Difference between dispatcher and scheduler
Last Updated : 28 Dec, 2024
Scheduler and the Dispatcher are the two most important terms in an operating system. which are critical in the management of processes as well as the execution of processes. While the scheduler chooses processes that must be run, the dispatcher is in charge of passing these processes to the CPU. Despite the interrelation that might be observed when comparing the roles of these elements, they serve different direct purposes, which are aimed at optimizing CPU usage. A scheduler and a dispatcher are two important concepts that are used in operating systems when it comes to multitasking and executing processes.
What is a Scheduler?
Schedulers are a special type of operating system software that manages process scheduling in a variety of ways. Its main function is to select the jobs that are to be submitted to the system and decide which process will run.
There are three types of schedulers, which are as follows:
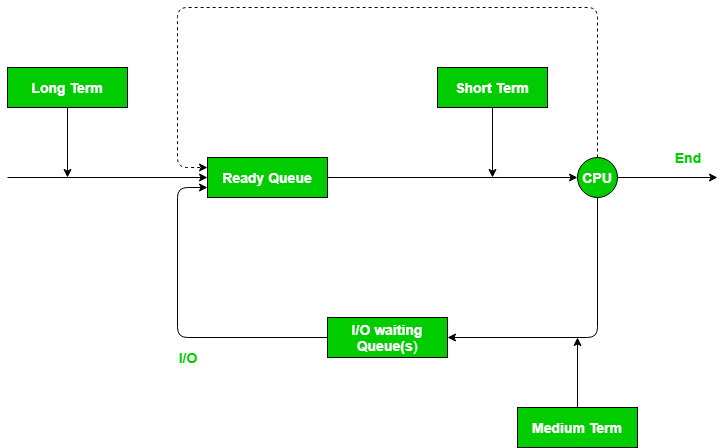
- Long-Term (job) Scheduler: Due to the small size of the main memory, initially all the programs are stored in secondary memory. When they are loaded or stored in main memory, then they are known as processes. The long-term scheduler decides how many processes will remain in the ready queue. So, in simple words, the long-term scheduler decides the degree of multiprogramming of the system.
- Medium-Term Scheduler: Often a running process needs an I/0 operation that does not require CPU time. That is why when a process needs I/O operation during its execution, the operating system sends that process to a blocked queue. When that process completes its I/O operation, then it is again shifted to the ready queue . All these decisions are taken by the medium-term scheduler. Medium-term scheduling is part of swapping.
- Short-Term (CPU) Scheduler: When there are many processes initially in the main memory, all are present in the ready queue. Out of all these processes, only one is selected for execution. This decision is in the hands of the short-term scheduler or CPU scheduler.
Advantages of a Scheduler
- Optimized CPU Utilization: It helps to check that the CPU is loaded to the maximum possible extent by frequently choosing tasks to execute.
- Fair Process Handling: Demands a fixed amount of CPU time for each process like FCFS, SJF, and RR in order to offer equal opportunity for processes in the system.
- Process Management: Oversees the processes in different states (for instance, ready, blocked, or running).
Disadvantages of a Scheduler
- Complexity: They may also not be well suited for all system designs and can also be very hard to actually schedule.
- Overhead: There are some drawbacks in maintaining the scheduler, as the latter could present some overhead to the system, and this could be especially so in a real-time environment where decisions require to be made rapidly.
What is a Dispatcher?
Dispatcher is a special type of program whose work starts after the scheduler. When the scheduler completes its task of selecting a process, it is the dispatcher that moves the process to the queue it needs to go to.
The dispatcher is the module that hands over control of the CPU to the process that has been selected by the short-term scheduler.
The following things happen in this function:
- switching context: Cores the current process and restores the state of the process to be run next.
- Switching to User Mode: Makes sure that it runs in the user mode and not kernel mode, which is for security and privilege break-
- Jumps to the correct location in the user program from where the program can be restarted.
Advantages of a Dispatcher
- Fast Process Switching: Evaluates circumstances where a procedure shifts from the ready queue to the execution phase in a way that causes less delay.
- Efficient CPU Time Allocation: Is important in making sure that processes receive CPU time, hence giving the necessary support for multitasking to occur.
Disadvantages of a Dispatcher
- Dispatch Latency: Although the time taken is considerably small, this lateness in dispatching the requests can slow down the system.
- Dependent on Scheduler: The dispatcher hence cannot work on her own since she is reliant on the decisions made by the scheduler.
Difference Between Dispatcher and Scheduler
Consider a situation, where various processes are residing in the ready queue waiting to be executed. The CPU cannot execute all of these processes simultaneously, so the operating system has to choose a particular process on the basis of the scheduling algorithm used. So, this procedure of selecting a process among various processes is done by the scheduler. Once the scheduler has selected a process from the queue, the dispatcher comes into the picture, and it is the dispatcher who takes that process from the ready queue and moves it into the running state. Therefore, the scheduler gives the dispatcher an ordered list of processes which the dispatcher moves to the CPU over time.
Example - There are 4 processes in the ready queue, P1, P2, P3, P4; Their arrival times are t0, t1, t2, t3 respectively. A First in First out (FIFO) scheduling algorithm is used. Because P1 arrived first, the scheduler will decide it is the first process that should be executed, and the dispatcher will remove P1 from the ready queue and give it to the CPU. The scheduler will then determine P2 to be the next process that should be executed, so when the dispatcher returns to the queue for a new process, it will take P2 and give it to the CPU. This continues in the same way for P3, and then P4. 
| Properties | DISPATCHER | SCHEDULER |
|---|
| Definition | Dispatcher is a module that gives control of CPU to the process selected by short term scheduler | Scheduler is something which selects a process among various processes |
| Types | There are no different types in dispatcher.It is just a code segment. | There are 3 types of scheduler i.e. Long-term, Short-term, Medium-term |
| Dependency | Working of dispatcher is dependent on scheduler.Means dispatcher have to wait until scheduler selects a process. | Scheduler works independently. It works immediately when needed |
| Algorithm | Dispatcher has no specific algorithm for its implementation | Scheduler works on various algorithm such as FCFS, SJF, RR etc. |
| Time Taken | The time taken by dispatcher is called dispatch latency. | Time taken by scheduler is usually negligible.Hence we neglect it. |
| Functions | Dispatcher is also responsible for:Context Switching, Switch to user mode, Jumping to proper location when process again restarted | The only work of scheduler is selection of processes. |
| Tasks | Dispatcher allocates the CPU to the process selected by the short-time scheduler. | Scheduler performs three task. Job scheduling (Long-term scheduler), CPU scheduling (Short-term scheduler) and swapping (Medium-term scheduler). |
| Purpose | To move the process from the ready queue to the CPU | To select the process and decide which process to run
|
| Execution time | It takes a very short execution time | It takes longer execution time than dispatcher
|
| Interaction | The dispatcher works with the CPU and the selected process | The scheduler works with the ready queue and the dispatcher
|
Conclusion
The scheduler and the dispatcher play very important roles in AOS in that they help the operating system to coordinate the processes well. The scheduler is the one that determines what processes are executed and when, while the dispatcher is the one that swaps out those processes into the CPU. It is important to understand process or task workload and how the two are different when getting to know how an operating system deals with such processes effectively. Together, they protect the system from getting slow and unproductive and make sure that it is able to handle multitasking.