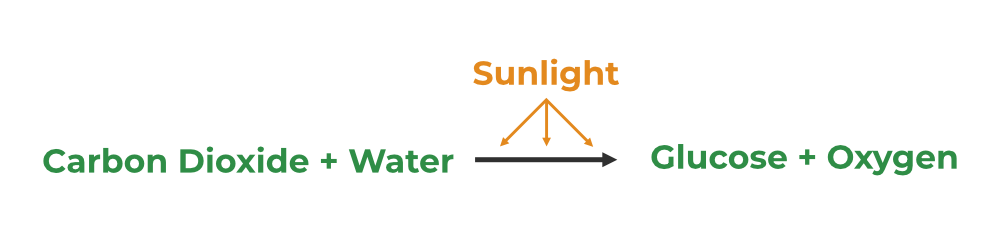
Photosynthesis is a complex and natural process, where green plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert sunlight (light energy), carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (chemical energy) and oxygen. Photosynthesis uses sunlight along with carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. The produced oxygen is released into the atmosphere while glucose is used as chemical energy by the plant. Photosynthesis, in short, is the process of food-making by the plants for their energy requirements.
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis word originates from the Greek terms "phōs" (pronounced as "fos") and "σύνθεσις" (pronounced as "synthesis"). In this context, "phōs" signifies "light," and "σύνθεσις" represents "combining." Hence, "photosynthesis" can be rephrased as "the process of combining elements with the aid of light.
The conversion of sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water into food (sugars) and oxygen are known as photosynthesis. This process is seen in plants, algae, and some microorganisms. The word photosynthesis is taken from the Greek words photo (light) and synthesis (merge together) which means (merging together with the aid of light). Light is the main important factor in the photosynthesis process.
Photosynthesis, which occurs in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is more common and they follow very similar principles. The light energy is used to turn the water (H2O) received by plant roots into CO2 and produce carbohydrates. The CO2 is "reduced," or gets electrons, while the water is "oxidized," or loses electrons, during this process. Both oxygen and carbohydrates i.e., glucose and fructose are produced.
- Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast.
- Chloroplast carries the green fluid known as chlorophyll present in the leaves which helps in photosynthesis.
- Light is captured by the chlorophyll and CO2 is come from the stomata and then photosynthesis takes place. Later on, the end product is also secreted with the help of stomata.
- End product - carbohydrate is later sent to the roots, stem leaves, and different parts of a plant.
Photosynthesis Diagram
A diagram of Photosynthesis is shown below:

Where Does Photosynthesis take place?
Chloroplasts, a type of plastid (an organelle with a membrane) are organelle that contains chlorophyll. They are typically found in plant leaves and perform photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll pigments in plants absorb light energy. When a chlorophyll pigment releases an electron, it can then go on to an appropriate recipient, converting the energy into chemical energy. Reaction centers are the pigments and proteins that transform light energy into chemical energy and start the process of electron transfer.
Also Read: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Notes Chapter 11
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
There are some factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis.
- Temperature: The optimum temperature for the most efficient photosynthesis is 25° to 35° C.
- Light: The light intensity if high directly affects the rate of photosynthesis.
- Carbon Dioxide: CO2 directly affects the rate of photosynthesis. If the concentration of CO2 is low then the photosynthesis rate also decreased.
- Pollution: Pollutants settle on the upper surface of the leaf because of which gas exchange does not occur properly and it affects the rate of photosynthesis.
- Water: Water is an important factor and if it is below the optimum level it decreases the rate of photosynthesis. A low level of water does not let the stomata open and CO2 does not come inside.
Also Read: Transpiration in Plants
Photosynthesis Equation
Despite the fact that both types of photosynthesis are complex, multistep processes, the entire procedure can be neatly condensed into a chemical equation.
The oxygenic (with oxygen usage) photosynthesis equation is:
6CO2 + 12H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Here, light energy is used to mix 12 molecules of water (H2O) with six molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2). As a result, six molecules each of oxygen and water are formed, as well as one molecule of a carbohydrate (C6H12O6, or glucose).
Similarly, a single generalized formula can be used to express all anoxygenic (without oxygen usage) photosynthesis reactions:
CO2 + 2H2A + Light Energy → [CH2O] + 2A + H2O
Through tiny holes on their leaves known as stomata, plants take in CO2 from the atmosphere and release it along with water and oxygen. The guardians of gas exchange between a plant's interior and the outside world are stomata.
Stomata release oxygen and allow water vapor to secrete out while they are open, allowing CO2 to enter the system. Stomata close in an effort to lessen the amount of water lost, but doing so prevents the plant from absorbing CO2 for photosynthesis. For plants that grow in hot, dry climates, this trade-off between CO2 intake and water loss presents a unique challenge.
Photosynthetic Pigments
Pigments are present in the leaves, and they provide the color to leaf. In plants, 4 types of photosynthetic pigments are:
- Chlorophyll A
- Chlorophyll B
- Xanthophylls
- Carotenoids
Structure of Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in the chloroplast. The green color of the leaf is due to chlorophyll. It has a significant role in the photosynthesis process. Chlorophyll absorbs the sun's rays and helps in photosynthesis. There are different types of photosynthetic pigments are present.

Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in the special cell organelles known as chloroplast at the cellular level. The lamina of the leaf helps in absorbing CO2 and sunlight. The process of photosynthesis is classified into two stages on the basis of light i.e., Light-dependent and Light independent reaction
Light-Dependent Reactions
- Normally photosynthesis occurred during the day under the presence of sun rays called Light-Dependant Reaction. This reaction takes place in the thylakoid membrane.
- On the membrane, different proteins are presently known as Photosystems which are of 2 types :
- Photosystem-I
- Photosystem-II
- In light-dependent photosynthesis, solar energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
2H2O + 2NADP+ +3 ADP + 3Pi ⇢ O2+ 2NADPH + 3ATP
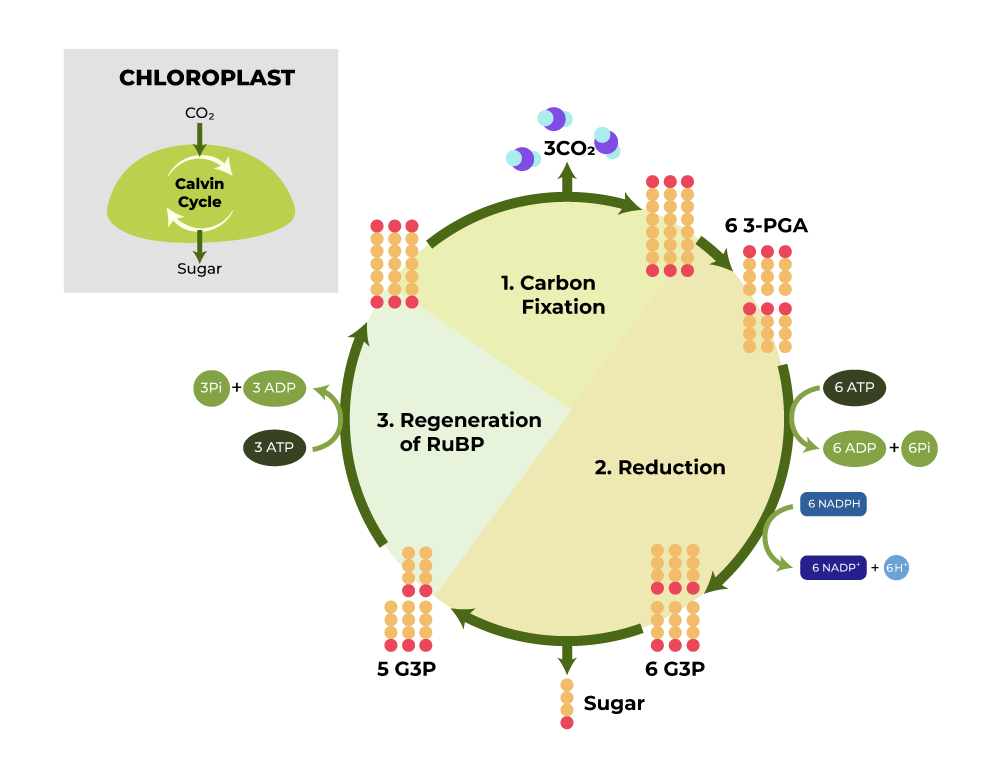
Light-Independent Reactions
Light Independent reaction is also known as Dark reaction or Carbon-fixing reaction.
- In this reaction, monosaccharides are formed with the utilization of CO2 and H2O
- A dark reaction takes place in the stroma.
- Plants take the CO2 from the stomata and start the Calvin cycle.
- In the Calvin cycle, 6 molecules of CO2 are used to form one molecule of sugar (monosaccharides)
3Co2 + 6 NADPH + 5H2O + 9ATP ⇢ G3P + 2H+ + 6NADP+ + 9ADP + 8Pi
Types of Photosynthesis
The C3, C4, and CAM pathways are the three basic categories of photosynthetic pathways. They all use the Calvin cycle to convert CO2 into sugars, but each pathway does so in a somewhat different way.
- C3 photosynthesis: Majority of plants, including cereals (wheat and rice), cotton, potatoes, and soybeans, utilize C3 photosynthesis. The three-carbon molecule 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA), which is a byproduct of C3 photosynthesis, gives the process its name. When Rubisco fixes CO2, a three-carbon molecule called 3-PGA is created.
- C4 photosynthesis: C4 photosynthesis is used by plants like sugarcane and maize. A four-carbon chemical intermediate called oxaloacetate, which is transformed into malate, is used in this process. C4 plants can continue to fix carbon even while their stomata are closed, which lowers their risk of photorespiration and they are also better adapted to hot, dry settings.

- CAM photosynthesis: Plants accustomed to extremely hot and dry settings, like cactus and pineapples, have a process called Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM). CAM is one modification where plants open their stomata at night (when temperatures are lower and water loss is less of a risk). Stomata close, lowering the likelihood of water loss, and the CO2 is then available for light-dependent processes during the day.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Following are the importance of photosynthesis are given below:
- Because of the process of photosynthesis, oxygen level of the environment is maintained.
- Food is generated from solar energy which plays a significant role in the food chain.
- Photosynthesis provides food to other living organisms.
Also Read: