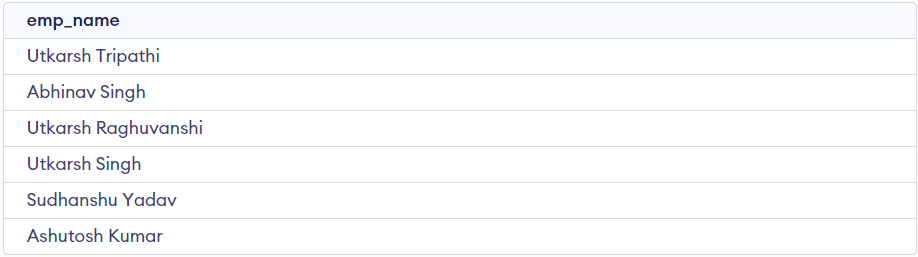 output
outputExplanation:
The output includes the employee names because the EXISTS operator checks if there are any employees from Patna. If any rows are returned from the subquery, the EXISTS operator returns TRUE, and the employee names are included in the result. The query will return all employees as long as there are employees from Patna.
10. SOME Operator
The SOME operator in SQL is used in conjunction with comparison operators such as <, >, =, <=, etc., to compare a value with the results of a subquery. It returns TRUE if the condition is met with any value returned by the subquery. The SOME operator allows us to perform comparisons with any of the values returned by a subquery, and it is particularly useful when we want to match a value against a set of values rather than a single value.
Example
Retrieve the records of employees from the employee table where the emp_id is less than any of the emp_id values from employees located in 'Patna'.
Query:
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE emp_id < SOME
(SELECT emp_id FROM employee WHERE emp_city = 'Patna');
Output
 output
outputExplanation:
The output includes employees whose emp_id is less than any of the emp_id values of employees located in 'Patna'. In this case, the query checks if the emp_id values are less than the corresponding emp_id values from the 'Patna' employees. If the condition is satisfied for at least one of the values in the subquery, those employees are included in the result.
Conclusion
SQL Logical Operators are crucial for building complex queries that filter and retrieve data efficiently. From combining conditions with AND and OR to using pattern-matching capabilities with LIKE, these operators enhance the functionality of SQL queries. By mastering these operators, developers can optimize their queries and achieve precise data manipulation. Understanding these operators is essential for database management, whether we are working with small-scale projects or enterprise-level systems
Similar Reads
SQL for Data Science Mastering SQL (Structured Query Language) has become a fundamental skill for anyone pursuing a career in data science. As data plays an increasingly central role in business and technology, SQL has emerged as the most essential tool for managing and analyzing large datasets. Data scientists rely on
7 min read
Introduction to SQL
What is SQL?SQL was invented in the 1970s by IBM and was first commercially distributed by Oracle. The original name was SEQUEL (Structured English Query Language), later shortened to SQL. It is a standardized programming language used to manage, manipulate and interact with relational databases. It allow users
9 min read
Difference Between RDBMS and DBMSDatabase Management System (DBMS) is a software that is used to define, create, and maintain a database and provides controlled access to the data. Why is DBMS Required?Database management system, as the name suggests, is a management system that is used to manage the entire flow of data, i.e, the i
4 min read
Difference between SQL and NoSQLChoosing between SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases is a critical decision for developers, data engineers, and organizations looking to handle large datasets effectively. Both database types have their strengths and weaknesses, and understanding the key differences ca
6 min read
SQL Data TypesSQL Data Types are very important in relational databases. It ensures that data is stored efficiently and accurately. Data types define the type of value a column can hold, such as numbers, text, or dates. Understanding SQL Data Types is critical for database administrators, developers, and data ana
5 min read
SQL | DDL, DML, TCL and DCLData Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Transaction Control Language (TCL), and Data Control Language (DCL) form the backbone of SQL. Each of these languages plays a critical role in defining, managing, and controlling data within a database system, ensuring both structural
6 min read
Setting Up the Environment
SQL Basics
Relational Model in DBMSThe Relational Model organizes data using tables (relations) consisting of rows and columns. Each column represents a specific attribute with a unique name, while each row holds data about a real-world entity or relationship. As a record-based model, it stores data in fixed-format records with defin
10 min read
SQL SELECT QueryThe SQL SELECT query is one of the most frequently used commands to retrieve data from a database. It allows users to access and extract specific records based on defined conditions, making it an essential tool for data management and analysis. In this article, we will learn about SQL SELECT stateme
4 min read
SQL Data TypesSQL Data Types are very important in relational databases. It ensures that data is stored efficiently and accurately. Data types define the type of value a column can hold, such as numbers, text, or dates. Understanding SQL Data Types is critical for database administrators, developers, and data ana
5 min read
SQL | WITH ClauseSQL queries can sometimes be complex, especially when you need to deal with multiple nested subqueries, aggregations, and joins. This is where the SQL WITH clause also known as Common Table Expressions (CTEs) comes in to make life easier. The WITH Clause is a powerful tool that simplifies complex SQ
6 min read
SQL | GROUP BYThe SQL GROUP BY clause is a powerful tool used to organize data into groups based on shared values in one or more columns. It is most often used with aggregate functions like SUM, COUNT, AVG, MIN and MAX to perform summary operations on each group, helping us extract meaningful analysis from large
5 min read
PHP | MySQL LIMIT ClauseIn MySQL the LIMIT clause is used with the SELECT statement to restrict the number of rows in the result set. The Limit Clause accepts one or two arguments which are offset and count.The value of both the parameters can be zero or positive integers. Offset:It is used to specify the offset of the fir
3 min read
SQL LIMIT ClauseThe LIMIT clause in SQL is used to control the number of rows returned in a query result. It is particularly useful when working with large datasets, allowing us to retrieve only the required number of rows for analysis or display. Whether we're looking to paginate results, find top records, or just
5 min read
SQL Distinct ClauseThe SQL DISTINCT keyword is used in queries to retrieve unique values from a database. It helps in eliminating duplicate records from the result set. It ensures that only unique entries are fetched. Whether you're analyzing datasets or performing data cleaning, the DISTINCT keyword is Important for
4 min read
SQL Operators
SQL Comparison OperatorsSQL Comparison Operators are used to compare two values and check if they meet the specific criteria. Some comparison operators are = Equal to, > Greater than , < Less than, etc. Comparison Operators in SQLThe below table shows all comparison operators in SQL : OperatorDescription=The SQL Equa
3 min read
SQL - Logical OperatorsSQL Logical Operators are essential tools used to test the truth of conditions in SQL queries. They return boolean values such as TRUE, FALSE, or UNKNOWN, making them invaluable for filtering, retrieving, or manipulating data. These operators allow developers to build complex queries by combining, n
9 min read
SQL | Arithmetic OperatorsPrerequisite: Basic Select statement, Insert into clause, Sql Create Clause, SQL Aliases We can use various Arithmetic Operators on the data stored in the tables. Arithmetic Operators are: + [Addition] - [Subtraction] / [Division] * [Multiplication] % [Modulus] Addition (+) : It is used to perform a
5 min read
SQL | String functionsSQL String Functions are powerful tools that allow us to manipulate, format, and extract specific parts of text data in our database. These functions are essential for tasks like cleaning up data, comparing strings, and combining text fields. Whether we're working with names, addresses, or any form
7 min read
SQL Wildcard CharactersSQL wildcard characters are powerful tools that enable advanced pattern matching in string data. They are especially useful when working with the LIKE and NOT LIKE operators, allowing for efficient searches based on partial matches or specific patterns. By using SQL wildcard characters, we can great
6 min read
SQL AND and OR OperatorsThe SQL AND and OR operators are used to filter data based on multiple conditions. These logical operators allow users to retrieve precise results from a database by combining various conditions in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements.In this article, we'll learn the AND and OR operators, d
3 min read
SQL | Concatenation OperatorThe SQL concatenation operator (||) is a powerful feature that allows us to merge two or more strings into a single output. It is widely used to link columns, character strings, and literals in SQL queries. This operator makes it easier to format and present data in a user-friendly way, combining mu
3 min read
SQL | MINUS OperatorThe Minus Operator in SQL is used with two SELECT statements. The MINUS operator is used to subtract the result set obtained by first SELECT query from the result set obtained by second SELECT query. In simple words, we can say that MINUS operator will return only those rows which are unique in only
2 min read
SQL | DIVISIONDivision in SQL is typically required when you want to find out entities that are interacting with all entities of a set of different types of entities. The division operator is used when we have to evaluate queries that contain the keyword 'all'. When to Use the Division OperatorYou typically requi
4 min read
SQL NOT OperatorThe SQL NOT Operator is a logical operator used to negate or reverse the result of a condition in SQL queries. It is commonly used with the WHERE clause to filter records that do not meet a specified condition, helping you exclude certain values from your results.In this article, we will learn every
3 min read
SQL | BETWEEN & IN OperatorIn SQL, the BETWEEN and IN operators are widely used for filtering data based on specific criteria. The BETWEEN operator helps filter results within a specified range of values, such as numbers, dates, or text, while the IN operator filters results based on a specific list of values. Both operators
5 min read
Working with Data
SQL | WHERE ClauseThe SQL WHERE clause allows filtering of records in queries. Whether you are retrieving data, updating records, or deleting entries from a database, the WHERE clause plays an important role in defining which rows will be affected by the query. Without WHERE clause, SQL queries would return all rows
4 min read
SQL ORDER BYThe ORDER BY clause in SQL is a powerful feature used to sort query results in either ascending or descending order based on one or more columns. Whether you are presenting data to users or analyzing large datasets, sorting the results in a structured way is essential. In this article, we will explo
5 min read
SQL INSERT INTO StatementThe SQL INSERT INTO statement is one of the most essential commands for adding new data into a database table. Whether you are working with customer records, product details or user information, understanding and mastering this command is important for effective database management. How SQL INSERT I
6 min read
SQL UPDATE StatementIn SQL, the UPDATE statement is used to modify existing records in a table. Whether you are updating a single record or multiple records at once, SQL provides the necessary functionality to make these changes. Whether you are working with a small dataset or handling large-scale databases, the UPDATE
6 min read
SQL DELETE StatementThe SQL DELETE statement is an essential command in SQL used to remove one or more rows from a database table. Unlike the DROP statement, which removes the entire table, the DELETE statement removes data (rows) from the table retaining only the table structure, constraints, and schema. Whether you n
4 min read
SQL Data TypesSQL Data Types are very important in relational databases. It ensures that data is stored efficiently and accurately. Data types define the type of value a column can hold, such as numbers, text, or dates. Understanding SQL Data Types is critical for database administrators, developers, and data ana
5 min read
ALTER (RENAME) in SQLIn SQL, making structural changes to a database is often necessary. Whether it's renaming a table or a column, adding new columns, or modifying data types, the SQL ALTER TABLE command plays a critical role. This command provides flexibility to manage and adjust database schemas without affecting the
5 min read
SQL ALTER TABLEThe SQL ALTER TABLE statement is a powerful tool that allows you to modify the structure of an existing table in a database. Whether you are adding new columns, modifying existing ones, deleting columns or renaming them, the ALTER TABLE statement enables you to make changes without losing the data s
5 min read
SQL Queries
SQL | SubqueryIn SQL, subqueries are one of the most powerful and flexible tools for writing efficient queries. A subquery is essentially a query nested within another query, allowing users to perform operations that depend on the results of another query. This makes it invaluable for tasks such as filtering, cal
6 min read
Nested Queries in SQLA nested query (also called a subquery) is a query embedded within another SQL query. The result of the inner query is used by the outer query to perform additional operations. Subqueries can be used in various parts of an SQL query such as SELECT, FROM or WHERE Clauses. They are commonly used for p
7 min read
Joining Three or More Tables in SQLSQL joins are an essential part of relational database management, allowing users to combine data from multiple tables efficiently. When the required data is spread across different tables, joining these tables efficiently is necessary.In this article, we’ll cover everything we need to know about jo
5 min read
Inner Join vs Outer JoinInner Join and Outer Join are the types of join. The inner join has the work to return the common rows between the two tables, whereas the Outer Join has the work of returning the work of the inner join in addition to the rows that are not matched. Let's discuss both of them in detail in this articl
9 min read
SQL | Join (Cartesian Join & Self Join)In SQL, CARTESIAN JOIN (also known as CROSS JOIN) and SELF JOIN are two distinct types of joins that help combine rows from one or more tables based on certain conditions. While both joins may seem similar, they serve different purposes. Let’s explore both in detail.CARTESIAN JOINA Cartesian Join or
4 min read
How to Get the Names of the Table in SQLRetrieving table names in SQL is a common task that aids in effective database management and exploration. Whether we are dealing with a single database or multiple databases, knowing how to retrieve table names helps streamline operations. SQL provides the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES view, which offe
3 min read
SQL | SubqueryIn SQL, subqueries are one of the most powerful and flexible tools for writing efficient queries. A subquery is essentially a query nested within another query, allowing users to perform operations that depend on the results of another query. This makes it invaluable for tasks such as filtering, cal
6 min read
How to Fetch Duplicate Rows in a Table?Identifying duplicate rows in a database table is a common requirement, especially when dealing with large datasets. Duplicates can arise due to data entry errors, system migrations, or batch processing issues. In this article, we will explain efficient SQL techniques to identify and retrieve duplic
3 min read
Data Manipulation
SQL Joins (Inner, Left, Right and Full Join)SQL joins are fundamental tools for combining data from multiple tables in relational databases. Joins allow efficient data retrieval, which is essential for generating meaningful observations and solving complex business queries. Understanding SQL join types, such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JO
5 min read
SQL Inner JoinSQL INNER JOIN is a powerful and frequently used operation in relational databases. It allows us to combine two or more tables based on a related column, returning only the records that satisfy the join conditionThis article will explore the fundamentals of INNER JOIN, its syntax, practical examples
4 min read
SQL Outer JoinSQL Outer Joins allow retrieval of rows from two or more tables based on a related column. Unlike inner Joins, they also include rows that do not have a corresponding match in one or both of the tables. This capability makes Outer Joins extremely useful for comprehensive data analysis and reporting,
4 min read
SQL Self JoinA Self Join in SQL is a powerful technique that allows one to join a table with itself. This operation is helpful when you need to compare rows within the same table based on specific conditions. A Self Join is often used in scenarios where there is hierarchical or relational data within the same ta
3 min read
How to Group and Aggregate Data Using SQL?In SQL, grouping and aggregating data are essential techniques for analyzing datasets. When dealing with large volumes of data, we often need to summarize or categorize it into meaningful groups. The combination of the GROUP BY clause and aggregate functions like COUNT(), SUM(), AVG(), MIN(), and MA
4 min read
SQL HAVING Clause with ExamplesThe HAVING clause in SQL is used to filter query results based on aggregate functions. Unlike the WHERE clause, which filters individual rows before grouping, the HAVING clause filters groups of data after aggregation. It is commonly used with functions like SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), and MIN().
4 min read
Data Analysis
CTE in SQLIn SQL, a Common Table Expression (CTE) is an essential tool for simplifying complex queries and making them more readable. By defining temporary result sets that can be referenced multiple times, a CTE in SQL allows developers to break down complicated logic into manageable parts. CTEs help with hi
6 min read
Window Functions in SQLSQL window functions are essential for advanced data analysis and database management. It is a type of function that allows us to perform calculations across a specific set of rows related to the current row. These calculations happen within a defined window of data and they are particularly useful
6 min read
Pivot and Unpivot in SQLIn SQL, PIVOT and UNPIVOT are powerful operations used to transform data and make it more readable, efficient, and manageable. These operations allow us to manipulate tables by switching between rows and columns, which can be crucial for summarizing data, reporting, and data analysis. Understanding
4 min read
Data Preprocessing in Data MiningData preprocessing is the process of preparing raw data for analysis by cleaning and transforming it into a usable format. In data mining it refers to preparing raw data for mining by performing tasks like cleaning, transforming, and organizing it into a format suitable for mining algorithms. Goal i
6 min read
SQL Functions (Aggregate and Scalar Functions)SQL Functions are built-in programs that are used to perform different operations on the database. There are two types of functions in SQL: Aggregate FunctionsScalar FunctionsSQL Aggregate FunctionsSQL Aggregate Functions operate on a data group and return a singular output. They are mostly used wit
4 min read
MySQL Date and Time FunctionsHandling date and time data in MySQL is essential for many database operations, especially when it comes to handling timestamps, scheduling tasks, or generating time-based. MySQL provides a variety of date and time functions that help users work with date values, perform calculations, and format the
6 min read
SQL | Date Functions (Set-1)SQL Date Functions are essential for managing and manipulating date and time values in SQL databases. They provide tools to perform operations such as calculating date differences, retrieving current dates and times and formatting dates. From tracking sales trends to calculating project deadlines, w
5 min read
SQL | Date Functions (Set-2)SQL Date Functions are powerful tools that allow users to manipulate, extract , and format date and time values within SQL databases. These functions simplify handling temporal data, making them indispensable for tasks like calculating intervals, extracting year or month values, and formatting dates
5 min read
SQL | Numeric FunctionsSQL Numeric Functions are essential tools for performing mathematical and arithmetic operations on numeric data. These functions allow you to manipulate numbers, perform calculations, and aggregate data for reporting and analysis purposes. Understanding how to use SQL numeric functions is important
3 min read
SQL Aggregate functionsSQL Aggregate Functions are used to perform calculations on a set of rows and return a single value. These functions are particularly useful when we need to summarize, analyze, or group large datasets in SQL databases. Whether you are working with sales data, employee records or product inventories,
4 min read
Data Visualization