Plant Cell - Definition, Diagram, Structure, & Functions
Last Updated : 16 Apr, 2025
A plant cell is a fundamental unit of a Plant's structure. A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell, i.e., it has a defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane. Plant cells and animal cells difference occurs as they possess unique features that allow them to carry out essential functions.
Plant cell structure consists of a freely permeable cell wall. In this article, we will discuss plant cell parts and functions, its diagram and more in detail.
What is a Plant Cell?
Plant cells are one type of eukaryotic cell. Plant and animal cell contains the nucleus. The presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane is one of the distinguishing characteristics of a plant cell. Plant cells also have different organelles with specific functions. The cell wall surrounds the plant cell membrane and the cell wall also provides shape to the cell. Plant cells have different components with specific functions.
Plant Cell Diagram
Plant cells are rectangular in shape and larger in size compared to animal cells. Given below is labeled diagram of plant cell.

Plant Cell Structure
The structure of a plant cell is made up of several parts known as cell organelles that serve the cell's various needs for survival. Among these organelles are:
Cell Wall
The polysaccharides cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose make up this hard layer known as cell wall. The cell wall is present outside the cell membrane in plant cells. Additionally, it contains polymers like lignin, cutin, and suberin as well as glycoproteins. The main purpose of the cell wall is protection and support of the cell from the external environments. The plant cell wall also helps provide the cell form and structure while defending it from mechanical stress.

Cell Membrane
The plant cell consists of a semi-permeable membrane within cell wall. A thin coating of protein and fat makes up its structure. The cell membrane is crucial in controlling how certain molecules enter and leave the cell. For instance, the cell membrane transports nutrition and vital minerals while preventing the entry of contaminants.
.png)
Nucleus
The nucleus is present in every eukaryotic cell, a structure that is membrane-bound. A nucleus's essential function is to store the DNA or genetic material needed for cell division, metabolism, and growth. Nucleus is further divided into:
- Nucleolus: It creates the ribosomes and protein-producing components of cells.
- Nucleopore: Nucleopores, which are gaps in the nuclear membrane that allow proteins and nucleic acids to flow through, are present.
Plastids
Plastids are DNA-containing membrane-bound organelles of plant cell. They help in photosynthesis and store starch. Additionally, it is employed in the synthesis of several compounds, which serve as cellular building blocks.
Following is a list of some important plastid kinds and their roles:
Leucoplasts
They are located in plants' non-photosynthetic tissue. They are employed for carbohydrate, fat, and protein storage.
Chloroplasts
It is an extended organelle with a phospholipid membrane surrounding it. The fluid contained within the disc-shaped chloroplast, known as the stroma, contains circular DNA. Chlorophyll, a pigment with green color needed for photosynthesis, is found in every chloroplast. The sun's light energy is captured by chlorophyll, which is then used to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose.
.jpg)
Chromoplasts
They are a type of colored, heterogeneous plastid that produces and stores pigment in plant cells. Red, orange, and yellow pigments found in chromoplasts give all ripe fruits and flowers their color.
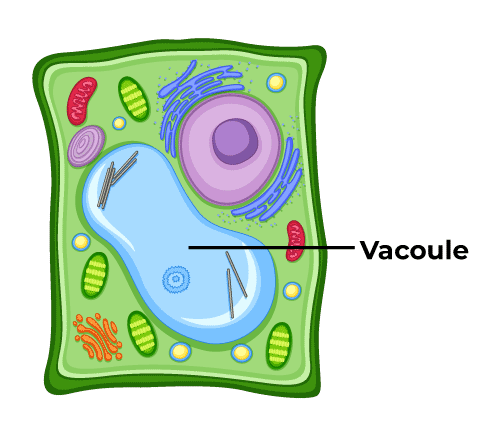
Central Vacuole
In an adult plant cell, vacuoles take up around 30% to even 90% of the total volume. A membrane called the tonoplast encircles the core vacuole. Aside from storage, the central vacuole's essential job is to maintain turgor pressure on the cell wall. Cell sap fills the central vacuole of the body. Salts, enzymes, and other compounds are mixed in with it.
Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus are present in all eukaryotic cells and are responsible for dispersing synthesized macromolecules to different cell regions. The Golgi body is made up of five to eight cisternae, or cup-shaped series of compartments. The Golgi apparatus is made up of layered pouches that are flattened and disc-shaped.
.jpg)
Ribosomes
They are the tiniest membrane-bound organelles of plant cell that contain both protein and RNA. They are also known as the cell's protein factories since they are the sites of protein synthesis. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain ribosomes, which are specialized cell organelles. Ribosomes are essential for the synthesis of proteins in every living cell.

Mitochondria
All plant cells have these double-membraned organelles in their cytoplasm. Mitochondria produce energy via breakdown of sugar and carbohydrate molecules into the energy rich molecule i.e., ATP, and known as the "Powerhouse of the Cell." They play crucial role in the breakdown of nutrients and the production of molecules that are high in energy for the plant cell

Centrosomes
These are the plant cell organelles that are responsible for the synthesis of microtubules and is also useful in the process of cell division by forming the mitotic spindle. They are composed of the centrioles that was first discovered in animal cells.

Endoplasmic Reticulum
These are the cell organelles that are formed by by a complex network of membranous tubules that are located in the cell cytoplasm. The ER is of two types; rough endoplasmic reticulum, and soft endoplasmic reticulum. The RER is embedded with ribosomes that are responsible for the protein synthesis. The SER are responsible for lipid synthesis and metabolism.

Peroxisomes
These are the plant cell organelles that have single membrane and small structure similar to lysosomes. They also contains hydrolytic enzymes that are used to hydrolysed fatty acids and other molecules. They also help in the detoxification of the cell.

Types of Plant Cell
A mature and higher plant develops specialized cells that carry out specific crucial functions that are necessary for their survival. A small number of plant cells are responsible for transporting nutrients and water, while others are responsible for storing food. Included among the specialized plant cells are parenchyma, sclerenchyma, collenchyma, xylem, and phloem cells. Here are a few examples of the various plant cell types:
- Collenchyma Cells: When a plant's growth is constrained due to a lack of a hardening agent in the major walls, these hard or rigid cells perform a crucial role in supporting the plant.
- Sclerenchyma Cells: Due to the presence of a hardening agent, these cells are more rigid than collenchyma cells. These cells are typically present in all plant roots and serve mostly to support the plants.
- Parenchyma Cells: In all plants cells, parenchyma cells perform a crucial role. They play a role in the development of leaves. Additionally, they have a role in the metabolism of cells, food generation, storage of organic materials, and gas exchange. Because they are thinner than other cells, these cells are usually more flexible.
- Xylem Cells: In vascular plants, the transport cells are called xylem cells. They help in moving minerals and water from the roots of the plant to the leaves and other regions.
- Phloem Cells: Other transport cells in vascular plants are called phloem cells. They move the food that the leaves have prepared to other plant components.
Function of Plant Cell
Major functions of plant cells are:
- The primary function of the plant cell is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which sun's light energy is converted into chemical energy. It takes place in the chloroplast of plant cells.
- Some plant cells also transport water and minerals from roots and leaves to the different parts of the plant.
- They perform cellular respiration to synthesize energy.
- They store nutrients and water in their vacuoles.
- They perform the synthesis of organic compounds like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, etc.
- They perform cell to cell communication to share chemical signalling.
- They provide support and protection by the help of sclerenchyma and collenchyma cells.
Plant Cell and Animal Cell Difference
The difference between plant cell and animal cell is given below:
Feature | Plant Cells | Animal Cells |
| Cell Wall | The cell wall is present in plant cells and is made up of cellulose. The cell wall is the outermost layer of plant cells. | it is absent in the animal cell. |
| Shape | They have a definite and rigid shape which means they usually exist in rectangular or cubical shapes. | They exist in round and irregular shapes. |
| Chloroplast | Chloroplasts are present in plant cells that make their own food. | Chloroplast absent in animal cell |
| Mitochondria | It is present in a small number in plant cells. Plants cells generally have approximately 200-600 mitochondria per cell. | It is present in a large number compared to plant cells, Animal cells generally have approximately 2000 per cell. |
| Nucleus | It is present and controls the functioning of cells. | It is present and stores the cell’s DNA, |
| Plasma Membrane | PM is present and it is surrounded by cell walls in the plant cell. | PM is present in animal cells. it provides protection for the cell. |
| Vacuoles | Vacuoles are few large or single and centrally positioned and provide structural support. One huge vacuole. | Vacuoles are commonly small in size and sometimes they are absent. |
| Mode of Nutrition | It is the present mainly autotrophic mode of nutrition which means they synthesize their own nutrients such as amino acids, vitamins coenzymes that are required by the plant. | The mode of nutrition is heterotrophic. which means they cannot synthesize their own nutrients. |
| Golgi apparatus | A Single highly difficult and prominent Golgi apparatus is present. | The mode of nutrition is heterotrophic. which means they cannot synthesize their own nutrients. |
Conclusion - Plant Cell - Definition, Diagram, Structure, & Functions
In conclusion, the plant cell serves as the fundamental building block of plant structure, featuring a eukaryotic composition with unique organelles such as the nucleus, cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. These specialized components enable crucial functions like photosynthesis, nutrient transportation, energy production, and structural support, contributing to the plant's growth, metabolism, and survival in its environment.
Also Read:
Similar Reads
Chloroplasts: Diagram, Structure and Functions The structure and function of chloroplast are adapted for photosynthesis. Chloroplast is an eukaryotic organelle found in plant cells and some algal cells which forms the site for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll, which captures light energy and uses it to synthesize orga
8 min read
Androecium - Definition, Components, Structure, Functions Reproduction is a biological process in which living organisms produce offspring similar to them. Reproduction is an important event to ensure the continuity of species on earth. In sexual reproduction, there is a chance of evolution due to mutation, linkage, etc. which is necessary for adapting and
9 min read
Phloem - Structure and Function Phloem is a type of vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting organic nutrients, especially sugars, from the parts of the plant where they are made (sources) to where they are needed or stored (sinks). It is one of the two types of vascular tissue found in vascular plants, the other bei
9 min read
Cell - Structure and Function The cell is the fundamental and structural unit of all forms of life. Every cell is made up of cytoplasm that is enclosed in a membrane and includes many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites as well as many macromolecules including proteins, DNA, and RNA. The term "cell" is derived from the
9 min read
Parts Of Plants, Diagram And Functions The part of the plant that developed beneath the soil is referred to as root and the part that grows outside of the soil is known as shoot. The shoot consists of stems, branches, leaves, fruits, and flowers. Plants are made up of six main parts: roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. Each
8 min read