Pacman command in Arch Linux
Last Updated : 21 Dec, 2021
Pacman is a package manager for the arch Linux and arch-based Linux distributions. If you have used Debian-based OS like ubuntu, then the Pacman is similar to the apt command of Debian-based operating systems. Pacman contains the compressed files as a package format and maintains a text-based package database. Pacman keeps the system up to date by synchronizing package lists with the master server. Pacman can install the packages from the official repositories or your own build packages.
In this article, we are going to see how to use Pacman to manage the software in arch-based systems. Now let's see how to use Pacman.
Installing Packages using the Pacman
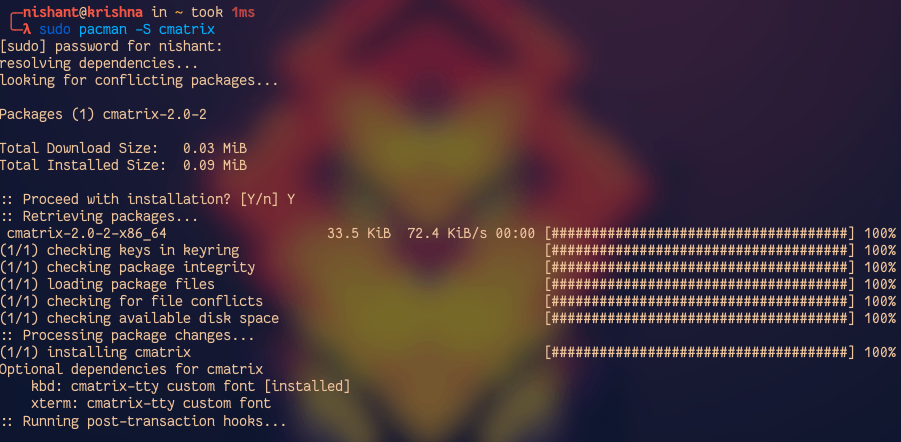
When we install any new operating system on our machine, the first task we do is to install the software packages on the system. Now, to install the packages on Arch Linux, use the command Pacman with -S option and mention the package name. The -S option tells the Pacman to synchronize and to continue. Here is one example
sudo pacman -S cmatrix
We can mention the many package names after the -S option, separated by space.
sudo pacman -S package1 package2 package3
Then Pacman will show the download and install size of the package and ask for to proceed, then simply press the Y key. Pacman categorizes the installed packages into two categories.
- Implicitly Installed: The package that was installed using the -S or -U option.
- Dependencies: The package is installed because it is required by another package.
Now let's see how to remove the installed package.
Removing packages using the Pacman
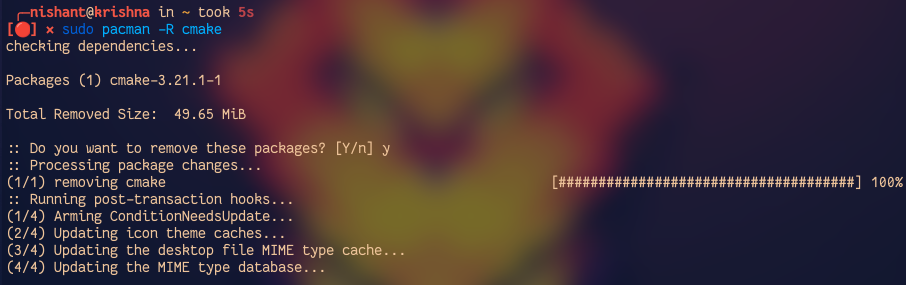
When we don't need the package anymore, then we should remove the package from the system. To remove the package with all its dependencies which are not required by other packages, use the following command:
sudo pacman -Rs <package_name>
To remove the package without removing its dependency use the following command:
sudo pacman -R <package_name>
To remove the dependencies which are not required anymore, use the following command:
pacman -Qdtq | pacman -Rs -

Upgrading packages
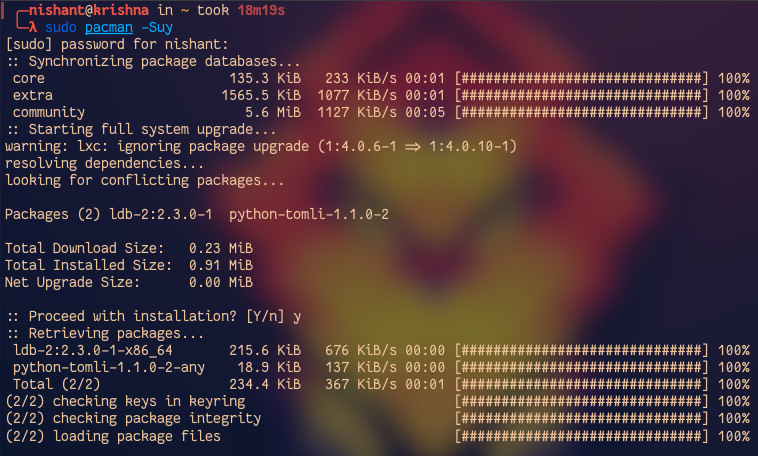
In arch Linux, we can upgrade the full system by only one command using the Pacman. Use the following command to update the system:
sudo pacman -Suy
Let's understand the meaning, S tell the pacman to synchronize the local database with the main database. u tells the pacman to upgrade the packages and y update the local catch on the system. Basically, this command synchronizes the local pacman database with the main repository database and then updates the system.
Searching for a Package
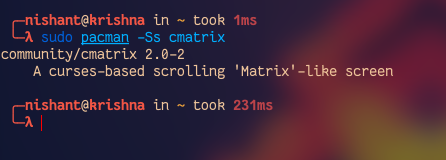
Now let's see how we can search the package into the database of pacman. To search query in the name and description of the package in the database use the following command:
sudo pacman -Ss <query1> <query2>
To search into already installed packages on the system, use the following command:
sudo pacman -Qs query1> <query2>
To search the query into the local database use the following command:
sudo pacman -F query1> <query2>

Cleaning the Package Cache
When pacman downloads the packages it stores the packages into the /var/cache/pacman/pkg/ and while uninstalling the package pacman does not delete these files. Pacman uses these files to downgrade the package or install the package. But it can take a lot of space to store these packages. So to delete the stored packages, use the following command:
sudo pacman -Sc

To remove all stored packages and catch, use the following command:
sudp pacman -Scc

Installing local packages
By using pacman we can install packages other than the main repository of Arch Linux. Use the following command to install the packages
For local:
sudo pacman -U path_to_file.pkg.tar.xz
For remote package:
sudo pacman -U http://www.example.com/repo/example.pkg.tar.xz

Troubleshooting
Sometimes installing the packages with pacman we face some errors. Following are the mainly occurred errors with pacman:
- Conflicting file error: This error occurs due to some conflict packages present in the repository. To solve this error we can manually rename the file or force the overwrite function. We can use the following command to overwrite the function:
pacman -S --overwrite glob package
- Invalid package: This error can occur due to the partial installation of the packages. We can solve this error by deleting .part files in /var/cache/pacman/pkg/.
- Locking database: This error can occur when pacman is interrupted while updating the database. To solve this error, delete the file /var/lib/pacman/db.lock and update the database. Use the following command to delete the file:
rm /var/lib/pacman/db.lock
Similar Reads
RPM Command in Linux The RPM (Red Hat Package Manager) command is a fundamental tool in the world of Linux package management. It is widely used in Red Hat-based distributions like Fedora and CentOS, as well as other RPM-based distributions. The RPM command allows users to install, query, verify, and manage software pac
6 min read
Unzip Command in Linux As an open-source operating system, Linux presents plenty of powerful and versatile instructions for dealing with files and directories. One such command that performs an important role in coping with compressed files is the "unzip" command.Compressed files are a common way to keep space and share d
8 min read
arch command in Linux with examples The arch command is a simple yet powerful utility in Linux used to display the architecture of the system's hardware. By running this command, users can quickly determine the type of processor their system is running on, such as i386, x86_64, or arm. Knowing the architecture is crucial for installin
2 min read
Chaining Commands in Linux Chaining commands in Linux is a powerful technique that allows you to execute multiple commands sequentially or simultaneously through the terminal. This approach resembles writing short shell scripts that can be directly executed in the terminal, enhancing the efficiency of your workflow. By using
7 min read
dnf Command in Linux Linux is a versatile operating system. It has many commands that can change the Linux working functionality of the operating system. Every Linux has a different package manager that helps us to install the software in the Linux operating system. The `dnf` command is a package manager command in Red-
4 min read