n-bit Johnson Counter in Digital Logic
Last Updated : 23 Aug, 2024
Prerequisite - Counters
Johnson counter also known as creeping counter, is an example of synchronous counter. In Johnson counter, the complemented output of last flip flop is connected to input of first flip flop and to implement n-bit Johnson counter we require n flip-flop. It is one of the most important type of shift register counter. It is formed by the feedback of the output to its own input. Johnson counter is a ring with an inversion. Another name of Johnson counter are creeping counter, twisted ring counter, walking counter, mobile counter and switch tail counter.
What is Johnson Counter?
A Johnson counter is a type of a synchronous counter with a special counting pattern in this case being Johnson counter. It operates by the complemented output of the last flip flop feed back into the input of the first flip flop. What results from this setup is a series of states which forms a sequence that is not characteristic of normal ring counters.
The Johnson counter can be implemented using n flip flops to count 2n distinct states – a feature that makes it better than a ring counter that uses an equal number of flip flops, as it serves twice the number of states. This counter is used in applications where the number of states is higher than the number of flip-flops; besides, it has a distinguishing feature of self-decodability.
Total number of used and unused states in n-bit Johnson counter:
number of used states=2n
number of unused states=2n - 2*n
Example:
If n=4
4-bit Johnson counter
Initially, suppose all flip-flops are reset.
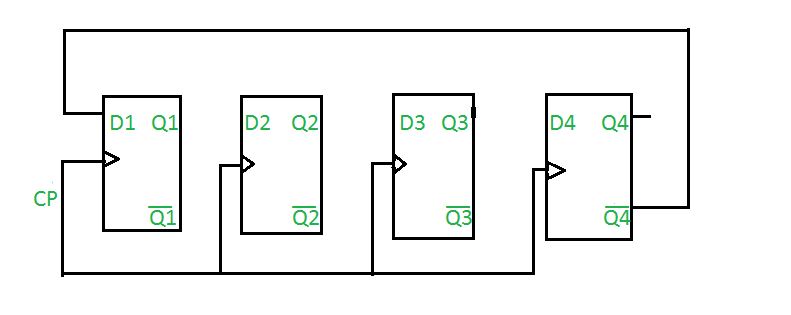
Truth Table

where,
CP is clock pulse and
Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 are the states.
Question: Determine the total number of used and unused states in 4-bit Johnson counter.
Answer: Total number of used states= 2*n
= 2*4
= 8
Total number of unused states= 2n - 2*n
= 24-2*4
= 8
Difference Between Ring Counter and Johnson Counter
Parameters | Ring Counter | Johnson Counter |
|---|
Configuration | A ring counter employs the carry-in of the last flip-flop into the input of the first flip-flop without any manipulation. | In Johnson counter, the complement of output of the last flip-flop is applied to the input of the first flip-flop. |
|---|
Number of Flip- Flops | 'n' flip-flops are required to count 'n' states. | 'n' flip-flops are required to count '2n' states. |
|---|
Counting Sequence | It counts in a simple binary sequence often having one '1' and the rest '0's in each state. | It counts in a twisted sequence, where the output is a mixture of binary 1s and 0s. |
|---|
Number of States | It can Generate 'n' unique states | It can Generate '2n' unique states |
|---|
Unused states
| None, because all the states are utilized | '2n-2n' states are unused
|
|---|
Self-Decoding Capability | Its not self-decoding since additional circuitry is needed | Its self-decoding makes it simpler for certain applications |
|---|
Circuit Complexity
| Since it does not require inversion feedback, thus the circuit is simple | Due to inversion, the circuit is slightly more complex
|
|---|
Advantages of Johnson counter
- The Johnson counter has same number of flip flop but it can count twice the number of states the ring counter can count.
- It can be implemented using D and JK flip flop.
- Johnson ring counter is used to count the data in a continuous loop.
- Johnson counter is a self-decoding circuit.
Disadvantages of Johnson counter
- Johnson counter doesn't count in a binary sequence.
- In Johnson counter more number of states remain unutilized than the number of states being utilized.
- The number of flip flops needed is one half the number of timing signals.
- It can be constructed for any number of timing sequence.
Applications of Johnson counter
- Johnson counter is used as a synchronous decade counter or divider circuit.
- It is used in hardware logic design to create complicated Finite states machine. ex: ASIC and FPGA design.
- The 3 stage Johnson counter is used as a 3 phase square wave generator which produces 1200 phase shift.
- It is used to divide the frequency of the clock signal by varying their feedback.
Conclusion
This article has covered a number of aspects of Johnson counters ranging from how the system operates to the benefits of using the technology as well as shortcomings of the Johnson counters. Johnson counters are a subtype of shift register counter and they are capable of counting twice more states than a ring counter with similar flip flops. It can be seen that the fundamental differences between the ring counters and Johnson counters have been discussed above which can be used in selecting the proper counter circuits for certain digital circuit applications.
Similar Reads
Multiplexers in Digital Logic In this article we will go through the multiplexer, we will first define what is a multiplexer then we will go through its types which are 2x1 and 4x1, then we will go through the Implementation of the 2x1 mux and higher mux with lower order mux, at last we will conclude our article with some applic
10 min read
Carry Look-Ahead Adder The adder produce carry propagation delay while performing other arithmetic operations like multiplication and divisions as it uses several additions or subtraction steps. This is a major problem for the adder and hence improving the speed of addition will improve the speed of all other arithmetic o
5 min read
Parallel Adder and Parallel Subtractor An adder adds two binary numbers one bit at a time using carry from each step. A subtractor subtracts one binary number from another using borrow when needed. A parallel adder adds all bits at once, making addition faster. Similarly, a parallel subtractor subtracts all bits at the same time for quic
5 min read
BCD Adder in Digital Logic BCD stands for binary coded decimal. It is used to perform the addition of BCD numbers. A BCD digit can have any of ten possible four-bit representations. Suppose, we have two 4-bit numbers A and B. The value of A and B can vary from 0(0000 in binary) to 9(1001 in binary) because we are considering
8 min read
Magnitude Comparator in Digital Logic A magnitude digital Comparator is a combinational circuit that compares two digital or binary numbers in order to find out whether one binary number is equal, less than, or greater than the other binary number. We logically design a circuit for which we will have two inputs one for A and the other f
7 min read
BCD to 7 Segment Decoder Prerequisite - Number System and base conversionsBinary Coded Decimal (BCD)BCD is the encoding scheme each of the decimal numbers(0-9) is represented by its equivalent binary pattern(which is generally of 4-bits). Seven segment Seven Segment display is an electronic device which consists of seven Li
5 min read
Classification and Programming of Read-Only Memory (ROM) Read-Only Memory or ROM is another significant non Volatile storage control in computed systems which mainly stores data permanently whether the power is off or not. While RAM is a temporary storage type used in computers and printers, ROM contains firmware and other instructions which are burnt, in
15+ min read
Static Hazards in Digital Logic A hazard, if exists, in a digital circuit causes a temporary fluctuation in the output of the circuit. In other words, a hazard in a digital circuit is a temporary disturbance in the ideal operation of the circuit which if given some time, gets resolved itself. These disturbances or fluctuations occ
4 min read
Introduction of Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are digital circuits that store and use the previous state information to determine their next state. Unlike combinational circuits, which only depend on the current input values to produce outputs, sequential circuits depend on both the current inputs and the previous state stor
7 min read
Flip-Flop types, their Conversion and Applications In this article, we will go through the Flip-Flop types, their Conversion and their Applications, First, we will go through the definition of the flip-flop with its types in brief, and then we will go through the conversion of the flip-flop with its applications, At last, we will conclude our articl
7 min read