Spring Boot - AOP After Returning Advice
Last Updated : 07 Mar, 2022
Prerequisite: Aspect Oriented Programming and AOP in Spring Framework
Aspect-oriented programming(AOP) as the name suggests uses aspects in programming. It can be defined as the breaking of code into different modules, also known as modularisation, where the aspect is the key unit of modularity. Aspects enable the implementation of crosscutting concerns such as transaction, logging not central to business logic without cluttering the code core to its functionality. It does so by adding additional behavior that is the advice to the existing code. For example- Security is a crosscutting concern, in many methods in an application security rules can be applied, therefore repeating the code at every method, defining the functionality in a common class and control were to apply that functionality in the whole application. In this article, we will be covering a working example of After Returning Advice.
After Returning Advice is executed after a join point method is executed successfully. It is denoted by @AfterReturning annotation. If any exception is raised from the method, then after returning advice will not be executed.
Steps to Implement AOP After Returning Advice in Spring Boot Application
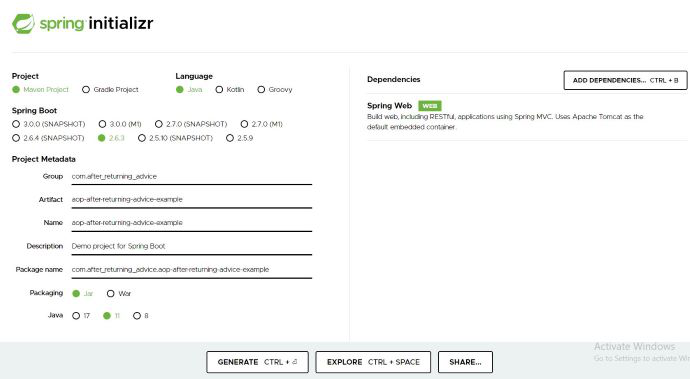
Step 1: Open Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io
Step 2: Provide the Group name: com.after_returning_advice
Step 3: Provide the Artifact Id: aop-after-returning-advice-example
Step 4: Add the Spring Web dependency.
Step 5: Click on the Generate button. A zip file will be downloaded into the system. Extract it.
Step 6: Import the folder in the IDE by using the following steps:
File -> Import -> Existing Maven Projects -> Next -> Browse -> Look for the folder aop-after-returning-advice-example -> Finish. When the project is imported, it will install the dependencies. Once it is done, follow the next steps.
Step 7: Add the dependency for spring AOP in pom.xml
pom.xml
XML <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.before_advice</groupId> <artifactId>aop-before-advice-example</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>aop-before-advice-example</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- dependency for spring web --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- added dependency for spring aop --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
Save the changes and it will download the jars. Once it is done, move ahead with the next steps.
Note: If the jars are not added properly, you may get some errors.
Step 8: Create a package with the name com.after_returning_advice.model. and add a Student model class to it.
Student class:
Java package com.after_returning_advice.model; public class Student { private String firstName; private String secondName; public Student() { } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getSecondName() { return secondName; } public void setSecondName(String secondName) { this.secondName = secondName; } } Step 9: Create a package with the name com.after_returning_advice.service and add a Student Service class to it. Add a method to add students with given name arguments.
StudentService class:
Java package com.after_returning_advice.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.after_returning_advice.model.Student; @Service public class StudentService { public Student addStudent(String fname, String sname) { System.out.println("Add student service method called"); Student stud = new Student(); stud.setFirstName(fname); stud.setSecondName(sname); if(fname.length()<=3) throw new RuntimeException("Length of firstname must be 4 or more" ); return stud; } }
Step 10: Create a package with the name com.after_returning_advice.controller. and add a Student Controller class to it. Add a method to handle Get requests and call Student Service from it.
StudentController class:
Java package com.after_returning_advice.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.after_returning_advice.model.Student; import com.after_returning_advice.service.StudentService; @RestController public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @GetMapping(value = "/add") public Student addStudent(@RequestParam("firstName") String firstName, @RequestParam("secondName") String secondName) { return studentService.addStudent(firstName, secondName); } }
Step 11: Create a package with the name com.after_returning_advice.aspect and add a Student Service Aspect class to it. Here we will add our Advice method and PointCut expression.
StudentServiceAspect class:
Java package com.after_returning_advice.aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class StudentServiceAspect { // the pointcut expression specifying execution of any // method in com.after_returning_advice.service.StudentService // class of any return type with 0 or more number of arguments @Pointcut("execution(* com.after_returning_advice.service.StudentService.*(..)) ") // the pointcut signature private void anyStudentService() {} @AfterReturning("anyStudentService() && args(fname, sname)") public void afterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, String fname, String sname) { System.out.println("After Returning method:" + joinPoint.getSignature()+"\n " + "Added Student with first name - " + fname + ", second name - " + sname ); } } Step 12: We are done with the code structure. Now to run the application, start the application as "run as boot application". Open the browser and hit the following URL to make a get request call: http://localhost:{portNumber}/add?firstName={fname}&secondName={sname}
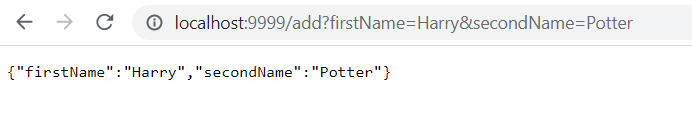
For the demo, we are hitting URL with fname as Harry and sname as Potter. In this case, the method will be executed normally.

When we hit URL with fname as Tom, the service method will throw an exception. The After Returning advice will not be executed.


As seen in the output, after returning advice is called after the service method is executed successfully.
Similar Reads
Spring Boot - Auto-configuration Spring Boot is heavily attracting developers toward it because of three main features as follows: Auto-configuration - such as checking for the dependencies, the presence of certain classes in the classpath, the existence of a bean, or the activation of some property.An opinionated approach to confi
5 min read
Spring Boot - EhCaching EhCache is an open-source and Java-based cache. It is used to boost performance. Its current version is 3. EhCache provides the implementation of the JSR-107 cache manager. Features of EhCache are given below: It is fast, lightweight, Flexible, and Scalable.It allows us to perform Serializable and O
5 min read
Difference Between Spring Boot Starter Web and Spring Boot Starter Tomcat Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read
Spring Boot - Starter Test Spring Boot is built on top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. It is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment, which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and setup.
5 min read
Exception Handling in Spring Boot Exception handling in Spring Boot helps deal with errors and exceptions present in APIs, delivering a robust enterprise application. This article covers various ways in which exceptions can be handled and how to return meaningful error responses to the client in a Spring Boot Project. Key Approaches
8 min read
Spring Boot - Project Deployment Using Tomcat Spring Boot is a microservice-based framework and making a production-ready application in it takes very little time. Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because it’s a rapid production-ready envir
5 min read
Spring Boot - Difference Between AOP and OOP AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming) complements OOP by enabling modularity of cross-cutting concerns. The Key unit of Modularity(breaking of code into different modules) in Aspect-Oriented Programming is Aspect. one of the major advantages of AOP is that it allows developers to concentrate on business
3 min read
Spring Boot - Difference Between AOP and AspectJ Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read
Spring Boot - Logging Logging in Spring Boot plays a vital role in Spring Boot applications for recording information, actions, and events within the app. It is also used for monitoring the performance of an application, understanding the behavior of the application, and recognizing the issues within the application. Spr
8 min read
Advantages of Spring Boot JDBC Spring JDBC is used to build the Data Access Layer of enterprise applications, it enables developers to connect to the database and write SQL queries and update data to the relational database. The code related to the database has to be placed in DAO classes. SpringJDBC provides a class called JdbcT
3 min read