Soil formation occurs continuously but slowly, from the gradual breaking down of the rocks by the processes of weathering. Weathering can be physical, chemical as well and biological processes. The soil is considered to be one of the most essential natural resources and is the base for the growth of vegetation, on which our nutrition and livelihood depend. Soil is also the main source on which many microorganisms such as earthworms, rates, and several other species live. The soil forms continuously but slowly, from a gradual breakdown of rocks by weathering.
What is Soil?
Soil refers to the uppermost layer of the surface of the Earth and is formed by the processes of weathering of mountains over thousands of years. The main components soil is made of include minerals, organic materials, water, and air. The essential components on which the texture of soil depends include sand, silt, and clay. Leaves as well as organic constituents help in decomposing the upper organic layer, known as the humus and the humus plays a very significant role in fertility.
Soil formation takes place through a plethora of processes, which include the weathering of rocks and mixing of rock materials with organic debris which is formulated by the decay of plants; other processes include a slow chemical alteration of water that seeps through the weathered rock materials after rains.
Weathering is the process by which rocks are broken down to form smaller particles which ultimately leads to soil formation that includes both geological sediments and organic debris. It takes around 500 years for the formation of 1 cm of soil from harder rocks. Combined processes of physical, chemical, and biological factors including weathering of rocks, under environmental conditions, lead to soil formation; a mixture of biotic and abiotic components; all of which make the soil fertile which is suitable for the growth of plants or agriculture.
 Soil Formation Diagram
Soil Formation DiagramThe soil formation depends on the processes which are listed below:
Parent material
Few soils weather directly from underlying rocks. These "residual" soils have the same general chemistry as the original rocks. The material in which soil forms is called parent material. The parent material is mostly weathered by chemical and physical processes and transported, which is then deposited to form layers of soil. Bedrock is usually the parent material, but soil also gets transported because of factors like wind and water.
Organisms
Organisms include plants, animals, microorganisms, and fungi. They play a vital role in the formation of soil and are important determinants of the impact on the physical and chemical environments of the soil.
Climate
Soil formation prefers heat and moisture. In case, the climate is dry and cool, the rate of soil formation decreases. The prevailing climatic conditions determine the nature of weathering process, the place, and rates of both physical and chemical processes. Climate affects the kind of vegetation in an area, which affects the process of soil formation.
Topography
Topography refers to the configuration of the surface of the land and the relation of land with man-made and also natural features. The shape of the land and also the position of the slope on the landscape are important parts of topography.
Time
The time taken for the soil formation affects the quality of the soil. Soil formation tends to take place over thousands of years by undergoing significant changes and eventual formation. Soils within certain age brackets are young and tend to have weak soil horizon development.
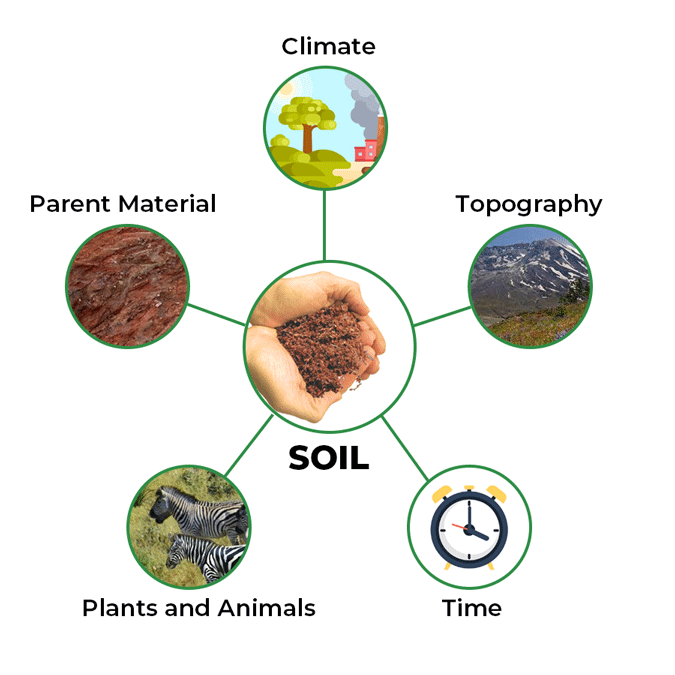 Factors for Soil Formation
Factors for Soil FormationThe types of soil formation can be classified primarily into three types based on their texture. This includes sand, silt and clay. The percentage of these textures can vary, resulting in various types of soil which include loamy, sand, sandy, clay, silty clay etc.
4 important processes of soil formation include:
- Additions
- Losses
- Transformations
- Translocation
Carriers or Weathering Agents
The important carriers or the weathering agents of soil formation are as mentioned below:
Glacier
When the glaciers tend to move from one part to another, the soil is pushed further with them and the drifted materials are deposited miles away from the place of its formation and when the glaciers tend to melt, huge heaps of soil are left and part of that soil is carried by the streams.
Water
The soil particles are transported with water, as the rivers flow. The smallest particles of the soil are transported further and heavier particles are settled down earlier soils are deposited along banks of rivers, termed to be alluvial soil, which is rich in mineral contents and rainfall also tends to play a very important role.
Wind
Wind plays a vital role in the transportation of huge quantities of soil from one place to another and loose soils are carried away by the wind from one place to the next.
The following are important weathering processes on which soil formation depends:
Freezing and Melting
A process of continuous freezing and melting, results in the formation of cracks in the rocks, and the presence of the sun expands the surface of the rock. Coming in contact with water bodies, these pores are filled with water and the water tends to be expanded when frozen, which kind of pushes the particles apart and breaks them. With the melting of ice, rocks are broken into loose particles of soil.
Heating and Cooling
In places of extreme climatic conditions, like arctic or arid regions, the rocks tend to be subjected to sudden expansion as well as contraction, which results in the loosening of the particles, and air content increases. Over time, rocks are reduced to loose soil with significant effects working on it.
Wetting and Drying
The rocks tend to shrink when dry and expand/swell when they are wet. Daily wetting as well as drying of rocks results in the process of loosening the grains.
Grinding or Rubbing
At the time of waves, the rocks are pounded along the seashore, and the processes of abrasion of the upper layer occur with fragmentation into smaller rocks and which further break into smaller particles.
Organisms
Organisms play a very vital role in churning way through the soil and by eating it. This results in the formation of nutrient-rich manure in form of their excreta and their movements help in the mixing and aeration of the given soil.
Soil Profile
It is a vertical cross-section of soil, made of layers parallel to the surface. Each layer of soil has a different texture and is called a horizon.
- Horizon A (Topsoil): It is the topmost layer where organic materials are engulfed with mineral matter, nutrients, and water; essential elements for the growth of plants.
- Horizon B (Subsoil): This zone has a greater content of minerals and humus is present in lesser quantities. Contains materials from both above and below layers.
- Horizon C ( weathered and decomposed rock): Comprises loose parent rock materials and is the first stage of soil formation.
Soil Profile Diagram
 Soil Formation Diagram
Soil Formation DiagramAlso, Read
Similar Reads
Preparation of Soil Soil is a critical natural resource. Soil is the earth's thin surface layer composed of mineral particles formed by the breakdown (weathering) of rocks, decayed organic materials, living organisms, water, and air. Soil formation occurs through a variety of processes, including weathering of rocks an
6 min read
Soil Pollution Soil Pollution refers to the process of contamination of soil which is caused because of high concentrations of toxic substances. Human activities are the primary reasons for soil pollution and land degradation. Let's learn about soil pollution in detail, including its causes and effects. Soil Pollu
7 min read
Soil Conservation Methods The ground is a critical condition and local weather because plants as sustain human beings namely nicely so homegrown creatures then restless life. Since the near flora can not dwell without earth, such is influential for utilizing that commodity sparingly. The methodology empowers us in conformity
7 min read
Soil Formation| Class 11 Geography Notes Soil is a dynamic medium with constant chemical, physical, and biological activities. Soil is a result of decay, it is also the medium for growth. It is a changing and developing body. It has many characteristics that fluctuate with the seasons. Organic matter increases when leaves fall or grasses d
8 min read
Phytoremediation Phytoremediation is an emerging technology that uses living plants to remove, degrade, or contain environmental contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, solvents, explosives, and crude oil. There are various phytoremediation types including phytoextraction, phytostabilization, rhizofiltration,
9 min read