7 Pandas Plotting Functions for Data Visualization
Last Updated : 17 Mar, 2025
Data visualization is an essential component of data analysis, enabling us to acquire understanding, detect regularities, and convey discoveries efficiently. In this article we will examine seven fundamental Pandas charting functions, including examples and explanations for each kind of plot.

Types of Pandas Plotting Functions
Pandas has a range of charting methods that are based on the matplotlib package. This allows for the convenient creation of charts straight from DataFrame objects. These functions include a diverse array of plot forms, such as line graphs, bar plots, histograms, scatter plots, and further variations. By using these functions, users may effectively depict trends, distributions, correlations, and linkages within their data.
Pandas plotting capabilities facilitate the process of data visualization, making it smooth and effortless. Users may easily invoke the required charting function on a DataFrame or Series object and modify the plot using different parameters. In addition, Pandas seamlessly interfaces with Matplotlib, enabling advanced customization and precise adjustments of visuals.
Creating Sample DataFrame
Before diving into the plotting functions, let's create a sample DataFrame to work with with some sample data for TV serials, including spiritual shows. We'll include features like title, genre, release year etc.
Python import pandas as pd data = { 'Title': ['The Crown', 'Stranger Things', 'Breaking Bad', 'The Mandalorian', 'Avatar: The Last Airbender', 'The Office', 'Game of Thrones', 'Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey', 'The Good Place', 'Black Mirror', 'The Chosen', 'The Bible'], 'Genre': ['Drama', 'Sci-Fi', 'Drama', 'Sci-Fi', 'Animation', 'Comedy', 'Fantasy', 'Documentary', 'Comedy', 'Sci-Fi', 'Drama', 'Drama'], 'Release_Year': [2016, 2016, 2008, 2019, 2005, 2005, 2011, 2014, 2016, 2011, 2019, 2013], 'Director': ['Peter Morgan', 'The Duffer Brothers', 'Vince Gilligan', 'Jon Favreau', 'Michael Dante DiMartino, Bryan Konietzko', 'Greg Daniels', 'David Benioff, D. B. Weiss', 'Brannon Braga', 'Michael Schur', 'Charlie Brooker', 'Dallas Jenkins', 'Various'], 'Seasons': [4, 4, 5, 2, 3, 9, 8, 1, 4, 5, 2, 1], 'Duration_Minutes': [60, 50, 47, 40, 23, 22, 57, 60, 22, 60, 45, 43] } tv_serials_df = pd.DataFrame(data) tv_serials_df.head() Output:

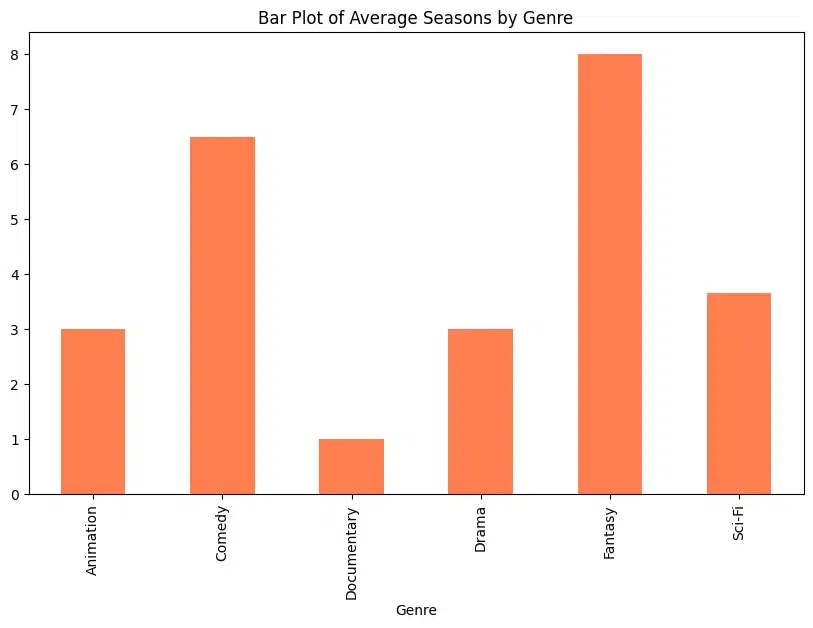
Bar Plot
A bar plot is a graphical representation of categorical data where the length of each bar represents the frequency or value of the category. Here a bar plot is used to compare the average value of a numerical variable (e.g., seasons) across different categories (e.g., genres) of TV serials. The plot is crafted using DataFrame.plot.bar()
Python genre_seasons = tv_serials_df.groupby('Genre')['Seasons'].mean() genre_seasons.plot.bar(figsize=(10, 6), color='coral', title='Bar Plot of Average Seasons by Genre') Output:
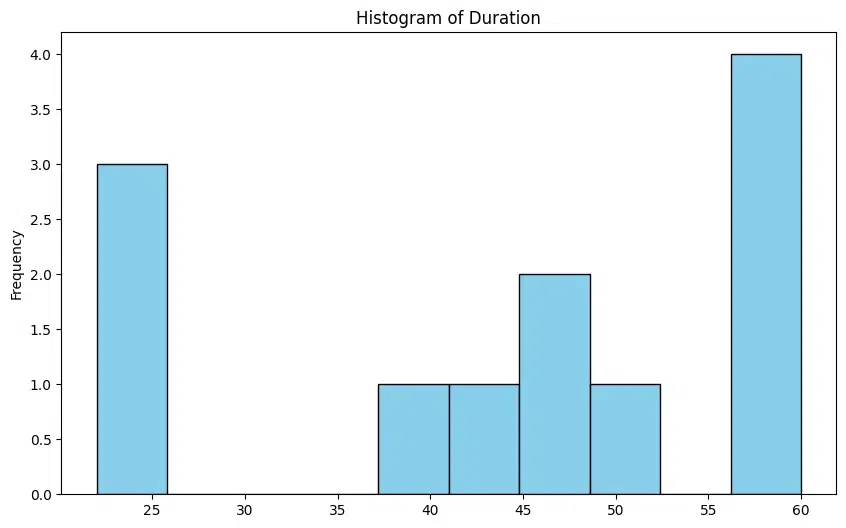
Histogram
A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data. It consists of a series of bars, where each bar represents a range of values, and the height of the bar represents the frequency of values in that range. Histograms are useful for understanding the distribution, shape, and spread of data. They can help identify patterns and outliers in the data. In the DataFrame context, a histogram is used to visualize the distribution of the duration of TV serials using plot.hist()
Python tv_serials_df['Duration_Minutes'].plot.hist(bins=10, figsize=(10, 6), color='skyblue', edgecolor='black', title='Histogram of Duration')
Output:
Scatter Plot
A scatter plot is a type of plot that displays values for two variables as points on a two-dimensional plane. Each point represents an observation in the data. Below, scatter plot is used to visualize the relationship between two numerical variables, such as release year and the number of seasons for TV serials using plot.scatter().
Python # Scatter Plot: Release_Year vs Seasons tv_serials_df.plot.scatter(x='Release_Year', y='Seasons', figsize=(10, 6), title='Release Year vs Number of Seasons')
Output:

Box Plot
Box plots describe the distribution of numerical data and indicate outliers. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data through quartiles. It displays the median, quartiles, and potential outliers in the data. Box plots are useful for comparing the distribution of numerical data across different categories or groups and indicate outliers using dataframe.boxplot().
Python # Box Plot Duration_Minutes tv_serials_df.boxplot(column='Duration_Minutes', figsize=(12, 6), showfliers=False)
Output:

Pie Chart
Pie charts are a circular statistical graphic divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole. Pie charts are useful for displaying the relative sizes or proportions of different categories within a dataset. Pie chart is used to visualize the distribution of genres within the dataset using DataFrame.plot.pie()
Python genre_distribution = tv_serials_df['Genre'].value_counts() genre_distribution.plot(kind='pie', figsize=(8, 8), autopct='%1.1f%%', startangle=140, title='Pie Chart of Genre Distribution')
Output:

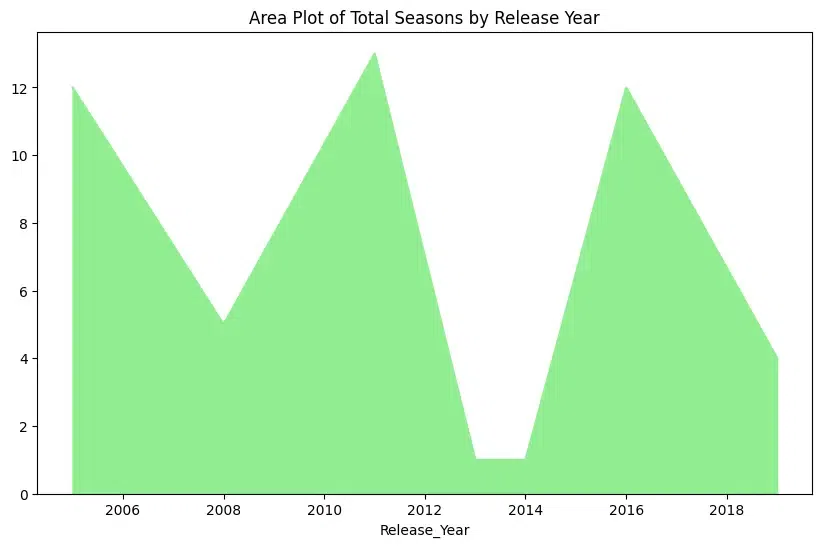
Area Plot
An area plot is a type of plot that displays data points connected by straight lines and the area between the lines and the x-axis is filled with color. It is similar to a line plot but emphasizes the cumulative change in values. An area plot is used to visualize the cumulative change in total seasons over the years with DataFrame.plot.area()
Python tv_serials_df.groupby('Release_Year')['Seasons'].sum().plot(kind='area', figsize=(10, 6), color='lightgreen', title='Area Plot of Total Seasons by Release Year') Output:
Line Plot
A line plot is a type of plot that displays data points connected by straight line segments. It is commonly used to visualize trends or changes over time. Line plots are useful for showing trends, patterns, or relationships between two variables over time or any other ordered variable. In below plot, a line plot is seen representing genre vs release year using DataFrame.plot.line()
Python tv_serials_df.plot.line(x='Genre', y='Release_Year', figsize=(10, 6), title='Genre vs Release Year', marker='o', linestyle='-')
Output:

Best Practices for Efficient Plotting
Efficient plotting is crucial for creating visually appealing and informative plots, especially when dealing with large datasets or when generating plots in real-time applications.
- Choose the Right Library: Different plotting libraries have different strengths and weaknesses. Matplotlib is a powerful and flexible library that is suitable for most plotting tasks. Seaborn provides high-level abstractions for statistical visualization. Plotly offers interactive plots suitable for web applications. Choose the library that best fits your needs.
- Use Efficient Plotting Functions: Many plotting libraries offer high-level plotting functions optimized for common use cases. For example Matplotlib's plt.plot() function is suitable for basic line plots while plt.scatter() is better for scatter plots.
- Use Plotting Defaults Wisely: Customize the default plotting settings to match your preferences and the requirements of your audience. However avoid excessive customization that could obscure the underlying data or make your plots difficult to interpret.
Similar Reads
Plotly for Data Visualization in Python Plotly is an open-source Python library designed to create interactive, visually appealing charts and graphs. It helps users to explore data through features like zooming, additional details and clicking for deeper insights. It handles the interactivity with JavaScript behind the scenes so that we c
12 min read
Top R Libraries for Data Visualization in 2024 When you are talking about data analysis, don’t forget data visualization! It is a very important part of data analysis that can reveal hidden trends and provide more insight into the data. Data visualization can provide information just by looking at it, whereas it would take much more time to obta
7 min read
Top 8 Python Libraries for Data Visualization Data Visualization is an extremely important part of Data Analysis. After all, there is no better way to understand the hidden patterns and layers in the data than seeing them in a visual format! Don’t trust me? Well, assume that you analyzed your company data and found out that a particular product
7 min read
Data Visualization using Matplotlib in Python Matplotlib is a widely-used Python library used for creating static, animated and interactive data visualizations. It is built on the top of NumPy and it can easily handles large datasets for creating various types of plots such as line charts, bar charts, scatter plots, etc. These visualizations he
10 min read
Top Free Data Visualization Tools Data visualization tools refer to software applications that convert data inputs into attractive visual representations such as maps, graphs and charts for analysis. These tools help businesses and individuals to understand complex data sets, identify trends and make informed decisions. In this arti
5 min read