Lists in Python are the most flexible and commonly used data structure for sequential storage. They are similar to arrays in other languages but with several key differences:
- Dynamic Typing: Python lists can hold elements of different types in the same list. We can have an integer, a string and even other lists all stored within a single list.
- Dynamic Resizing: Lists are dynamically resized, meaning you can add or remove elements without declaring the size of the list upfront.
- Built-in Methods: Python lists come with numerous built-in methods that allow for easy manipulation of the elements within them, including methods for appending, removing, sorting and reversing elements.
Example:
Python a = [1, "Hello", [3.14, "world"]] a.append(2) # Add an integer to the end print(a)
Output[1, 'Hello', [3.14, 'world'], 2]
Note: Python does not have built-in array support in the same way that languages like C and Java do, but it provides something similar through the array module for storing elements of a single type.
NumPy Arrays
NumPy arrays are a part of the NumPy library, which is a powerful tool for numerical computing in Python. These arrays are designed for high-performance operations on large volumes of data and support multi-dimensional arrays and matrices. This makes them ideal for complex mathematical computations and large-scale data processing.
Key Features:
- Multi-dimensional support: NumPy arrays can handle more than one dimension, making them suitable for matrix operations and more complex mathematical constructs.
- Broad broadcasting capabilities: They can perform operations between arrays of different sizes and shapes, a feature known as broadcasting.
- Efficient storage and processing: NumPy arrays are stored more efficiently than Python lists and provide optimized performance for numerical operations.
Example Code:
Python import numpy as np # Creating a NumPy array arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) # Element-wise operations print(arr * 2) # Multi-dimensional array arr2d = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) print(arr2d * 2)
Output[2 4 6 8] [[2 4] [6 8]]
Note: Choose NumPy arrays for scientific computing, where you need to handle complex operations or work with multi-dimensional data.
Use Python's array module when you need a basic, memory-efficient container for large quantities of uniform data types, especially when your operations are simple and do not require the capabilities of NumPy.
Python Arrays
In Python, array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. Unlike Python lists (can store elements of mixed types), arrays must have all elements of same type. Having only homogeneous elements makes it memory-efficient.
Python Array Example:
Python import array as arr # creating array of integers a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3]) # accessing First Araay print(a[0]) # Adding element to array a.append(5) print(a) Output1 array('i', [1, 2, 3, 5]) Create an Array in Python
Array in Python can be created by importing an array module. array( data_type , value_list ) is used to create array in Python with data type and value list specified in its arguments.
Python import array as arr # creating array a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3]) # iterating and printing each item for i in range(0, 3): print(a[i], end=" ") 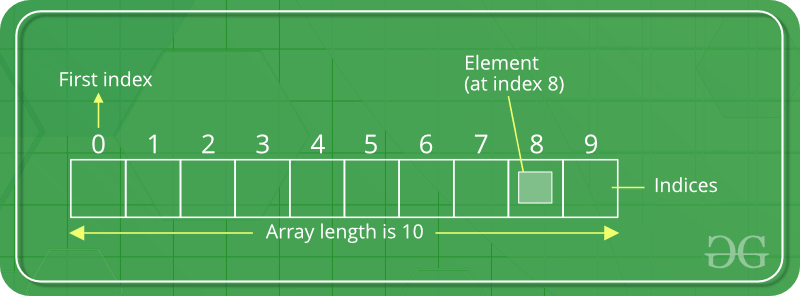 Python Array Index
Python Array IndexAdding Elements to an Array
Elements can be added to the Python Array by using built-in insert() function. Insert is used to insert one or more data elements into an array. Based on the requirement, a new element can be added at the beginning, end, or any given index of array. append() is also used to add the value mentioned in its arguments at the end of the Python array.
Python import array as arr # Integer array example a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3]) print("Integer Array before insertion:", *a) a.insert(1, 4) # Insert 4 at index 1 print("Integer Array after insertion:", *a) OutputInteger Array before insertion: 1 2 3 Integer Array after insertion: 1 4 2 3
Note: We have used *a and *b for unpacking the array elements.
Accessing Array Items
In order to access the array items refer to the index number. Use the index operator [ ] to access an item in a array in Python. The index must be an integer.
Python import array as arr a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) print(a[0]) print(a[3]) b = arr.array('d', [2.5, 3.2, 3.3]) print(b[1]) print(b[2]) Removing Elements from the Array
Elements can be removed from the Python array by using built-in remove() function. It will raise an Error if element doesn’t exist. Remove() method only removes the first occurrence of the searched element. To remove range of elements, we can use an iterator.
pop() function can also be used to remove and return an element from the array. By default it removes only the last element of the array. To remove element from a specific position, index of that item is passed as an argument to pop() method.
Python import array arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 1, 5]) # using remove() method to remove first occurance of 1 arr.remove(1) print(arr) # pop() method - remove item at index 2 arr.pop(2) print(arr) Outputarray('i', [2, 3, 1, 5]) array('i', [2, 3, 5]) Slicing of an Array
In Python array, there are multiple ways to print the whole array with all the elements, but to print a specific range of elements from the array, we use Slice operation .
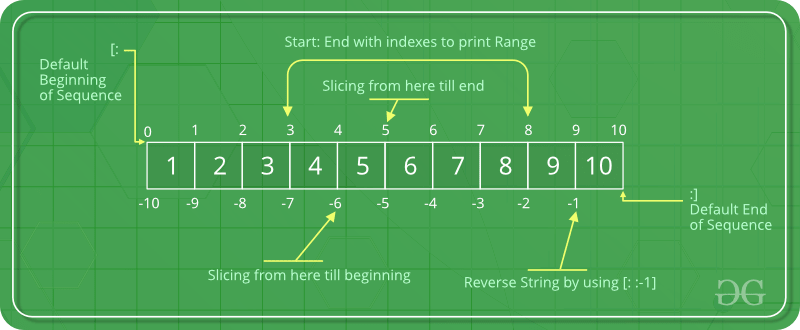
- Elements from beginning to a range use [:Index]
- Elements from end use [:-Index]
- Elements from specific Index till the end use [Index:]
- Elements within a range, use [Start Index:End Index]
- Print complete List, use [:].
- For Reverse list, use [::-1].
Python import array as arr l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] a = arr.array('i', l) Sliced_array = a[3:8] print(Sliced_array) Sliced_array = a[5:] print(Sliced_array) Sliced_array = a[:] print(Sliced_array) Outputarray('i', [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) array('i', [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) Searching Element in an Array
In order to search an element in the array we use a python in-built index() method. This function returns the index of the first occurrence of value mentioned in arguments.
Python import array arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 5]) # index of 1st occurrence of 2 print(arr.index(2)) # index of 1st occurrence of 1 print(arr.index(1)) Updating Elements in an Array
In order to update an element in the array we simply reassign a new value to the desired index we want to update.
Python import array arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 5]) # update item at index 2 arr[2] = 6 print(arr) # update item at index 4 arr[4] = 8 print(arr) Outputarray('i', [1, 2, 6, 1, 2, 5]) array('i', [1, 2, 6, 1, 8, 5]) Different Operations on Python Arrays
Counting Elements in an Array
We can use count() method to count given item in array.
Python import array arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 5, 2]) count = arr.count(2) print("Number of occurrences of 2:", count) OutputNumber of occurrences of 2: 3
Reversing Elements in an Array
In order to reverse elements of an array we need to simply use reverse method.
Python import array arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) arr.reverse() print("Reversed array:", *arr) OutputReversed array: 5 4 3 2 1
Extend Element from Array
In Python, an array is used to store multiple values or elements of the same datatype in a single variable. The extend() function is simply used to attach an item from iterable to the end of the array. In simpler terms, this method is used to add an array of values to the end of a given or existing array.
list.extend(iterable)
Here, all the element of iterable are added to the end of list1
Python import array as arr a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3,4,5]) # using extend() method a.extend([6,7,8,9,10]) print(a) Outputarray('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) Quiz:
Related Articles:
Recommended Problems:
Similar Reads
Python Tutorial | Learn Python Programming Language Python Tutorial – Python is one of the most popular programming languages. It’s simple to use, packed with features and supported by a wide range of libraries and frameworks. Its clean syntax makes it beginner-friendly.Python is:A high-level language, used in web development, data science, automatio
10 min read
Python Data Types Python Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value that tells what operations can be performed on a particular data. Since everything is an object in Python programming, Python data types are classes and variables are instances (objects) of thes
9 min read
Python Numbers In Python, numbers are a core data-type essential for performing arithmetic operations and calculations. Python supports three types of numbers, including integers, floating-point numbers and complex numbers. Here's an overview of each:Pythona = 4 # integer b = 4.5 # float c = 4j # complex number pr
6 min read
Python Boolean Python Boolean type is one of the built-in data types provided by Python, which represents one of the two values i.e. True or False. Generally, it is used to represent the truth values of the expressions.Python Boolean TypeBoolean value can be of two types only i.e. either True or False. The output
7 min read
Python String A string is a sequence of characters. Python treats anything inside quotes as a string. This includes letters, numbers, and symbols. Python has no character data type so single character is a string of length 1.Pythons = "GfG" print(s[1]) # access 2nd char s1 = s + s[0] # update print(s1) # printOut
6 min read
Python Lists In Python, a list is a built-in dynamic sized array (automatically grows and shrinks). We can store all types of items (including another list) in a list. A list may contain mixed type of items, this is possible because a list mainly stores references at contiguous locations and actual items maybe s
6 min read
Python Arrays Lists in Python are the most flexible and commonly used data structure for sequential storage. They are similar to arrays in other languages but with several key differences:Dynamic Typing: Python lists can hold elements of different types in the same list. We can have an integer, a string and even
9 min read
Python Tuples A tuple in Python is an immutable ordered collection of elements. Tuples are similar to lists, but unlike lists, they cannot be changed after their creation (i.e., they are immutable). Tuples can hold elements of different data types. The main characteristics of tuples are being ordered , heterogene
6 min read
Dictionaries in Python Python dictionary is a data structure that stores the value in key: value pairs. Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be duplicated, whereas keys can't be repeated and must be immutable. Example: Here, The data is stored in key:value pairs in dictionaries, which makes it easier to
5 min read
Python Sets Python set is an unordered collection of multiple items having different datatypes. In Python, sets are mutable, unindexed and do not contain duplicates. The order of elements in a set is not preserved and can change.Creating a Set in PythonIn Python, the most basic and efficient method for creating
10 min read