Python Django Queryset Filtering
Last Updated : 22 May, 2025
In Django, QuerySet filtering allows you to retrieve only the data you need from the database. QuerySets help you filter, sort and organize your data efficiently, making it easy to interact with your models.
This article will explore how to filter datasets using Django’s filter(), exclude() and advanced filtering with Q objects, let's create a model named "user".
Define the User Model
In projectApp/models.py, define a User model with fields like user_name, city and country:
Python from django.db import models class User(models.Model): user_name = models.CharField(max_length=20) city = models.CharField(max_length=20, blank=True, null=True) country = models.CharField(max_length=20, blank=True, null=True) def __str__(self): return self.user_name
Register the Model in Django Admin
To make the User model accessible in the Django Admin interface, register it in projectApp/admin.py:
Python from django.contrib import admin from .models import User admin.site.register(User)
Create a superuser to access the model through admin panel.
python manage.py createsuperuser
Suppose we have the following the entries in our User model:
 Snapshot of the database
Snapshot of the databaseQuerySet Filtering Examples
Now that we have our User model, let’s explore how to filter data using QuerySets.
1. Filtering All Users:
To retrieve all users from a specific country, use filter():
users = User.objects.filter(country='India')
This retrieves all users where the country is 'India':
 Snapshot of the command in shell
Snapshot of the command in shell2. Excluding Specific Records:
To exclude records that match a condition, use exclude():
users = User.objects.filter(country='India').exclude(city='Mumbai')
This retrieves all users from India, excluding those from Mumbai.
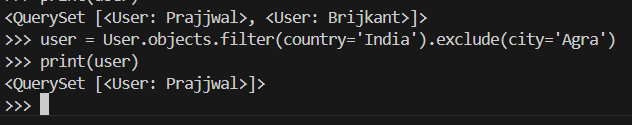 Snapshot of shell
Snapshot of shell3. Using Q Objects for Advanced Filtering:
Q objects allow for more complex queries, like OR conditions:
from django.db.models import Q
users = User.objects.filter(Q(country='India') | Q(city='New York'))
This returns users who are from either India or New York.
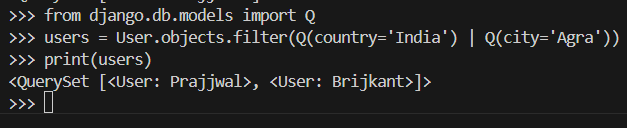 Snapshot of shell
Snapshot of shell Similar Reads
Django URL patterns | Python In Django, views are Python functions that handle HTTP requests. These views process the request and return an HTTP response or an error (e.g., 404 if not found). Each view must be mapped to a specific URL pattern. This mapping is managed through URLConf (URL Configuration).In this article, we'll ex
3 min read
Views In Django | Python Django Views are one of the vital participants of the MVT Structure of Django. As per Django Documentation, A view function is a Python function that takes a Web request and returns a Web response. This response can be the HTML contents of a Web page, a redirect, a 404 error, an XML document, an ima
6 min read
Django Query Set - get A QuerySet is a collection of data retrieved from the database. You can think of it as a list of objects. QuerySets make it easier to get only the data you need by letting you filter, sort, and organize your data early on before actually fetching it from the database.In this article, we will learn h
3 min read
How to Perform Query Filtering in Django Templates Sometimes we may want to filter or modify the list of objects within the template itself to tailor the data being displayed. While filtering should generally be done at the view level for clarity and separation of concerns, Django templates provide some basic filtering capabilities through template
5 min read
Count() vs len() on a Django QuerySet In Django, when working with database query sets, developers often need to determine the number of records that meet certain criteria. Django offers two primary ways to accomplish this: using the count() method on a QuerySet, or the Python built-in len() function. Each method has its specific use ca
3 min read