Python Web Scraping Tutorial
Last Updated : 19 Jun, 2025
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites automatically. Python is widely used for web scraping because of its easy syntax and powerful libraries like BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Selenium.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use these Python tools to scrape data from websites and understand why Python 3 is a popular choice for web scraping tasks.
To install the required libraries in this article, run the following commands in the terminal.
pip install requests
pip install beautifulsoup4
pip install selenium
pip install lxml
pip install schedule
pip install pyautogui
- requests: Sends HTTP requests to get webpage content (used for static sites).
- beautifulsoup4: Parses and extracts HTML content (like tags, text, links).
- selenium: Automates browsers (needed for dynamic sites with JavaScript).
- lxml: A fast HTML/XML parser, useful for large or complex pages.
- schedule: Lets you run scraping tasks repeatedly at fixed intervals.
- pyautogui: Automates mouse and keyboard; useful when dealing with UI-based interactions.
Requests Module
The requests library is used for making HTTP requests to a specific URL and returns the response. Python requests provide inbuilt functionalities for managing both the request and response.
pip install requests
Example: Send a GET request to a webpage
Python import requests response = requests.get('https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-programming-language/') print(response.status_code) print(response.content) Output:
 Snapshot of the raw html data using request module
Snapshot of the raw html data using request moduleExplanation:
- requests.get(url): Sends a GET request to the given URL.
- response.status_code: Returns HTTP status code (200 = success).
- response.content: Returns the raw HTML of the page in bytes.
For more information, refer to our Python Requests Tutorial .
Parsing HTML with BeautifulSoup
Once the raw HTML is fetched, the next step is to parse it into a readable structure. That’s where BeautifulSoup comes in. It helps convert the raw HTML into a searchable tree of elements.
Example: Parse HTML using BeautifulSoup
Python import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup response = requests.get('https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-programming-language/') soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, 'html.parser') print(soup.prettify()) Output:
 Snapshot of the beautified html response using beautifulsoap module
Snapshot of the beautified html response using beautifulsoap moduleExplanation:
- BeautifulSoup(html, parser): Converts HTML into a searchable object. 'html.parser' is the built-in parser.
- soup.prettify(): Formats the HTML nicely for easier reading.
At this point, the HTML is ready to be searched for tags, classes or content.
Extracting Content by Tag and Class
Once we have parsed the HTML using BeautifulSoup, the next step is to locate and extract specific content from the page. Websites usually wrap their main article content inside tags with identifiable classes like <div class="article--viewer_content">. We can target such elements and pull out useful data like text, links or images.
In this example, we'll extract all paragraph (<p>) text from the main content section of the GeeksforGeeks Python Tutorial page.
Example: Extract paragraph content by class and tag
Python import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # Fetch and parse the page response = requests.get('https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-programming-language-tutorial/') soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, 'html.parser') # Find the main content container content_div = soup.find('div', class_='article--viewer_content') if content_div: for para in content_div.find_all('p'): print(para.text.strip()) else: print("No article content found.") Output:
 Extracted text content from the given URL
Extracted text content from the given URLImage of the actual GeeksforGeeks Python Tutorial page:
 Snapshot of the actual webpage of the URL
Snapshot of the actual webpage of the URLNotice that the text output in the terminal contains the actual content from the web page.
For more information, refer to our Python BeautifulSoup .
Selenium
Some websites load their content dynamically using JavaScript. This means the data you're trying to scrape may not be present in the initial HTML source. In such cases, BeautifulSoup alone won’t work, because it only reads static HTML.
To handle this, we use Selenium that can automate browsers like Chrome or Firefox, wait for content to load, click buttons, scroll and extract fully rendered web pages just like a real user.
What is a WebDriver
A WebDriver is a software component that Selenium uses to interact with a web browser. It acts as the bridge between your Python script and the actual browser window.
Each browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.) has its own WebDriver:
- Chrome: ChromeDriver
- Firefox: GeckoDriver
- Edge: EdgeDriver
Selenium uses this WebDriver to:
- Open and control the browser
- Load web pages
- Extract elements
- Simulate clicks, scrolls and inputs
You can either manually download the WebDriver or use webdriver-manager which handles the download and setup automatically.
Example 1: Searching on Google with Firefox
In this example, we're directing the browser to the Google search page with the query parameter "geeksforgeeks". The browser will load this page and we can then proceed to interact with it programmatically using Selenium. This interaction could involve tasks like extracting search results, clicking on links or scraping specific content from the page.
Python # import webdriver from selenium import webdriver # create webdriver object driver = webdriver.Firefox() # get google.co.in driver.get("https://google.co.in / search?q = geeksforgeeks") Output

Example 2: Scrape Laptop Details from a Test Site using Chrome
Python from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager import time element_list = [] # Set up Chrome options (optional) options = webdriver.ChromeOptions() options.add_argument("--headless") # Run in headless mode (optional) options.add_argument("--no-sandbox") options.add_argument("--disable-dev-shm-usage") # Use a proper Service object service = Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()) for page in range(1, 3): # Initialize driver properly driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=service, options=options) # Load the URL url = f"https://webscraper.io/test-sites/e-commerce/static/computers/laptops?page={page}" driver.get(url) time.sleep(2) # Optional wait to ensure page loads # Extract product details titles = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "title") prices = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "price") descriptions = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "description") ratings = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "ratings") # Store results in a list for i in range(len(titles)): element_list.append([ titles[i].text, prices[i].text, descriptions[i].text, ratings[i].text ]) driver.quit() # Display extracted data for row in element_list: print(row) Output:
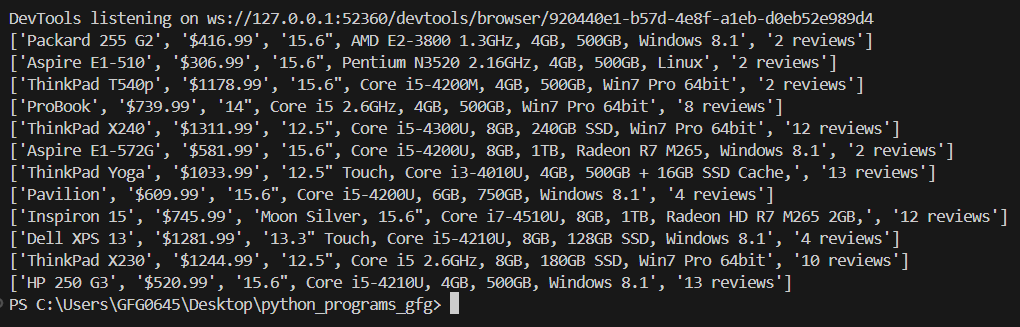 Snapshot of the output in Terminal
Snapshot of the output in TerminalExplanation:
- ChromeOptions() + --headless: Runs the browser in the background without opening a visible window — ideal for automation and speed.
- ChromeDriverManager().install(): Automatically downloads the correct version of ChromeDriver based on your Chrome browser.
- Service(...): Wraps the ChromeDriver path for proper configuration with Selenium 4+.
- webdriver.Chrome(service=..., options=...): Launches a Chrome browser instance with the given setup.
- driver.get(url): Navigates to the specified page URL.
- find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "class"): Extracts all elements matching the given class name like titles, prices, etc.
- .text: Retrieves the visible text content from an HTML element.
- element_list.append([...]): Stores each product's extracted data in a structured list.
- driver.quit(): Closes the browser to free system resources.
For more information, refer to our Python Selenium .
Parsing HTML with lxml and XPath
lxml is a high-speed parser that supports XPath queries, ideal when you need precision.
Example
Below is a simple example demonstrating how to use the lxml module for Python web scraping:
- We import the html module from lxml along with the requests module for sending HTTP requests.
- We define the URL of the website we want to scrape.
- We send an HTTP GET request to the website using the requests.get() function and retrieve the HTML content of the page.
- We parse the HTML content using the html.fromstring() function from lxml which returns an HTML element tree.
- We use XPath expressions to extract specific elements from the HTML tree. In this case, we're extracting the text content of all the <a> (anchor) elements on the page.
- We iterate over the extracted link titles and print them out.
Python from lxml import html import requests url = 'https://example.com' response = requests.get(url) tree = html.fromstring(response.content) # Extract all link texts link_titles = tree.xpath('//a/text()') for title in link_titles: print(title) Output in the Terminal
More information...
Below is the snapshot of the actual webpage of the URL: 'https://example.com'
 Snapshot of the webpage of URL used in the code
Snapshot of the webpage of URL used in the codeCode Explanation:
- html.fromstring(): Parses HTML into an element tree.
- tree.xpath(): Uses XPath to extract specific tags or data.
For more information, refer to our lxml
Urllib Module
The urllib module in Python is a built-in library that provides functions for working with URLs. It allows you to interact with web pages by fetching URLs (Uniform Resource Locators), opening and reading data from them and performing other URL-related tasks like encoding and parsing. Urllib is a package that collects several modules for working with URLs such as:
- urllib.request for opening and reading.
- urllib.parse for parsing URLs
- urllib.error for the exceptions raised
- urllib.robotparser for parsing robot.txt files
If urllib is not present in your environment, execute the below code to install it.
pip install urllib3
Example
Here's a simple example demonstrating how to use the urllib module to fetch the content of a web page:
- We define the URL of the web page we want to fetch.
- We use urllib.request.urlopen() function to open the URL and obtain a response object.
- We read the content of the response object using the read() method.
- Since the content is returned as bytes, we decode it to a string using the decode() method with 'utf-8' encoding.
- Finally, we print the HTML content of the web page.
Python import urllib.request # URL of the web page to fetch url = 'https://www.example.com' try: response = urllib.request.urlopen(url) data = response.read() # Decode the data (if it's in bytes) to a string html_content = data.decode('utf-8') # Print the HTML content of the web page print(html_content) except Exception as e: print("Error fetching URL:", e) Output:

For more information, refer to urllib module
Automating UI Tasks with PyAutoGUI
PyAutoGUI lets you simulate mouse and keyboard actions. It’s useful if elements aren’t reachable via Selenium like special pop-ups or custom scrollbars.
Example:
In this example, pyautogui is used to perform scrolling and take a screenshot of the search results page obtained by typing a query into the search input field and clicking the search button using Selenium.
Python import pyautogui # moves to (519,1060) in 1 sec pyautogui.moveTo(519, 1060, duration = 1) # simulates a click at the present mouse position pyautogui.click() pyautogui.moveTo(1717, 352, duration = 1) pyautogui.click()
Output

Explanation:
- moveTo(x, y): Moves the mouse to a screen position.
- click(): Clicks at the current mouse location.
For more information, refer to PyAutoGUI
Scheduling Scraping Jobs with schedule
The schedule module in Python is a simple library that allows you to schedule Python functions to run at specified intervals. It's particularly useful in web scraping in Python when you need to regularly scrape data from a website at predefined intervals such as hourly, daily or weekly.
Example: How to Schedule a Function call Every Minute
Python import schedule import time def func(): print("Geeksforgeeks") schedule.every(1).minutes.do(func) while True: schedule.run_pending() time.sleep(1) Output:
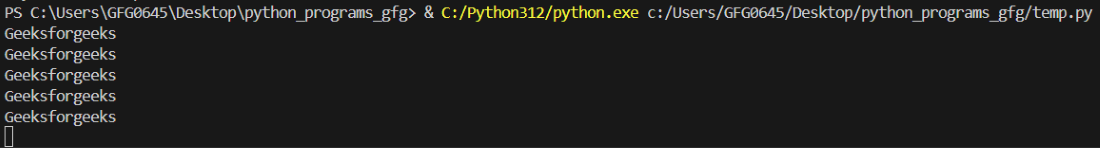 Snapshot of the terminal output after 4 minutes of running the program
Snapshot of the terminal output after 4 minutes of running the programExplanation:
You can notice in the output that the pragram is call the function "func" every minute, so you can implement the code for timely web scrapping in similar way.
- schedule.every().minutes.do(): Schedules your function.
- run_pending(): Checks if any job is due.
- time.sleep(): Prevents the loop from hogging CPU.
Why Python 3 for Web Scraping
Python 3 is the most modern and supported version of Python and it's ideal for web scraping because:
- Readable syntax: Easy to learn and write.
- Strong library support: Tools like BeautifulSoup and Selenium are built for it.
- Active community: Tons of support and examples online.
- Flexible: Can combine with data analysis, ML or APIs.
Similar Reads
Python Web Scraping Tutorial Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites automatically. Python is widely used for web scraping because of its easy syntax and powerful libraries like BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Selenium. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use these Python tools to scrape data from websites and
10 min read
Introduction to Web Scraping
Basics of Web Scraping
HTML BasicsHTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard markup language used to create and structure web pages. It defines the layout of a webpage using elements and tags, allowing for the display of text, images, links, and multimedia content. As the foundation of nearly all websites, HTML is used in over
7 min read
Tags vs Elements vs Attributes in HTMLIn HTML, tags represent the structural components of a document, such as <h1> for headings. Elements are formed by tags and encompass both the opening and closing tags along with the content. Attributes provide additional information or properties to elements, enhancing their functionality or
2 min read
CSS IntroductionCSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a language designed to simplify the process of making web pages presentable.It allows you to apply styles to HTML documents by prescribing colors, fonts, spacing, and positioning.The main advantages are the separation of content (in HTML) and styling (in CSS) and the
5 min read
CSS SyntaxCSS is written as a rule set, which consists of a selector and a declaration block. The basic syntax of CSS is as follows:The selector is a targeted HTML element or elements to which we have to apply styling.The Declaration Block or " { } " is a block in which we write our CSS.HTML<html> <h
2 min read
JavaScript Cheat Sheet - A Basic Guide to JavaScriptJavaScript is a lightweight, open, and cross-platform programming language. It is omnipresent in modern development and is used by programmers across the world to create dynamic and interactive web content like applications and browsersJavaScript (JS) is a versatile, high-level programming language
15+ min read
Setting Up the Environment
Extracting Data from Web Pages
Fetching Web Pages
HTTP Request Methods
Searching and Extract for specific tags Beautifulsoup
Scrapy Basics
Scrapy - Command Line ToolsPrerequisite: Implementing Web Scraping in Python with Scrapy Scrapy is a python library that is used for web scraping and searching the contents throughout the web. It uses Spiders which crawls throughout the page to find out the content specified in the selectors. Hence, it is a very handy tool to
5 min read
Scrapy - Item LoadersIn this article, we are going to discuss Item Loaders in Scrapy. Scrapy is used for extracting data, using spiders, that crawl through the website. The obtained data can also be processed, in the form, of Scrapy Items. The Item Loaders play a significant role, in parsing the data, before populating
15+ min read
Scrapy - Item PipelineScrapy is a web scraping library that is used to scrape, parse and collect web data. For all these functions we are having a pipelines.py file which is used to handle scraped data through various components (known as class) which are executed sequentially. In this article, we will be learning throug
10 min read
Scrapy - SelectorsScrapy Selectors as the name suggest are used to select some things. If we talk of CSS, then there are also selectors present that are used to select and apply CSS effects to HTML tags and text. In Scrapy we are using selectors to mention the part of the website which is to be scraped by our spiders
7 min read
Scrapy - ShellScrapy is a well-organized framework, used for large-scale web scraping. Using selectors, like XPath or CSS expressions, one can scrape data seamlessly. It allows systematic crawling, and scraping the data, and storing the content in different file formats. Scrapy comes equipped with a shell, that h
9 min read
Scrapy - SpidersScrapy is a free and open-source web-crawling framework which is written purely in python. Thus, scrapy can be installed and imported like any other python package. The name of the package is self-explanatory. It is derived from the word 'scraping' which literally means extracting desired substance
11 min read
Scrapy - Feed exportsScrapy is a fast high-level web crawling and scraping framework written in Python used to crawl websites and extract structured data from their pages. It can be used for many purposes, from data mining to monitoring and automated testing. This article is divided into 2 sections:Creating a Simple web
5 min read
Scrapy - Link ExtractorsIn this article, we are going to learn about Link Extractors in scrapy. "LinkExtractor" is a class provided by scrapy to extract links from the response we get while fetching a website. They are very easy to use which we'll see in the below post. Scrapy - Link Extractors Basically using the "LinkEx
5 min read
Scrapy - SettingsScrapy is an open-source tool built with Python Framework. It presents us with a strong and robust web crawling framework that can easily extract the info from the online page with the assistance of selectors supported by XPath. We can define the behavior of Scrapy components with the help of Scrapy
7 min read
Scrapy - Sending an E-mailPrerequisites: Scrapy Scrapy provides its own facility for sending e-mails which is extremely easy to use, and it’s implemented using Twisted non-blocking IO, to avoid interfering with the non-blocking IO of the crawler. This article discusses how mail can be sent using scrapy. For this MailSender
2 min read
Scrapy - ExceptionsPython-based Scrapy is a robust and adaptable web scraping platform. It provides a variety of tools for systematic, effective data extraction from websites. It helps us to automate data extraction from numerous websites. Scrapy Python Scrapy describes the spider that browses websites and gathers dat
7 min read
Selenium Python Basics