A wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities that is commonly described by a wave equation in physics, mathematics, and related subjects. Electromagnetic waves are a mix of electric and magnetic field waves produced by moving charges. The origin of all electromagnetic waves is a charged particle. This charged particle generates an electric field (which can exert a force on other nearby charged particles). When a charged particle accelerates as part of an oscillatory motion (as predicted by Maxwell's equations), it causes ripples, or oscillations, in its electric field, as well as a magnetic field. Let's take a closer look. The concept of electromagnetic waves!
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
Electromagnetic (EM) waves are waves that are related to both electricity and magnetism. These waves travel over space and are made up of time-varying electric and magnetic fields.
When electric and magnetic fields interact and change over time, electromagnetic waves are produced. These waves, which are linked to electricity and magnetism, would almost certainly travel beyond space.
The electromagnetic equations are derived using Maxwell's equations. These EM waves, according to Maxwell, have a wide range of unique properties that can be applied to a variety of purposes. Electromagnetic waves are the connected temporally changing electric and magnetic fields that flow through space.
The magnetic field varies with time and gives rise to the electric field; the electric field changes with time and gives rise to the magnetic field again, and so on. When time-varying electric and magnetic fields are coupled and propagate together in space, electromagnetic waves are formed.
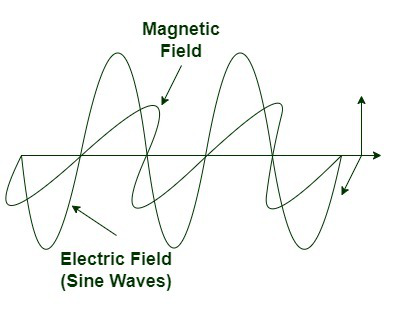 Electromagnetic Wave
Electromagnetic Wave The magnetic field, like the electric field, is a sine wave, except it goes in the opposite direction. Both of these fields (Electric and magnetic) generate electromagnetic fields. When the electric field is along the x-axis and the magnetic field is along the y-axis, the wave propagates on the z-axis. The propagation direction of waves and the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other.
Formation of Electromagnetic waves
In general, a charged particle generates an electric field. Other charged particles are pushed by this electric field. Negative charges accelerate in the opposite direction of the field, while positive charges accelerate in the field's direction. The magnetic field is created by a travelling charged particle. Other moving particles are pushed by this magnetic field. Because the force acting on these charges is always perpendicular to their motion, it only influences the velocity's direction, not its speed.
As a result, the electromagnetic field is created by an accelerating charged particle. Electric and magnetic fields travelling at the speed of light c through open space are referred to as electromagnetic waves. A charged particle is considered to be accelerating when it oscillates about an equilibrium place. The charged particle produces an electromagnetic wave of frequency f if its oscillation frequency is f. This wave's wavelength λ can be determined using the formula λ = c/f. Electromagnetic waves are a sort of space-based energy transfer.
Sources of Electromagnetic Wave (EM)
- Electromagnetic waves are created when electrically charged particles vibrate. The vibration of the electric field associated with the speeding charge produces an oscillating magnetic field. These vibrating electric and magnetic fields produce electromagnetic waves.
- When the charge is at rest, the electric field associated with it is also static. As a result, because the electric field does not change with time, no EM waves are generated.
- A charge travelling at uniform velocity has no acceleration. Because the change in electric field with time is also constant, no electromagnetic waves would be generated. This illustrates that the only way to make EM waves is to accelerate charges.
- Consider the instance of an oscillating charge particle. It has an oscillating electric field that creates an oscillating magnetic field. After then, the oscillating magnetic field generates an oscillating electric field, and so on.
- The propagation of the wave = the regeneration of electric and magnetic fields.
- All of these events are contained in an electromagnetic wave. It's also worth noting that the frequency of an EM wave is always equal to that of the oscillating particle that produces it.
Nature of Electromagnetic waves
- Transverse waves are Electromagnetic waves. The disturbance or displacement in the medium caused by transverse waves is perpendicular to the wave's propagation direction. In such a wave, the medium particles travel in a path perpendicular to the wave's propagation direction.
- The electric and magnetic fields will be perpendicular to an EM wave propagating along the x-axis. When wave propagation is parallel to the x-axis, the electric field is parallel to the y-axis, and the magnetic field is parallel to the z-axis.
- In nature, Electromagnetic waves are clearly transverse waves. The electric field of an EM wave is now provided by,
Ey = E0sin(kx-ωt )
where, Ey is the x-axis represents wave propagation, while the y-axis represents the electric field.
- The following formula is used to compute the wavenumber-
k = (2π/ωt)
- The magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave is created by,
Bz = B0sin( kx-ωt )
where, Bz is the electric field is along the z-axis, while the wave propagation direction is x.
B0 = (E0/c)
Here, we do some electromagnetic wave observations. In free space or vacuum, they're self-sustaining electric and magnetic field oscillations. The electric and magnetic field vibrations are unlike any other waves we've looked at so far in that there is no material medium involved. Longitudinal compression and rarefaction waves are compressions and rarefaction waves in the air. A rigid, shear-resistant solid can also propagate transverse elastic (sound) waves.
Energy of Electromagnetic waves
- EM waves carry energy with them as they move. As a result of this feature, they have a wide range of uses in our daily lives. The energy of an EM wave is carried in part by an electric field and partly by a magnetic field.
- The total energy stored per unit volume in an EM wave is calculated as,
ET = Per unit volume electric field energy is stored + stored magnetic field energy per unit volume
ET = (1/2)(E2ε0) + (1/2)(B2μ0)
- Experimentally, it has been discovered that,
Speed of an EM wave = Speed of light
ET = (1/2)(E2ε0) + (1/2)(E2/c2μ0)
ET = (1/2)(E2ε0) + (1/2)(E2μ0ε0)
ET = E2ε0
Mathematical Representation of Electromagnetic Wave
It's a plane we're talking about. In the x-direction, the shape of an electromagnetic wave is
E(x , t) = Emax cos(kx - ωt + φ)
B(x , t) = Bmax cos(kx - ωt + φ)
where,
- E = electric field vector in an electromagnetic wave,
- B = magnetic field vector in an electromagnetic wave.
Maxwell was the first to envision electromagnetic radiations, while Hertz was the first to experimentally confirm the presence of an electromagnetic wave. The propagation direction of an electromagnetic wave is determined by the vector cross product of the electric and magnetic fields. It's written like this:
\vec E\times\vec B
Characteristics of EM waves
- The velocity of EM waves in open space or vacuum is a fundamental constant. In experiments, the velocity of EM waves was discovered to be the same as the speed of light. (c = 3 × 108 m/s). c is a basic constant defined as follows :
c = 1/√μ0ε0
- EM waves require time-varying electric and magnetic fields to propagate. Electromagnetic waves convey both energy and velocity.
- ET=E2ε0 is the total energy stored per unit volume in EM waves (Partly carried by an electric field and partly by magnetic field). This is a vital element for EM waves practical applications since they carry both energy and momentum.
- EM waves are used in communication, such as in cell phone speech communication.
- Electromagnetic waves (EM waves) apply pressure. Because they carry energy and momentum, they exert pressure. The force exerted by electromagnetic waves is known as radiation pressure.
- The form of sunlight that we receive from the sun, for example, is visible light rays. These light beams are included in EM waves. Our hand will become warm and sweaty if we leave them in the sun for a long time. Because sunlight is transmitted in the form of energy-carrying electromagnetic waves (EM waves), this occurs.
- Assume that the total energy transferred to the hand is equal to E. Momentum = (E/c) Because c is so huge, the momentum appears to be little. The pressure is also low because the momentum is so low. Because of this, our hands are not affected by the sun's pressure.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
- These waves assist the pilot in navigating the aircraft and accomplishing a smooth take-off and landing. They're also used to figure out how fast planes are flying.
- Radio and television broadcasting signals are transmitted via electromagnetic waves.
- In the medical field, these waves can be used in a variety of ways. X-rays and laser eye surgery, for example.
- They are utilized in electronic equipment like television remote controls, remote vehicles, LED televisions, microwave ovens, and so on.
- Electromagnetic waves can be used to determine the speed of passing cars.
Sample Questions
Question 1: In free space, a planar electromagnetic wave with a frequency of 44 MHz moves in the x-direction. E = 7.3 \hat j V/m at a specific point in space and time. At this moment, what is B?
Answer:
Given : E = 7.3 V/m, c = 3 × 108 m/s
We have,
B = E/c
∴ B = 7.3 / 3 × 108
∴ B = 2.433 × 108 T
We may determine the direction by noting that E is along the y-axis and the wave propagates along the x-axis. As a result, B should be perpendicular to both the x- and y-axes. E × B should be along the x-axis, according to vector algebra. B is in the z-direction because-
(+\hat j ) × (+\vec k ) = (+\hat j)\times(+\hat k) =\hat i .
Thus,
B = 2.433 \times 10^8 \hat k\text{ T}
Question 2: The magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given by By =(2 × 10-7)T sin (0.5 × 103x + 1.5 × 1011t). What are the wave's wavelength and frequency?
Answer:
Comparing the given equation with
By = B0 sin[2π(x/λ + t/T)]
We have,
λ = (2π/0.5x103) m = 1.26 cm.
And 1/T = ν = 1.5 × 1011)/2π = 23.9 GHz.
Question 3: At normal incidence, light with an energy flow of 18 W/cm2 falls on a non-reflecting surface. Find the average force applied on the surface over a 30-minute period if the surface has an area of 20 cm2.
Answer:
The total amount of energy that falls on the surface is
U = (18 W/cm2) × (20 cm2) × (30 × 60 s)
∴ U = 6.48 × 105 J
As a result, the total delivered momentum (for complete absorption) is
p = U/c
∴ p = 6.48 × 105 J / 3 × 108 m/s
∴ p = 2.16 × 10–3 kg m/s
The surface is subjected to an average force of
F = p/t
∴ F = 2.16 × 10-3 / 0.18 × 104
∴ F = 1.2 × 10-6 N
Question 4: Write four applications of electromagnetic waves.
Answer:
Applications of electromagnetic waves :
- We can see everything around us thanks to electromagnetic radiation.
- These waves assist the pilot in navigating the aircraft and accomplishing a smooth take-off and landing. They're also used to figure out how fast planes are flying.
- In the medical field, these waves can be used in a variety of ways. X-rays and laser eye surgery, for example.
- Radio and television broadcasting signals are transmitted via electromagnetic waves.
Question 5: Explain the formation of electromagnetic waves.
Answer:
In general, a charged particle generates an electric field. Other charged particles are pushed by this electric field. Negative charges accelerate in the opposite direction of the field, while positive charges accelerate in the field's direction.
The magnetic field is created by a travelling charged particle. Other moving particles are pushed by this magnetic field. Because the force acting on these charges is always perpendicular to their motion, it only influences the velocity's direction, not its speed.
As a result, the electromagnetic field is created by an accelerating charged particle. Electric and magnetic fields travelling at the speed of light c through open space are referred to as electromagnetic waves. A charged particle is considered to be accelerating when it oscillates about an equilibrium place. The charged particle produces an electromagnetic wave of frequency f if its oscillation frequency is f. This wave's wavelength λ can be determined using the formula λ = c/f. Electromagnetic waves are a sort of space-based energy transfer.
Similar Reads
Physics Tutorial The term "physics" is derived from the Greek word physis (meaning “natureâ€) and physika (meaning “natural thingsâ€). It is the study of matter, energy, and the fundamental forces of nature, seeking to understand the behaviour of the universe from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest galaxi
15+ min read
Mechanics
Rest and MotionRest and motion describe the state of objects in relation to their surroundings. Whether an object is at rest or in motion, these states can be analyzed and understood through the principles of physics. When an object changes its position with respect to a stationary object with the passage of time,
10 min read
ForceForce is defined as an external cause that a body experiences as a result of interacting with another body. Whenever two objects interact, a force is exerted on each object. In general-term "To Push or Pull an Object" is defined as the force. The force is the interaction experience by the object be
11 min read
What is Pressure?Have you ever thought about why a needle is so thin, why fence spikes are pointed, or why a hammer's head is flat? It’s all about pressure. Pressure is the force applied to a specific area. A needle’s sharp tip concentrates the force, allowing it to easily pierce fabric. If it were blunt, the force
7 min read
FrictionFriction in Physics is defined as a type of force that always opposes the motion of the object on which it is applied. Suppose we kick a football and it rolls for some distance and eventually it stops after rolling for some time. This is because of the friction force between the ball and the ground.
8 min read
Inertia MeaningInertia is the basic concept of physics that is explained using the concept of Mass. The inertial concept was first explained by Sir Isaac Newton and the Law of Inertia is explained as any object in a state of rest or in a state of motion always staying in its state of rest or motion until an extern
8 min read
Newton's Laws of Motion | Formula, Examples and QuestionsNewton's Laws of Motion, formulated by the renowned English physicist Sir Isaac Newton, are fundamental principles that form the core of classical mechanics. These three laws explain how objects move and interact with forces, shaping our view of everything from everyday movement to the dynamics of c
9 min read
Universal Law of GravitationUniversal Law of Gravitation or Newton's law of Universal Gravitation as the name suggests is given by Sir Isaac Newton. This law helps us to understand the motion of very large bodies in the universe. According to this law, an attractive force always acts between two bodies that have masses. The st
15 min read
What is Gravity?There is a story about the discovery of gravity which says that Newton discovered gravity in the year 1665 when he was sitting under the apple tree, and suddenly an apple fell on his head, which led him to the question about falling objects. He questioned himself why all objects fall and also questi
12 min read
Law of Conservation of EnergyLaw of Conservation of Energy is the most fundamental law of physics which states that "Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed it can only change from one form of the energy to another form of the energy." It is the fundamental law of Physics that governs various processes in our environment
11 min read
Free Body DiagramFree Body Diagram often called FBD is a way of representing all the forces acting on a body at a particular instant in a simpler form. It enables the calculation of the net force acting on the body and its direction of motion by making a symbolic diagram of all the forces acting on a body. In this a
10 min read
Inclined PlaneInclined Plane is the most fundamental forms of mechanical devices used in physics. In order to get around physical obstacles and simplify tasks, inclined planes have been used for centuries in both ancient and recent construction projects. A flat surface that is angled with respect to the horizonta
10 min read
Work DoneEvery day, we are involved in countless activities—from lifting a school bag, climbing stairs, or opening a door to pushing a swing in the park. While these tasks may seem different, they all have something in common: they require effort. But what exactly makes something happen when we apply effort?
12 min read
Conservative Forces - Definition, Formula, ExamplesConservative Force is a type of force which is independent of path taken to do a work. This means when an when force applied in moving an object from one position to another is the same irrespective of the path taken, it is called conservative force. A force is a push or pull acting on an object. In
7 min read
EnergyEnergy is a word we hear frequently—whether it's about feeling energetic, saving energy, or generating power. However, in physics, energy carries a very precise meaning. It is defined as the capacity to perform work or bring about change. Everything around us involves energy in one form or another.
10 min read
Frame of ReferenceFrame of reference is a way to observe and measure objects' positions and movements. It acts like a coordinate system, helping us understand where things are and how they move. By using a frame of reference, we can describe motion accurately. It makes it clear if something is moving fast, slow, or a
6 min read
Kinematics
Kinematics | Definition, Formula, Derivation, ProblemsKinematics is the study of motion of points, objects, and systems by examining their motion from a geometric perspective, without focusing on the forces that cause such movements or the physical characteristics of the objects involved. This study area uses algebra to create mathematical models that
10 min read
What is Motion?Motion is the change in position over time, and it’s always measured with reference to a specific point, called the origin. To describe this change, we use two key terms: distance and displacement. Distance is the total path covered during motion and only has magnitude, while displacement is the sho
9 min read
Distance and DisplacementDistance and Displacement are two important terms of mechanics that may seem the same but have different meanings and definitions. Distance is a measure of "How much path is covered by an object in motion?" While Displacement is the measure of "How much path is covered by the object in a particular
5 min read
Speed and VelocityMechanics can be termed as the branch of physics concerned with the concepts of energy and forces and their effect on bodies. It governs the relationships related to the motion of objects, that is, between matter, force, and its associated energy. It is responsible for the motion of bodies and the a
13 min read
AccelerationAcceleration is defined as the rate of change in velocity. This implies that if an object’s velocity is increasing or decreasing, then the object is accelerating. Acceleration has both magnitude and direction, therefore it is a Vector quantity. According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, acceleratio
9 min read
What is Momentum Equation?What is Momentum in Physics?The concept of Momentum in physics is very important, without which most of the theories in physics will fail. The momentum can be calculated by multiplying the mass of the substance and its velocity. In physics, momentum is of different types and forms. Let's know more a
6 min read
Equations of Motion: Derivations and ExamplesEquations of Motion was given by Sir Issac Newton; who is considered the father of mechanics. He was the first to give the fundamental physical laws that deal with objects and their motion. He formulated three equations of motion of an object and published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Pri
11 min read
Uniform Circular MotionUniform Circular Motion as the name suggests, is the motion of a moving object with constant speed in a circular path. As we know, motion in a plane only has two coordinates, either x, and y, y and z, or z and x. Except for Projectile motion, circular motion is also an example of motion in a 2-D pla
9 min read
Projectile MotionProjectile motion refers to the curved path an object follows when it is thrown or projected into the air and moves under the influence of gravity. In this motion, the object experiences two independent motions: horizontal motion (along the x-axis) and vertical motion (along the y-axis). Projectile
15+ min read
Relative MotionRelative motion explains how the movement of an object is perceived differently depending on the observer’s frame of reference. For instance, while sitting on a moving train, a stationary train on the track appears to move backwards. This happens because the motion of the train you are in influences
10 min read
Rotational Mechanics
Concepts of Rotational MotionRotational motion refers to the movement of an object around a fixed axis. It is a complex concept that requires an understanding of several related concepts. Some of the important concepts related to rotational motion include angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, torque, the
10 min read
Angular MotionAngular Motion is the motion of an object around a fixed axis or point, or along a curved path with a constant angular velocity. It is also known as rotational motion. Another motion of an object is termed linear motion, which is a motion along a straight route. Linear motion variables are measured
7 min read
Angular FrequencyAngular frequency is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in studying wave motion and oscillations. It measures the angular displacement of a particle per unit time. In this article, we will learn about the meaning and definition of angular frequency, the formula of angular frequency, the
10 min read
Rotational Kinetic EnergyRotational Kinetic Energy is described as the kinetic energy associated with the rotation of an object around an axis. It is also known as angular kinetic energy. It is dependent on the mass of an object and its angular velocity. In this article, we will learn about rotational kinetic energy, its fo
7 min read
TorqueTorque is the effect of force when it is applied to an object containing a pivot point or the axis of rotation (the point at which an object rotates), which results in the form of rotational motion of the object. The Force causes objects to accelerate in the linear direction in which the force is ap
10 min read
Angular MomentumAngular Momentum is a kinematic characteristic of a system with one or more point masses. Angular momentum is sometimes called Rotational Momentum or Moment of Momentum, which is the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity as it is conserved for a closed system
10 min read
Centre of MassCentre of Mass is the point of anybody where all the mass of the body is concentrated. For the sake of convenience in Newtonian Physics, we take the body as the point object where all its mass is concentrated at the centre of mass of the body. The centre of mass of the body is a point that can be on
15 min read
Centre of GravityCentre of Gravity is one of the fundamental concepts in the study of gravitational force. Engineers and Scientists while dealing with mechanics and gravity often come across solid bodies which can't be represented by point masses such as celestial objects. In those cases, it is assumed as well as pr
8 min read
Radius of GyrationRadius of gyration, R, is a measure used in mechanics and engineering to describe the distribution of mass or inertia of an object relative to its axis of rotation. Radius of Gyration, or the radius of a body, is always centered on its rotational axis. It is a geometric characteristic of a rigid bod
11 min read
Moment of InertiaMoment of Inertia is a property of a body in rotational motion that resists changes in its rotational state. It is analogous to mass (inertia) in linear motion. Mathematically, it is defined as the sum of the product of each particle’s mass and the square of its distance from the axis of rotation: I
15+ min read
Fluid Mechanics
Mechanical Properties of FluidsFluids are substances that can flow and adapt to the shape of their container, including liquids and gases like water and air. Mechanical properties of fluids refer to viscosity, density, and pressure, which describe how fluids respond to external forces and influence their behavior in various situa
11 min read
What is Viscosity?Viscosity is a fundamental property of liquids that describes their internal resistance to flow. Imagine three bowls—one filled with water and the other with oil and honey. If you were to tip the three bowls and observe the flow, you’d quickly notice that water pours out much faster than oil and hon
10 min read
Buoyant ForceBuoyancy is a phenomenon due to the buoyant force that causes an object to float. When you put an object in a liquid, an upward force is exerted on the object by the liquid. This force is equal to the weight of the liquid that has been displaced. The amount of liquid that has been displaced depends
13 min read
Archimedes PrincipleArchimedes Principle is a fundamental concept in fluid mechanics, credited to the ancient Greek mathematician and physicist Archimedes. According to Archimedes' Principle, when an object is immersed in a fluid the object experiences an upward force whose magnitude is equal to the weight of the fluid
12 min read
Pascal's LawPascal's law establishes the relation between pressure and the height of static fluids. A static fluid is defined as a fluid that is not in motion. When the fluid is not flowing, it is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium. For a fluid to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, the net force on the fluid mus
10 min read
Reynolds NumberAs liquid runs into a channel, it collides with the pipe. Engineers ensure that the liquid flow through the city's pipes is as consistent as possible. As a result, a number known as the Reynolds number predicts whether the flow of the liquid will be smooth or turbulent. Sir George Stoke was the firs
6 min read
Streamline FlowThe substance that can change its form under an external force is defined as fluid. Whenever an external force is applied to a fluid, it begins to flow. The study of fluids in motion is defined as fluid dynamics. Have you ever noticed a creek flowing beneath the bridge? When you see a streamline, wh
7 min read
Laminar and Turbulent FlowLaminar flow and turbulent flow describe the movement patterns of fluids. Laminar flow is characterized by smooth, orderly layers of fluid sliding over one another without mixing, ideal for scenarios where minimal resistance is desired. Turbulent flow features chaotic, swirling patterns with irregul
9 min read
Bernoulli's PrincipleBernoulli's Principle, formulated by Daniel Bernoulli and later expressed as Bernoulli's Equation by Leonhard Euler in 1752, is a fundamental concept in fluid mechanics. It describes the relationship between the pressure (P), velocity, and height (h) of a fluid in motion. The principle states that i
14 min read
Poiseuilles Law FormulaAccording to Poiseuille's law, the flow of liquid varies depending on the length of the tube, the radius of the tube, the pressure gradient and the viscosity of the fluid. It is a physical law that calculates the pressure drop in an incompressible Newtonian fluid flowing in laminar flow through a lo
4 min read
Stoke's LawStoke's Law: Observe a raindrop falling from a height if you look closely you will notice that the speed of all the raindrops is constant and even though it falls from a height under the influence of gravity its velocity seems constant. These questions are answered using Stoke's lawStoke's law was f
11 min read
Solid Mechanics
What is Stress?Stress in physics is defined as the force exerted on the unit area of a substance. Stress affects the body as strain in which the shape of the body changes if the stress is applied and sometimes it gets permanently deformed. On the basis of the direction of force applied to the body, we can categori
9 min read
Stress and StrainStress and Strain are the two terms in Physics that describe the forces causing the deformation of objects. Deformation is known as the change of the shape of an object by applications of force. The object experiences it due to external forces; for example, the forces might be like squeezing, squash
12 min read
Stress-Strain CurveStress-Strain Curve is a very crucial concept in the study of material science and engineering. It describes the relationship between stress and the strain applied on an object. We know that stress is the applied force on the material, and strain, is the resulting change (deformation or elongation)
11 min read
Elasticity and PlasticityYou've undoubtedly heard of the idea of elasticity by now. In layman's words, it indicates that after being stretched, some substances return to their former form. You've experimented with a slingshot. Didn't you? That is an elastic substance. Let us go into the ideas of elasticity and plasticity to
9 min read
Modulus of ElasticityModulus of Elasticity or Elastic Modulus is the measurement of resistance offered by a material against the deformation force acting on it. Modulus of Elasticity is also called Young's Modulus. It is given as the ratio of Stress to Strain. The unit of elastic modulus is megapascal or gigapascal Modu
12 min read
Modulus of RigidityModulus of rigidity also known as shear modulus, is used to measure the rigidity of a given body. It is the ratio of shear stress to shear strain and is denoted by G or sometimes by S or μ. The modulus of rigidity of a material is directly proportional to its elastic modulus which depends on the mat
11 min read
Young's ModulusYoung's Modulus is the ratio of stress and strain. It is named after the famous British physicist Thomas Young. It is also known as the "Modulus of Elasticity" and is a fundamental property that describes the relationship between stress and strain in elastic materials. It explains how a material def
8 min read
Bulk Modulus FormulaThe modulus of elasticity measures a material's resistance to elastic deformation under external forces. Understanding this property is important for designing structures with materials like metals, concrete, and polymers to ensure they can withstand stresses without permanent deformation.The modulu
7 min read
Shear Modulus and Bulk ModulusA rigid body model is an idealised representation of an item that does not deform when subjected to external forces. It is extremely beneficial for evaluating mechanical systems—and many physical items are quite stiff. The degree to which an item may be regarded as stiff is determined by the physica
7 min read
Poisson's RatioPoisson's Ratio is the negative ratio of transversal strain or lateral strain to the longitudinal strain of a material under stress. When a material particularly a rubber-like material undergoes stress the deformation is not limited to only one direction, rather it happens along both transversal and
9 min read
Stress, Strain and Elastic Potential EnergyElasticity, this term always reminds of objects like Rubber bands, etc. However, if the question arises, which one is more elastic- A rubber or an Iron piece? The answer will be an Iron piece. Why? The answer lies in the definition of Elasticity, elasticity is known to be the ability of the object t
9 min read
Thermodynamics
Basics Concepts of ThermodynamicsThermodynamics is concerned with the ideas of heat and temperature, as well as the exchange of heat and other forms of energy. The branch of science that is known as thermodynamics is related to the study of various kinds of energy and its interconversion. The behaviour of these quantities is govern
12 min read
Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsZeroth Law of Thermodynamics states that when two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with another third body than the two bodies are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. Ralph H. Fowler developed this law in the 1930s, many years after the first, second, and third laws of thermodynamics had a
7 min read
First Law of ThermodynamicsFirst Law of Thermodynamics adaptation of the Law of Conservation of Energy differentiates between three types of energy transfer: Heat, Thermodynamic Work, and Energy associated with matter transfer. It also relates each type of energy transfer to a property of a body's Internal Energy. The First L
8 min read
Second Law of ThermodynamicsSecond Law of Thermodynamics defines that heat cannot move from a reservoir of lower temperature to a reservoir of higher temperature in a cyclic process. The second law of thermodynamics deals with transferring heat naturally from a hotter body to a colder body. Second Law of Thermodynamics is one
10 min read
Thermodynamic CyclesThermodynamic cycles are used to explain how heat engines, which convert heat into work, operate. A thermodynamic cycle is used to accomplish this. The application determines the kind of cycle that is employed in the engine. The thermodynamic cycle consists of a series of interrelated thermodynamic
15 min read
Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of StateThe branch of thermodynamics deals with the process of heat exchange by the gas or the temperature of the system of the gas. This branch also deals with the flow of heat from one part of the system to another part of the system. For systems that are present in the real world, there are some paramete
5 min read
Enthalpy: Definition, Formula and ReactionsEnthalpy is the measurement of heat or energy in the thermodynamic system. It is the most fundamental concept in the branch of thermodynamics. It is denoted by the symbol H. In other words, we can say, Enthalpy is the total heat of the system. Let's know more about Enthalpy in detail below.Enthalpy
12 min read
State FunctionsState Functions are the functions that are independent of the path of the function i.e. they are concerned about the final state and not how the state is achieved. State Functions are most used in thermodynamics. In this article, we will learn the definition of state function, what are the state fun
7 min read
Carnot EngineA Carnot motor is a hypothetical motor that works on the Carnot cycle. Nicolas Leonard Sadi Carnot fostered the fundamental model for this motor in 1824. In this unmistakable article, you will find out about the Carnot cycle and Carnot Theorem exhaustively. The Carnot motor is a hypothetical thermod
5 min read
Heat Engine - Definition, Working, PV Diagram, Efficiency, TypesHeat engines are devices that turn heat energy into motion or mechanical work. Heat engines are based on the principles of thermodynamics, specifically the conversion of heat into work according to the first and second laws of thermodynamics. They are found everywhere, from our cars, power plants to
14 min read
Wave and Oscillation
Introduction to Waves - Definition, Types, PropertiesA wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities in physics, mathematics, and related subjects, commonly described by a wave equation. At least two field quantities in the wave medium are involved in physical waves. Periodic waves occur when variables o
11 min read
Wave MotionWave Motion refers to the transfer of energy and momentum from one point to another in a medium without actually transporting matter between the two points. Wave motion is a kind of disturbance from place to place. Wave can travel in solid medium, liquid medium, gas medium, and in a vacuum. Sound wa
12 min read
OscillationOscillations are defined as the process of repeating vibrations of any quantity about its equilibrium position. The word “oscillation†originates from the Latin verb, which means to swing. An object oscillates whenever a force pushes or pulls it back toward its central point after displacement. This
8 min read
Oscillatory Motion FormulaOscillatory Motion is a form of motion in which an item travels over a spot repeatedly. The optimum situation can be attained in a total vacuum since there will be no air to halt the item in oscillatory motion friction. Let's look at a pendulum as shown below. The vibrating of strings and the moveme
3 min read
Amplitude FormulaThe largest deviation of a variable from its mean value is referred to as amplitude. It is the largest displacement from a particle's mean location in to and fro motion around a mean position. Periodic pressure variations, periodic current or voltage variations, periodic variations in electric or ma
6 min read
What is Frequency?Frequency is the rate at which the repetitive event that occurs over a specific period. Frequency shows the oscillations of waves, operation of electrical circuits and the recognition of sound. The frequency is the basic concept for different fields from physics and engineering to music and many mor
9 min read
Amplitude, Time Period and Frequency of a VibrationSound is a form of energy generated by vibrating bodies. Its spread necessitates the use of a medium. As a result, sound cannot travel in a vacuum because there is no material to transfer sound waves. Sound vibration is the back and forth motion of an entity that causes the sound to be made. That is
5 min read
Energy of a Wave FormulaWave energy, often referred to as the energy carried by waves, encompasses both the kinetic energy of their motion and the potential energy stored within their amplitude or frequency. This energy is not only essential for natural processes like ocean currents and seismic waves but also holds signifi
7 min read
Simple Harmonic MotionSimple Harmonic Motion is a fundament concept in the study of motion, especially oscillatory motion; which helps us understand many physical phenomena around like how strings produce pleasing sounds in a musical instrument such as the sitar, guitar, violin, etc., and also, how vibrations in the memb
15+ min read
Displacement in Simple Harmonic MotionThe Oscillatory Motion has a big part to play in the world of Physics. Oscillatory motions are said to be harmonic if the displacement of the oscillatory body can be expressed as a function of sine or cosine of an angle depending upon time. In Harmonic Oscillations, the limits of oscillations on eit
10 min read
Sound
Production and Propagation of SoundHave you ever wonder how are we able to hear different sounds produced around us. How are these sounds produced? Or how a single instrument can produce a wide variety of sounds? Also, why do astronauts communicate in sign languages in outer space? A sound is a form of energy that helps in hearing to
6 min read
What are the Characteristics of Sound Waves?Sound is nothing but the vibrations (a form of energy) that propagates in the form of waves through a certain medium. Different types of medium affect the properties of the wave differently. Does this mean that Sound will not travel if the medium does not exist? Correct. It will not, It is impossibl
7 min read
Speed of SoundSpeed of Sound as the name suggests is the speed of the sound in any medium. We know that sound is a form of energy that is caused due to the vibration of the particles and sound travels in the form of waves. A wave is a vibratory disturbance that transfers energy from one point to another point wit
12 min read
Reflection of SoundReflection of Sound is the phenomenon of striking of sound with a barrier and bouncing back in the same medium. It is the most common phenomenon observed by us in our daily life. Let's take an example, suppose we are sitting in an empty hall and talking to a person we hear an echo sound which is cre
9 min read
Refraction of SoundA sound is a vibration that travels as a mechanical wave across a medium. It can spread via a solid, a liquid, or a gas as the medium. In solids, sound travels the quickest, comparatively more slowly in liquids, and the slowest in gases. A sound wave is a pattern of disturbance caused by energy trav
5 min read
How do we hear?Sound is produced from a vibrating object or the organ in the form of vibrations which is called propagation of sound and these vibrations have to be recognized by the brain to interpret the meaning which is possible only in the presence of a multi-functioning organ that is the ear which plays a hug
7 min read
Audible and Inaudible SoundsWe hear sound whenever we talk, listen to some music, or play any musical instrument, etc. But did you ever wondered what is that sound and how is it produced? Or why do we hear to our own voice when we shout in a big empty room loudly? What are the ranges of sound that we can hear? In this article,
10 min read
Explain the Working and Application of SONARSound energy is the type of energy that allows our ears to sense something. When a body vibrates or moves in a ‘to-and-fro' motion, a sound is made. Sound needs a medium to flow through in order to propagate. This medium could be in the form of a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Sound propagates through a
8 min read
Noise PollutionNoise pollution is the pollution caused by sound which results in various problems for Humans. A sound is a form of energy that enables us to hear. We hear the sound from the frequency range of 20 to 20000 Hertz (20kHz). Humans have a fixed range for which comfortably hear a sound if we are exposed
8 min read
Doppler Effect - Definition, Formula, ExamplesDoppler Effect is an important phenomenon when it comes to waves. This phenomenon has applications in a lot of fields of science. From nature's physical process to planetary motion, this effect comes into play wherever there are waves and the objects are traveling with respect to the wave. In the re
7 min read
Doppler Shift FormulaWhen it comes to sound propagation, the Doppler Shift is the shift in pitch of a source as it travels. The frequency seems to grow as the source approaches the listener and decreases as the origin fades away from the ear. When the source is going toward the listener, its velocity is positive; when i
3 min read
Electrostatics
ElectrostaticsElectrostatics is the study of electric charges that are fixed. It includes an study of the forces that exist between charges as defined by Coulomb's Law. The following concepts are involved in electrostatics: Electric charge, electric field, and electrostatic force.Electrostatic forces are non cont
13 min read
Electric ChargeElectric Charge is the basic property of a matter that causes the matter to experience a force when placed in a electromagnetic field. It is the amount of electric energy that is used for various purposes. Electric charges are categorized into two types, that are, Positive ChargeNegative ChargePosit
8 min read
Coulomb's LawCoulomb’s Law is defined as a mathematical concept that defines the electric force between charged objects. Columb's Law states that the force between any two charged particles is directly proportional to the product of the charge but is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between t
9 min read
Electric DipoleAn electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite electric charges that are separated, by a small distance. An example of an electric dipole includes two atoms separated by small distances. The magnitude of the electric dipole is obtained by taking the product of either of the charge and
11 min read
Dipole MomentTwo small charges (equal and opposite in nature) when placed at small distances behave as a system and are called as Electric Dipole. Now, electric dipole movement is defined as the product of either charge with the distance between them. Electric dipole movement is helpful in determining the symmet
6 min read
Electrostatic PotentialElectrostatic potential refers to the amount of electrical potential energy present at a specific point in space due to the presence of electric charges. It represents how much work would be done to move a unit of positive charge from infinity to that point without causing any acceleration. The unit
12 min read
Electric Potential EnergyElectrical potential energy is the cumulative effect of the position and configuration of a charged object and its neighboring charges. The electric potential energy of a charged object governs its motion in the local electric field.Sometimes electrical potential energy is confused with electric pot
15+ min read
Potential due to an Electric DipoleThe potential due to an electric dipole at a point in space is the electric potential energy per unit charge that a test charge would experience at that point due to the dipole. An electric potential is the amount of work needed to move a unit of positive charge from a reference point to a specific
7 min read
Equipotential SurfacesWhen an external force acts to do work, moving a body from a point to another against a force like spring force or gravitational force, that work gets collected or stores as the potential energy of the body. When the external force is excluded, the body moves, gaining the kinetic energy and losing a
9 min read
Capacitor and CapacitanceCapacitor and Capacitance are related to each other as capacitance is nothing but the ability to store the charge of the capacitor. Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits that store electrical energy in the form of an electric charge. They are widely used in various applications,
11 min read