The useRef Hook is a built-in React Hook that returns a mutable reference object (ref) that persists across renders. Unlike state variables, updating a ref does not trigger a component re-render.
Syntax
const refContainer = useRef(initialValue);
- useRef returns an object { current: initialValue }.
- The .current property can be updated without re-rendering the component.
Implementing the useRef hook
1. Accessing the DOM using useRef hook.
In this example, we have a button called ACTION, whenever we click on the button the onClickHandler gets triggered and it focuses the textarea with the help of useRef hook.
JavaScript import React, { Fragment, useRef } from 'react'; function App() { const focusPoint = useRef(null); const onClickHandler = () => { focusPoint.current.value = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"; focusPoint.current.focus(); }; return ( <Fragment> <div> <button onClick={onClickHandler}> ACTION </button> </div> <label> Click on the action button to focus and populate the text. </label><br /> <textarea ref={focusPoint} /> </Fragment> ); }; export default App; Output
 React JS useRef Hook
React JS useRef HookIn this example
- useRef creates a reference focusPoint, which allows direct manipulation of the DOM element.
- Clicking the "ACTION" button triggers onClickHandler, which sets text in the textarea and focuses it.
- <Fragment> (<>...</>) is used to group multiple elements without adding extra wrappers in the DOM.
2. Persisting Values Across Renders
In addition to accessing DOM elements, useRef is useful for storing values that persist across renders. A common use case is storing a previous value, such as the previous state or props.
JavaScript import React, { useState, useRef, useEffect } from "react"; function PreviousValue() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); const prevCountRef = useRef(); useEffect(() => { prevCountRef.current = count; }, [count]); return ( <div> <p>Current count: {count}</p> <p>Previous count: {prevCountRef.current}</p> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increment</button> </div> ); } export default PreviousValue; Output
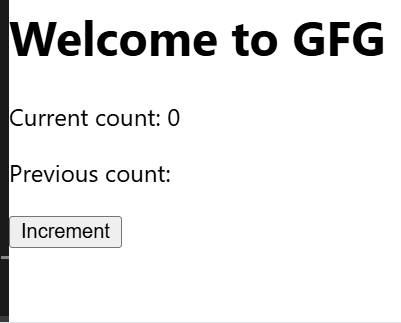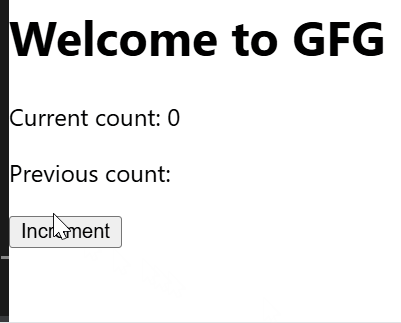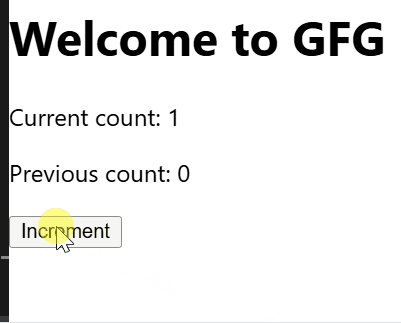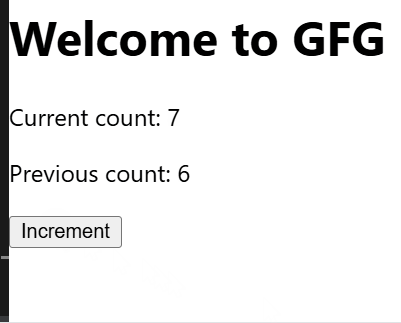 Persisting Values Across Renders
Persisting Values Across RendersIn this example
count is a state variable that tracks the current count.- prevCountRef is a reference created with useRef to store the previous count value.
- Whenever count changes, the useEffect hook updates prevCountRef.current to store the previous count.
- Clicking the button increases the count by 1 and updates both the current and previous counts.
Interesting Things About useRef Hook
- Does Not Cause Re-renders: Unlike state variables, updating a useRef value does not trigger a component re-render. This makes it useful for storing values that persist across renders without causing unnecessary updates.
- Accessing DOM Elements: useRef is commonly used to reference DOM elements directly, allowing operations such as focusing input fields, managing animations, and interacting with elements without causing re-renders.
- Tracking State Changes: It can be used to store previous state values and track changes between renders, which is helpful for comparing current and previous values without affecting component updates.
When to Use useRef?
You should use useRef when
- Accessing and manipulating DOM elements without triggering re-renders.
- Persisting values across renders without causing re-renders.
- Storing previous state values to compare changes between renders.
- Optimizing performance by avoiding unnecessary state updates.
useRef vs useState
While both useRef and useState can store values, they behave differently:
- useRef does not trigger re-renders when updated, making it ideal for persisting values between renders.
- useState triggers re-renders whenever the state value is updated.
- Use useRef for storing references and preserving values, and useState for UI updates.
Performance Considerations
Using useRef correctly can enhance performance, but excessive use may introduce unnecessary complexity.
- Use it for non-rendered values: Ideal for persisting values like timers, previous states, or DOM elements.
- Avoid using it as state replacement: If UI updates are needed, use useState instead.
- Measure before optimizing: Use React DevTools to analyze performance.