Standard Deviation in Discrete Series
Last Updated : 05 Jun, 2024
A scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of values is taken from the arithmetic mean of the given set of data. Standard Deviation can be calculated in three different series; viz., Individual, Discrete, and Frequency Distribution or Continuous Series.
Methods of Calculating Standard Deviation in Discrete Series
- Actual Mean Method
- Direct Method
- Short-cut Method or Assumed Mean Method
- Step Deviation Method
1. Actual Mean Method
In actual mean method, the standard deviation is calculated by taking deviations from the actual mean. The steps taken to determine standard deviation through the actual mean method are as follows:
Step 1: Determine the actual mean (\bar{X}) of the given observation, using the formula, \frac{\sum{fX}}{N}
Step 2: Now, calculate the deviation of each item of the given series from the mean calculated in the first step; i.e., calculate (X-\bar{X}). Denote the deviations with x.
Step 3: After finding out the deviation, square these deviations and multiply them with their respective frequencies (f), and determine its total; i.e., ∑fx2
Step 4: Apply the following formula:
\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fx^2}}{N}}
Where,
σ = Standard Deviation
∑fx2 = Sum total of the squared deviations multiplied by frequency
N = Number of pairs of observations
Example:
Calculate the Standard Deviation for the following data by using the Actual Mean Method.

Solution:
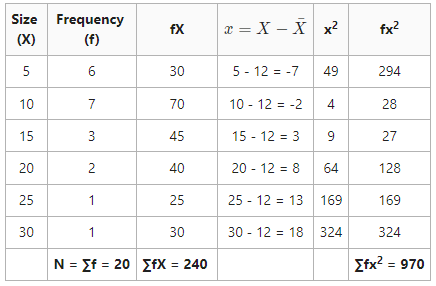
Arithmetic Mean (\bar{X})=\frac{\sum{fX}}{N}=\frac{240}{20}=12
Standard Deviation (σ) = \sqrt{\frac{\sum{fx^2}}{N}}=\sqrt{\frac{970}{20}}=\sqrt{48.5}=6.9
Standard Deviation = 6.9 or 7
2. Direct Method
In Direct Method, there is no need to determine the deviation from the actual mean to calculate standard deviation. The steps taken to determine standard deviation through the direct method are as follows:
Step 1: First of all, calculate the actual mean (\bar{X}) of the given observations, using the formula, \frac{\sum{fX}}{f}
Step 2: Now square the observations and determine their total; i.e., ∑X2.
Step 3: Multiply frequency (f) by their respective X2 and determine the total; i.e., ∑fX2.
Step 4: Now, apply the following formula:
\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fX^2}}{N}-(\bar{X})^2}
Or
=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fX^2}}{N}-(\frac{\sum{fX}}{N})^2}
Where,
σ = Standard Deviation
∑fx2 = Sum total of the squared deviations multiplied by frequency
\bar{X} = Actual Mean
N = Number of Observations
Example:
Calculate the Standard Deviation for the following data by using the Direct Method.

Solution:

Arithmetic Mean (\bar{X})=\frac{\sum{fX}}{N}=\frac{240}{20}=12
Standard Deviation (\sigma)=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fX^2}}{N}-(\bar{X})^2}=\sqrt{\frac{3,850}{20}-(12)^2}
=\sqrt{192.5-144}=\sqrt{48.5}=6.9
Standard Deviation = 6.9 or 7
3. Short-Cut Method or Assumed Mean Method
Actual Mean can sometimes come in fractions, which can make the calculation of standard deviation complicated and difficult. In those cases, it is suggested to use Short-Cut Method to simplify the calculations. The steps taken to determine standard deviation through the assumed mean method are as follows:
Step 1: First of all, take any value of X in the series as Assumed Mean (A).
Step 2: Now determine the deviations of the items from an assumed mean and denote the deviations by d; i.e., d = X - A.
Step 3: Multiply the deviations calculated in the previous step by their respective frequencies and calculate their sum; i.e., ∑fd.
Step 4: Determine the square of the deviations, multiply it by their respective frequencies, and obtain the total; i.e., ∑fd2.
Step 5: Now, apply the following formula:
\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fd^2}}{N}-(\frac{\sum{fd}}{N})^2}
Or
=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fd^2}}{N}-(\frac{\sum{fd}}{N})^2}
Where,
σ = Standard Deviation
∑fd = Sum total of deviations multiplied by frequencies
∑d2 = Sum total of the squared deviations multiplied by frequencies
N = Number of pairs of observations
Example:
Calculate the Standard Deviation for the following data by using the Assumed Mean Method.

Solution:

Arithmetic Mean (\bar{X})=\frac{\sum{fX}}{N}=\frac{240}{20}=12
Standard Deviation (\sigma)=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fd^2}}{N}-(\frac{\sum{fd}}{N})^2}=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{1,150}}{20}-(\frac{-60}{20})^2}
=\sqrt{57.5-9}=\sqrt{48.5}=6.9
Standard Deviation = 6.9 or 7
Also Read:
Standard Deviation: Meaning, Coefficient of Standard Deviation, Merits, and Demerits
4. Step Deviation Method
This method is almost like the assumed mean method. The only difference in the formulas of both methods is that in the step deviation method, the deviations are divided by a common factor (C), and then the standard deviation is determined. The steps taken to determine standard deviation through the step deviation method are as follows:
Step 1: First of all take any value of X in the series as Assumed Mean (A).
Step 2: Now determine the deviations of the items from an assumed mean and denote the deviations by d; i.e., d = X - A.
Step 3: Divide these deviations by common factor (C) and obtain step deviations; i.e., d^\prime=\frac{d}{C}
Step 4: Multiply the step deviations determined in the previous step by their respective frequencies, and obtain their total; i.e., \sum{fd^\prime}
Step 5: Now determine the square of step deviations; i.e., d^\prime{^2}
Step 6: Multiply the squared step deviations by their respective frequencies and determine the total to get \sum{fd^\prime{^2}}
Step 7: Now, apply the following formula:
\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fd^\prime{^2}}}{N}-(\frac{\sum{fd^\prime}}{N})^2}\times{C}
Where,
σ = Standard Deviation
\sum{fd^\prime{^2}} = Sum total of the squared step deviations multiplied by frequencies
\sum{fd^\prime} = Sum total of step deviations multiplied by frequencies
N = Number of pairs of observations
Example:
Calculate the Standard Deviation for the following data by using the Step-Deviation Method.

Solution:

Arithmetic Mean (\bar{X})=\frac{\sum{fX}}{N}=\frac{240}{20}=12
Standard Deviation (\sigma)=\sqrt{\frac{\sum{fd^\prime{^2}}}{N}-(\frac{\sum{fd^\prime}}{N})^2}\times{C}
=\sqrt{\frac{46}{20}-(\frac{-12}{20})^2}\times{5}
=\sqrt{2.3-0.36}\times{5}=\sqrt{1.94}\times{5}=1.39\times{5}=6.9
Standard Deviation = 6.9 or 7
Also Read:
Standard Deviation in Individual Series
Standard Deviation in Frequency Distribution Series
Combined Standard Deviation: Meaning, Formula, and Example
Similar Reads
CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes Economic statistics is a topic in applied statistics that concerns the collection, organization, and presentation of data. GeeksforGeeks Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes have been designed according to the CBSE Syllabus for Class 11. These revision notes consist of detailed Chapterwise import
8 min read
Chapter 1: Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in Economics
Chapter 2: Collection of Data
Data Collection Methods | Primary and Secondary Data Data Collection refers to the systematic process of gathering, measuring, and analyzing information from various sources to get a complete and accurate picture of an area of interest. Data collection is a critical step in any research or data-driven decision-making process, ensuring the accuracy and
11 min read
Sources of Data Collection | Primary and Secondary SourcesData Collection refers to the systematic process of gathering, measuring, and analyzing information from various sources to get a complete and accurate picture of an area of interest. Different sources of data collection include Primary Sources and Secondary Sources. What is Data?Data is a collectio
8 min read
Direct Personal Investigation: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, Demerits and PrecautionsWhat is Direct Personal Investigation?Direct Personal Investigation or Personal Interview is a method of collecting primary data through which the investigator contacts the informant directly to collect data by conducting on-the-spot enquiry. He/she goes to the field personally, contacts the respond
4 min read
Indirect Oral Investigation : Suitability, Merits, Demerits and PrecautionsWhat is Indirect Oral Investigation?Indirect Oral Investigation is a method of collecting primary data through which the investigator approaches third parties who are in the possession of required information about the subject of enquiry. It is used when the area of investigation is large or the res
4 min read
Difference between Direct Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral InvestigationDirect Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral Investigation are two of the many methods of collecting primary data. What is Direct Personal Investigation? Direct Personal Investigation or Personal Interview is a method of collecting primary data through which the investigator contacts the informan
3 min read
Information from Local Source or Correspondents: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, and DemeritsData is the collection of measurements and facts and a tool that helps an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, infla
3 min read
Questionnaires and Schedules Method of Data CollectionQuestionnaires & Schedule method of data collection :The questionnaires are the fundamental instrument for gathering information in review research. Fundamentally, it is a bunch of standardized questions, frequently called items, which follow a decent plan to gather individual information around
5 min read
Difference between Questionnaire and ScheduleQuestionnaires and Schedules are two methods of collecting primary data and are different from each other in many ways. What is a Questionnaire? A questionnaire is a research instrument used by any researcher as a tool to collect data or gather information from any source or subject of his or her in
3 min read
Qualities of a Good Questionnaire and Types of QuestionnairesMeaning of QuestionnaireA questionnaire is a research instrument used by any researcher as a tool to collect data or gather information from any source or subject of his or her interest from the respondents. It has a specific goal to understand topics from the respondent's point of view. It consists
5 min read
What are the Published Sources of Collecting Secondary Data?What is Data?Data is the collection of measurements and facts and a tool that helps an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyse, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, p
3 min read
What Precautions should be taken before using Secondary Data?In the plural sense, Statistics refers to facts or quantitative information that can be used to draw significant conclusions. Hence, for a student of Economics, the main purpose to collect data is to recognize, evaluate, and describe a social issue. For example, the problem of poverty or the problem
3 min read
Two Important Sources of Secondary Data: Census of India and Reports & Publications of NSSOData is the collection of measurement and facts and a tool that help an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, inflati
3 min read
What is National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO)?National Sample Survey (NSS) was set up on the recommendations of the National Income Committee in 1950 and was chaired by the late Professor P.C. Mahalanobis. The basic aim behind setting up NSS was to fill up the large gaps in statistical data to calculate the national income aggregates (especiall
3 min read
What is Census Method of Collecting Data?Collection of Data is the first step of the statistical investigation and can be gathered through two different sources, namely, primary sources and secondary sources. Besides primary and secondary sources of collecting data, there are two essential methods of collecting data; i.e., Census Method an
4 min read
Sample Method of Collection of DataMeaning of Population:A population is a pool of similar objects, items, or events that are used to define the subject of study, which is related to some questions or events under study. In statistics, it means the aggregate of all items about which we want to collect information. The population can
6 min read
Methods of SamplingThe sampling method involves selecting a subset of individuals or observations from a larger population to collect data and make inferences about the entire population. It is a practical and efficient way to gather data when it is impractical or impossible to collect information from every member of
11 min read
Father of Indian CensusWho is the Father of Indian Census? Census, a systematic collection and recording of demographic, social, and economic data of a country's population, stands as one of the most crucial tools for understanding the dynamics of a society. In the context of India, the census has played an indispensable
5 min read
What makes a Sampling Data Reliable?Data is the collection of measurement and facts and a tool that help an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, inflati
2 min read
Difference between Census Method and Sampling Method of Collecting DataCollection of Data is the first step of the statistical investigation and can be gathered through two different sources, namely, primary sources and secondary sources. Besides primary and secondary sources of collecting data, there are two essential methods of collecting data; i.e., Census Method an
4 min read
What are Statistical Errors?Data is the collection of measurement and facts and a tool that help an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, inflati
3 min read
Chapter 3: Organisation of Data
Organization of DataWhat is Data Organization? The data collected by an investigator is in raw form and cannot offer any meaningful conclusion; hence, it needs to be organized properly. Therefore, the process of systematically arranging the collected data or raw data so that it can be easy to understand the data is kno
6 min read
Objectives and Characteristics of Classification of DataData can not always be found in an organised manner. Therefore, an analyst or investigator has to properly organise the collected data for a better analysis of information and to reach the desired results. One of the most important methods of organising such data is known as the classification of da
5 min read
Classification of Data in Statistics | Meaning and Basis of Classification of DataClassification of data refers to the systematic organization of raw data into groups or categories based on shared characteristics or attributes. This process transforms unstructured data into a structured format, making it easier to analyze and draw meaningful conclusions. Data can be classified ba
5 min read
Concept of Variable and Raw DataThe data collected by an investigator is in raw form and cannot offer any meaningful conclusion; hence, it needs to be organized properly. Therefore, the process of systematically arranging the collected data or raw data so that it can be easy to understand is known as the organization of data. With
4 min read
Types of Statistical SeriesIn statistics, data is often organized in series to facilitate analysis and interpretation. A statistical series refers to a set of observations arranged in a particular order based on one or more criteria. Understanding the different types of statistical series is crucial for effectively analyzing
12 min read
Difference between Frequency Array and Frequency DistributionThe number of times a specific value appears in a distribution is known as its frequency. For instance, there are 30 students in a class, and fifteen of them have received 80 points, ten have received 90 points, and five have received 100 points. The frequencies will now be 15, 10, and 5. A table in
4 min read
Types of Frequency DistributionFrequency distribution is a method of organizing and summarizing data to show the frequency (count) of each possible outcome of a dataset. It is an essential tool in statistics for understanding the distribution and pattern of data. There are several types of frequency distributions used based on th
10 min read
Chapter 4: Presentation of Data: Textual and Tabular
Textual Presentation of Data: Meaning, Suitability, and DrawbacksPresentation of Data refers to the exhibition of data in such a clear and attractive way that it is easily understood and analysed. Data can be presented in different forms, including Textual or Descriptive Presentation, Tabular Presentation, and Diagrammatic Presentation. Textual Presentation Textu
3 min read
Tabular Presentation of Data: Meaning, Objectives, Features and MeritsWhat is Tabulation?The systematic presentation of numerical data in rows and columns is known as Tabulation. It is designed to make presentation simpler and analysis easier. This type of presentation facilitates comparison by putting relevant information close to one another, and it helps in further
8 min read
Different Types of TablesThe tables can be categorised into various categories depending upon different aspects, such as the purpose, the nature of data used for the investigation, and the extent of coverage of the table. The following are the various kinds of tables that are commonly used in studies of statistics. (I) Clas
4 min read
Classification and Tabulation of DataClassification and Tabulation of Data are fundamental processes in the field of statistics, especially in the context of economics. They transform raw data into a structured form, enabling better analysis, interpretation, and presentation of economic data. Proper classification ensures that data is
11 min read
Chapter 5: Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: Meaning , Features, Guidelines, Advantages and DisadvantagesDiagrammatic Presentation of Data The technique of presenting statistical data in the form of diagrams such as bar diagrams, cartograms, pie diagrams, and pictograms is known as the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data. Statistics performs an important function by presenting a complex mass of data in a
6 min read
Types of DiagramsWhat is a Diagram?Statistics performs an important function by presenting a complex mass of data in a simple way that makes it easier to understand. Classification and tabulation are two techniques for presenting data in an understandable form. However, as the volume of data increases, it becomes in
7 min read
Bar Graph | Meaning, Types, and ExamplesBar graphs are one of the most common and versatile types of charts used to represent categorical data visually. They display data using rectangular bars, where the length or height of each bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar graphs are widely used in various fields such as business, edu
12 min read
Pie Diagrams | Meaning, Example and Steps to ConstructWhat is Pie Chart or Pie Diagram?A circle can be divided into parts to show the ratios of different components. A pie diagram is one such representation. Pie charts are also referred to as Angular Circle Diagrams. The circle is divided into as many sections as there are elements by drawing straight
2 min read
Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to DrawWhat is Histogram?A histogram is a graphical representation of the frequency distribution of continuous series using rectangles. The x-axis of the graph represents the class interval, and the y-axis shows the various frequencies corresponding to different class intervals. A histogram is a two-dimens
5 min read
Frequency Polygon | Meaning, Steps to Draw and ExamplesWhat is Frequency Polygon?A frequency polygon is another way to show a frequency distribution on a graph. In addition to being an alternate for the histogram, the frequency polygon is also an outcome of the histogram. While comparing two or more frequency distributions, a frequency polygon is more s
5 min read
Ogive (Cumulative Frequency Curve) and its TypesA method of presenting data in the form of graphs that provides a quick and easier way to understand the trends of the given set of data is known as Graphic Presentation. The two types of graphs through which a given set of data can be presented are Frequency Distribution Graphs and Time Series Grap
5 min read
What is Arithmetic Line-Graph or Time-Series Graph?A time series is an arrangement in which the values of variables are recorded in relation to the time of occurrence. In the case of a long series of data, time series helps identify the trend, periodicity, etc. The time period can be defined as a year, quarter, month, week, days, hours, and so on. A
6 min read
Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation of DataDiagrammatic and graphic presentation of data means visual representation of the data. It shows a comparison between two or more sets of data and helps in the presentation of highly complex data in its simplest form. Diagrams and graphs are clear and easy to read and understand. In the diagrammatic
4 min read
Chapter 6: Measures of Central Tendency: Arithmetic Mean
Measures of Central Tendency in StatisticsCentral tendencies in statistics are numerical values that represent the middle or typical value of a dataset. Also known as averages, they provide a summary of the entire data, making it easier to understand the overall pattern or behavior. These values are useful because they capture the essence o
11 min read
Arithmetic Mean: Meaning, Example, Types, Merits, and DemeritsA single value used to symbolise a whole set of data is called the Measure of Central Tendency. In comparison to other values, it is a typical value to which the majority of observations are closer. The arithmetic mean is one approach to measure central tendency in statistics. This measure of centra
8 min read
What is Simple Arithmetic Mean?Arithmetic Mean is one approach to measure central tendency in statistics. This measure of central tendency involves the condensation of a huge amount of data to a single value. Arithmetic mean can be determined using two methods; viz., Simple Arithmetic Mean and Weighted Arithmetic Mean. Meaning of
11 min read
Calculation of Mean in Individual Series | Formula of MeanWhat is Mean? Mean is the sum of a set of numbers divided by the total number of values. It is also referred to as the average. For instance, if there are four items in a series, i.e. 2, 5, 8, 3, and 9. The simple arithmetic mean is (2 + 5 + 8 + 3 + 9) / 5 = 5.4. What is Individual Series? The serie
2 min read
Calculation of Mean in Discrete Series | Formula of MeanWhat is Mean?Mean is the sum of a set of numbers divided by the total number of values. It is also referred to as the average. For instance, if there are four items in a series, i.e. 2, 5, 8, 3, and 9. The simple arithmetic mean is (2 + 5 + 8 + 3 + 9) / 5 = 5.4.What is Discrete Series?In discrete se
3 min read
Calculation of Mean in Continuous Series | Formula of MeanThe mean, also known as the average, is a measure of central tendency that summarizes a set of data by identifying the central point. In a continuous series, data is grouped into class intervals, and the mean is calculated differently than in a discrete series. The mean provides a comprehensive over
4 min read
Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Special CasesA single value used to symbolise a whole set of data is called the Measure of Central Tendency. In comparison to other values, it is a typical value to which the majority of observations are closer. The arithmetic mean is one approach to measure central tendency in statistics. This measure of centra
4 min read
Weighted Arithmetic MeanSimple Arithmetic Mean gives equal importance to all the variables in a series. However, in some situations, a greater emphasis is given to one item and less to others, i.e., ranking of the variables is done according to their significance in that situation. For example, during inflation, the price
3 min read
Chapter 7: Measures of Central Tendency: Median and Mode
Median(Measures of Central Tendency): Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and ExamplesWhat is Median?The median is a centrally located value that splits the distribution into two equal portions, one including all values more than or equal to the median and the other containing all values less than or equal to it. The median is the " middle " element when the data set is organized in
8 min read
Calculation of Median for Different Types of Statistical SeriesWhat is Median?When elements in the data set are organised sequentially, that is, in either an ascending or descending order of magnitude, the median can be referred to as the middle value of the data set. Its value is located in a distribution in such a way that 50% of the items are below it and 50
8 min read
Calculation of Median in Individual Series | Formula of MedianWhat is Median?When elements in the data set are organised sequentially, that is, in either an ascending or descending order of magnitude, the median can be referred to as the middle value of the data set. Its value locates in a distribution in such a way that 50% of the items are below it and 50% a
3 min read
Calculation of Median in Discrete Series | Formula of MedianWhat is Median?When elements in the data set are organised sequentially, that is, in either an ascending or descending order of magnitude, the median can be referred to as the middle value of the data set. Its value locates in a distribution in such a way that 50% of the items are below it and 50% a
3 min read
Calculation of Median in Continuous Series | Formula of MedianThe median is a measure of central tendency that represents the middle value of a data set when the values are arranged in order, either ascending or descending. In a continuous series (grouped data), where data is presented in class intervals with frequencies, the median divides the distribution su
5 min read
Graphical determination of MedianA measure of central tendency that determines the centrally located value of a given series is known as the Median. The number of values of the series below and above the given series is always equal. To determine the median value of a given series, it is first managed in increasing or decreasing or
5 min read
Mode: Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and ExamplesThe word mode is derived from the French word 'La Mode', meaning anything that is in fashion or vogue. A measure of central tendency in statistical series that determines the value occurring most frequently in a given series is known as mode. In other words, the modal value of the series has the hig
9 min read
Calculation of Mode in Individual Series | Formula of ModeThe word mode comes from the Latin word ‘Modus’, meaning measurements, quantity, way, or manner. In statistics, Mode refers to the variable that occurs most of the time or repeats itself most frequently in a given series of variables (say X). It is a maximum occurrence at a particular point or a val
5 min read
Calculation of Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of ModeThe word mode comes from the Latin word 'Modus', meaning measurements, quantity, way, or manner. In statistics, Mode refers to the variable that occurs most of the time or repeats itself most frequently in a given series of variables (say X). It is a maximum occurrence at a particular point or a val
6 min read
Grouping Method of Calculating Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of ModeMode is the value from a data set that has occurred the most number of times. It is one of the most crucial measures of central tendency and is represented by Z. For example, if, in a class of 35 students, 10 students are 10 years old, 20 students are 11 years old, and the rest 5 students are 9 year
5 min read
Calculation of Mode in Continuous Series | Formula of ModeMode, in statistics, refers to the variable that occurs most of the time in the given series. In simple words, a mode is a variable that repeats itself most frequently in a given series of variables (say X). We can determine the mode in two series; viz., individual and discrete series. Mode is denot
7 min read
Calculation of Mode in Special CasesThe word mode is derived from the French word ‘La Mode’, meaning anything that is in fashion or vogue. A measure of central tendency in statistical series that determines the value occurring most frequently in the given series is known as mode. In other words, the modal value of the series has the h
6 min read
Calculation of Mode by Graphical MethodThe word mode is derived from the French word 'La Mode', meaning anything that is in fashion or vogue. A measure of central tendency in statistical series that determines the value occurring most frequently in the given series is known as mode. In other words, the modal value of the series has the h
4 min read
Mean, Median and Mode| Comparison, Relationship and CalculationA single value used to symbolise a whole set of data is called the Measure of Central Tendency. In comparison to other values, it is a typical value to which the majority of observations are closer. Average and Measure of Location are other names for the Measure of Central Tendency. In statistical a
7 min read
Chapter 8: Measures of Dispersion
Measures of Dispersion | Meaning, Absolute and Relative Measures of DispersionAverages like mean, median, and mode can be used to represent any series by a single number. However, averages are not enough to describe the characteristics of statistical data. So, it is necessary to define some additional summary measures to adequately represent the characteristics of a distribut
5 min read
Range | Meaning, Coefficient of Range, Merits and Demerits, Calculation of RangeWhat is Range?Range is the easiest to understand of all the measures of dispersion. The difference between the largest and smallest item in a distribution is called range. It can be written as: Range (R) = Largest item (L) – Smallest item (S) For example, If the marks of 5 students of class Xth are
4 min read
Calculation of Range and Coefficient of RangeWhat is Range?Range is the easiest to understand of all the measures of dispersion. The difference between the largest and smallest item in a distribution is called range. It can be written as:Range (R) = Largest item (L) – Smallest item (S)For example, If the marks of 5 students of class XIth are 2
4 min read
Interquartile Range and Quartile DeviationThe extent to which the values of a distribution differ from the average of that distribution is known as Dispersion. The measures of dispersion can be either absolute or relative. The Measures of Absolute Dispersion consist of Range, Quartile Deviation, Mean Deviation, Standard Deviation, and Loren
3 min read
Partition Value | Quartiles, Deciles and PercentilesPartition values are statistical measures that divide a dataset into equal parts. They help in understanding the distribution and spread of data by indicating where certain percentages of the data fall. The most commonly used partition values are quartiles, deciles, and percentiles.Table of ContentW
9 min read
Quartile Deviation and Coefficient of Quartile Deviation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation, and ExamplesThe extent to which the values of a distribution differ from the average of that distribution is known as Dispersion. The measures of dispersion can be either absolute or relative. The Measures of Absolute Dispersion consist of Range, Quartile Deviation, Mean Deviation, Standard Deviation, and Loren
3 min read
Quartile Deviation in Discrete Series | Formula, Calculation and ExamplesWhat is Quartile Deviation?Quartile Deviation (absolute measure) divides the distribution into multiple quarters. Quartile Deviation is calculated as the average of the difference of the upper quartile (Q3) and the lower quartile (Q1).Quartile~Deviation=\frac{Q_3-Q_1}{2} Where,Q3 = Upper Quartile (S
2 min read
Quartile Deviation in Continuous Series | Formula, Calculation and ExamplesWhat is Quartile Deviation?Quartile Deviation (absolute measure) divides the distribution into multiple quarters. Quartile Deviation is calculated as the average of the difference of the upper quartile (Q3) and the lower quartile (Q1).Quartile~Deviation=\frac{Q_3-Q_1}{2} Where,Q3 = Upper Quartile (S
3 min read
Mean Deviation: Coefficient of Mean Deviation, Merits, and DemeritsRange, Interquartile range, and Quartile deviation all have the same defect; i.e., they are determined by considering only two values of a series: either the extreme values (as in range) or the values of the quartiles (as in quartile deviation). This approach of analysing dispersion by determining t
5 min read
Calculation of Mean Deviation for different types of Statistical SeriesWhat is Mean Deviation?The arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode) is known as the Mean Deviation of a series. Other names for Mean Deviation are the First Moment of Dispersion and Average Deviation. Mean deviation is calculate
3 min read
Mean Deviation from Mean | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous SeriesMean Deviation of a series can be defined as the arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode). Mean Deviation is also known as the First Moment of Dispersion or Average Deviation. Mean Deviation is based on all the items of the seri
4 min read
Mean Deviation from Median | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous SeriesWhat is Mean Deviation from Median?Mean Deviation of a series can be defined as the arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode). Mean Deviation is also known as the First Moment of Dispersion or Average Deviation. Mean Deviation is
5 min read
Standard Deviation: Meaning, Coefficient of Standard Deviation, Merits, and DemeritsThe methods of measuring dispersion such as quartile deviation, range, mean deviation, etc., are not universally adopted as they do not provide much accuracy. Range does not provide required satisfaction as in the entire group, range's magnitude is determined by most extreme cases. Quartile Deviatio
6 min read
Standard Deviation in Individual SeriesA scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of valu
3 min read
Standard Deviation in Discrete SeriesA scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of valu
5 min read
Standard Deviation in Frequency Distribution SeriesA scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. It is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of values is taken from
3 min read
Combined Standard Deviation: Meaning, Formula, and ExampleA scientific measure of dispersion, which is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of va
2 min read
Coefficient of Variation: Meaning, Formula and ExamplesWhat is Coefficient of Variation? As Standard Deviation is an absolute measure of dispersion, one cannot use it for comparing the variability of two or more series when they are expressed in different units. Therefore, in order to compare the variability of two or more series with different units it
2 min read
Lorenz Curveb : Meaning, Construction, and ApplicationWhat is Lorenz Curve?The variability of a statistical series can be measured through different measures, Lorenz Curve is one of them. It is a Cumulative Percentage Curve and was first used by Max Lorenz. Generally, Lorenz Curves are used to measure the variability of the distribution of income and w
4 min read
Chapter 9: Correlation