Spring Boot - File Handling
Last Updated : 28 Apr, 2025
Spring Boot is a popular, open-source spring-based framework used to develop robust web applications and microservices. As it is built on top of Spring Framework it not only has all the features of Spring but also includes certain special features such as auto-configuration, health checks, etc. which makes it easier for the developers to set up Spring-based applications with minimal configuration thus facilitating Rapid Application Development.
Spring Boot File handling refers to downloading and uploading files using RESTful web services. This article illustrates a step-by-step guideline to implement restful web services that can be used to upload and download a file using Spring Boot.
Initial Setup for File Handling in Spring Boot
A Spring Boot Project needs to be created with Spring Web dependency as mentioned below using Spring Initializer. Please refer to this article to complete the setup.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Now let's start developing the Spring Boot App. It will provide restful web services for:
- Uploading a file
- Downloading a file
- Getting the list of filenames uploaded
Implementation of the Application
Step 1: Setting up the Application.Properties file with configurations required for multipart file upload.
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=10MB
These configurations can be explained as follows:
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled -> determines whether multipart has to be enabled or not
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file -> specifies the maximum size of the file allowed for uploading.
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size -> specifies the maximum size allowed for multipart/form-data requests.
Step 2: Create a RestController FileController that handles the following REST APIs:
1. Upload API
Usage: It can be used to upload a file. It consumes Multipart requests.
URL: /upload
HttpMethod: POST
Implementation Details:
For developing this API, we are using MultipartFile as a Request Parameter. The uploaded file is sent as form data which is then retrieved in the Rest controller as a Multipart file. So, MultipartFile is nothing but a representation of an uploaded file received in a multipart request.
2. getFiles API
Usage: It can be used to get a list of filenames that have been uploaded.
URL: /getFIles
HttpMethod: GET
Implementation Details:
It can be implemented by simply using the list() method of java.io.File which returns an array of strings naming the files and directories in the directory denoted by the given abstract pathname.
3. Download API
It can be used to download a previously uploaded file.
URL: /download/{filename}
HttpMethod: POST
Implementation Details:
To Implement this API, we first check whether the requested file for download exists or not in the uploaded folder. If the file exists, we use InputStreamResource to download the file. It is also required to set Content-Disposition in the response header as an attachment and MediaType as application/octet-stream.
The Content-Disposition response header as an attachment indicates that the content is to be downloaded. contentType is set as application/octet-stream so that when an attempt is made to download a file with a missing extension or unknown format, it will be recognized as an octet-stream file by the system. The implementation of FileController is as shown below:
Java // Java Program to Create Rest Controller // that Defines various API for file handling package com.SpringBootFileHandling.controller; // Importing required classes import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.util.Arrays; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamResource; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; // Annotation @RestController public class FileController { // Uploading a file @RequestMapping(value = "/upload", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file){ // Setting up the path of the file String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/Uploads" + File.separator + file.getOriginalFilename(); String fileUploadStatus; // Try block to check exceptions try { // Creating an object of FileOutputStream class FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(filePath); fout.write(file.getBytes()); // Closing the connection fout.close(); fileUploadStatus = "File Uploaded Successfully"; } // Catch block to handle exceptions catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); fileUploadStatus = "Error in uploading file: " + e; } return fileUploadStatus; } // Getting list of filenames that have been uploaded @RequestMapping(value = "/getFiles", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String[] getFiles() { String folderPath = System.getProperty("user.dir") +"/Uploads"; // Creating a new File instance File directory= new File(folderPath); // list() method returns an array of strings // naming the files and directories // in the directory denoted by this abstract pathname String[] filenames = directory.list(); // returning the list of filenames return filenames; } // Downloading a file @RequestMapping(value = "/download/{path:.+}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public ResponseEntity downloadFile(@PathVariable("path") String filename) throws FileNotFoundException { // Checking whether the file requested for download exists or not String fileUploadpath = System.getProperty("user.dir") +"/Uploads"; String[] filenames = this.getFiles(); boolean contains = Arrays.asList(filenames).contains(filename); if(!contains) { return new ResponseEntity("FIle Not Found",HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); } // Setting up the filepath String filePath = fileUploadpath+File.separator+filename; // Creating new file instance File file= new File(filePath); // Creating a new InputStreamResource object InputStreamResource resource = new InputStreamResource(new FileInputStream(file)); // Creating a new instance of HttpHeaders Object HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); // Setting up values for contentType and headerValue String contentType = "application/octet-stream"; String headerValue = "attachment; filename=\"" + resource.getFilename() + "\""; return ResponseEntity.ok() .contentType(MediaType.parseMediaType(contentType)) .header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, headerValue) .body(resource); } } Step 3: Running the Spring Boot Application and testing the APIs using postman as follows.
1. Upload API
In order to upload a file we need to hit http://localhost:8080/upload in Postman with form data as shown below:
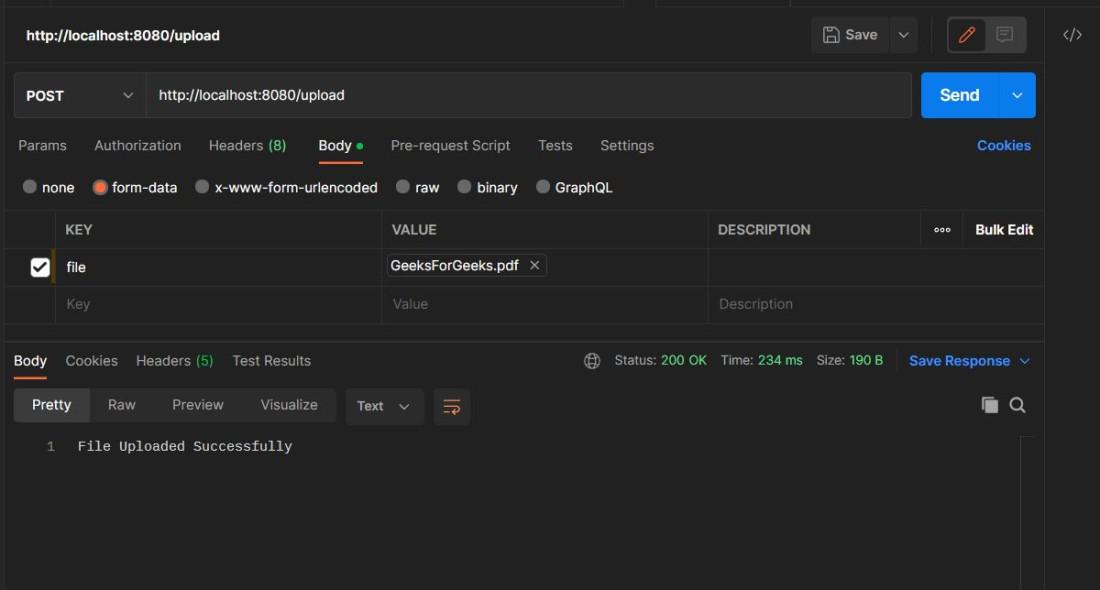
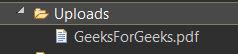
On Successful upload of the file, we can see the file in the Uploads folder as below:
2. getFiles API
We need to hit http://localhost:8080/getFiles in postman to get a list of filenames that have been uploaded.

3. Download API
In order to download a file we need to hit http://localhost:8080/download/{filename} in postman as shown below.

The Response received in postman can be downloaded as a file by clicking on Save Response -> Save to a File. The download URL can also be hit on the browser to get the file downloaded directly. If we attempt to download a file that doesn't exist then we get "File Not Found" in the response along with HttpStatus as NOT_FOUND.

Similar Reads
Spring Boot | How to consume JSON messages using Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a stream processing system that lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to publish JSON messages on the console of a Spring boot application using Apache Kafka. In order to learn how to create a Spring Boot project, refer
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to consume string messages using Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging queue used for real-time streams of data. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article we will see how to send string messages from apache kafka to the console of a spring boot application. Appro
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to publish String messages on Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to send string messages to Apache Kafka in a spring boot application. In order to learn how to create a spring boot project, r
2 min read
Spring Boot | How to publish JSON messages on Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to send JSON messages to Apache Kafka in a spring boot application. In order to learn how to create a spring boot project, ref
4 min read
Spring Boot - Consume JSON Object From Kafka Topics Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging system lets someone is sending messages between processes, applications, and servers. Broadly Speaking, Apache Kafka is software where topics (A topic might be a category) can be defined and further processed. Applications may connect
4 min read
Spring Boot Kafka Producer Example Spring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Spring Boot Kafka Consumer Example Spring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Message Compression in Apache Kafka using Spring Boot Generally, producers send text-based data, such as JSON data. It is essential to apply compression to the producer in this situation. Producer messages are transmitted uncompressed by default. There are two types of Kafka compression. 1. Producer-Level Kafka Compression When compression is enabled o
4 min read
Spring Boot - Create and Configure Topics in Apache Kafka Topics are a special and essential component of Apache Kafka that are used to organize events or messages. In other words, Kafka Topics enable simple data transmission and reception across Kafka Servers by acting as Virtual Groups or Logs that store messages and events in a logical sequence. In this
2 min read
How to Test Spring Boot Project using ZeroCode? Zerocode automated testing framework for a REST API project concept is getting seen via this tutorial by taking a sample spring boot maven project. Let us see the dependencies for Zerocode : <dependency> <groupId>org.jsmart</groupId> <artifactId>zerocode-tdd</artifactId
5 min read