Venn diagrams are visual tools used to show relationships between different sets. They use overlapping circles to represent how sets intersect, share elements, or stay separate. These diagrams help categorize items, making it easier to understand similarities and differences.
In mathematics, Venn diagrams are placed inside a rectangle, which represents the universal set—a set that contains all elements from all the sets shown. This visual method makes it easier to understand complex relationships between sets.

Venn Diagrams are used to represent the groups of data in circles, if the circles are overlapping, some elements in the groups are common, if they are not overlapping, there is nothing common between the groups or sets of data.
Venn Diagram Examples
Venn diagrams are highly useful in solving problems of sets and other problems. They are useful in representing the data in picture form. Let's learn more about the Venn diagram through an example,
Example 1: Take a set A representing even numbers up to 10 and another set B representing natural numbers less than 5 then their interaction is represented using the Venn diagram.
Solution:

How to Draw a Venn Diagram?
The above symbols are used while drawing and showing the relationship among sets. In order to draw a Venn diagram.
Step 1: Start by drawing a Rectangle showing the Universal Set.

Step 2: According to the number of sets given and the relationship between/among them, draw different circles representing different Sets.

Step 3: Find the intersection or union of the set using the condition given.

Read More: Representation of a Set
Venn Diagram for Sets Operations
There are different operations that can be done on sets in order to find the possible unknown parameter, for example, if two sets have something in common, their intersection is possible. The basic operations performed on the set are,
Let's look at these set operations and how they look on the Venn diagram.
Venn Diagram of Union of Sets
The Union of two or more two sets represents the data of the sets without repeating the same data more than once, it is shown with the symbol ⇢∪.
n(A∪ B) = {a: a∈ A OR a∈ B}

Venn Diagram of Intersection of Sets
The intersection of two or more two sets means extracting only the amount of data that is common between/among the sets. The symbol used for the intersection⇢ ∩.
n(A∩ B)= {a: a∈ A and a∈ B}

Venn Diagram of Complement of a Set
Complementing a set means finding the value of the data present in the Universal set other than the data of the set.
n(A') = U- n(A)

Venn Diagram of Difference of Set
Suppose we take two sets, Set A and Set B then their difference is given as A - B. This difference represents all the values of set A which are not present in set B.
For example, if we take Set A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} and set B = {2, 4, 6, 8} then A- B = {1, 3, 5}.
In the Venn diagram, we represent the A - B as the area of set A which is not intersecting with set B.
The concept of the Venn diagram is very useful for solving a variety of problems in Mathematics and others. To understand more about it lets learn some important terms related to it.
Universal Set
Universal Set is a large set that contains all the sets which we are considering in a particular situation.
For example, suppose we are considering the set of Honda cars in a society say set A, and let set B is the group of red car in the same society then the set of all the cars in that society is the universal set as it contains the values of both the sets, set A and set B in consideration.
The image representing the Universal set is discussed below,

Subset
Subset is actually a set of values that is contained inside another set i.e. we can say that set B is the subset of set A if all the values of set B are contained in set A.
For example, if we take N as the set of all the natural numbers and W as the set of all whole numbers then,
- N = Set of all Natural Numbers
- W = Set of all Whole Numbers
We can say that N is a subset of W all the values of set N are contained in set W i.e.,N ⊆ W
We use Venn diagrams to easily represent a subset of a set. The images discussing the subset of a set are given below,

Venn Diagram Symbols
In order to draw a Venn diagram, first, understand the type of symbols used in sets. Sets can be easily represented on the Venn diagram and the parameters are easily taken out from the diagram itself. We use various types of symbols in drawing Venn diagrams, some of the most important types of symbols used in drawing Venn diagrams are,
Venn Diagram Symbols | Name of Symbol | Description |
|---|
∪ | Union Symbol | Union symbol is used for taking the union of two or more sets. |
∩ | Intersection Symbol | Intersection symbol is used for taking the intersection of two or more sets. |
A' or Ac | Compliment Symbol | Complement symbol is used for taking the complement of a set. |
Types of Venn Diagrams
There are various types of Venn diagrams that are widely used in Mathematics and other related fields. They are categorized based on the number of sets involved or circles involved in the Universal set.
- Two-set Venn diagram
- Three-set Venn diagram
- Four-set Venn diagram
- Five-set Venn diagram
Venn Diagram for Three Sets
We can represent three sets easily using the Venn Diagram. Their representation is done by three overlapping circles. Suppose we take three sets of Set A of the people who play cricket. Set B of the people who are graduates and Set C of the people who are 18 years and above of the age.
Then the Venn diagram representing the above three sets is drawn using three circles and taking their intersection wherever required.
We can represent the intersection of three sets using the Venn diagram. The below image represents the intersection of three sets.
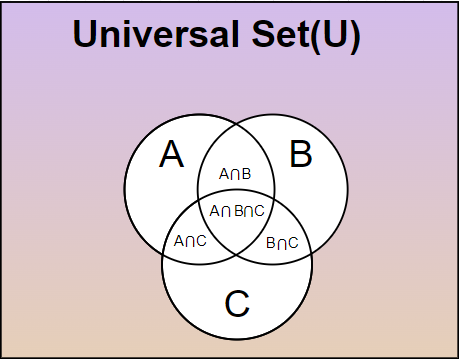
We can find the various parameters using the above Venn diagram.
Suppose we have to find,
- No of graduates who play cricket it is given by B⋂C
- No of graduates who play cricket and are at least 18 years old is given by A⋂B⋂C, etc.
Also Check:
We use various formulas of the set to find various parameters of the sets.
Let's take two sets, set A and set B then the various formulas of the sets are,
n(A U B) = n(A) + n(B) – n (A ⋂ B)
Where,
- n(A) represents the number of elements in set A,
- n(B) represents the number of elements in set B,
- n(A U B) represent the number of elements in A U B, and
- n(A ⋂ B) represent the number of elements in A ⋂ B
Similarly, for three sets, Set A, Set B, and Set C we get,
n (A U B U C) = n(A) + n(B) + n(C) - n(A ⋂ B) - n(B ⋂ C) - n(C ⋂ A) + n(A ⋂ B ⋂ C)
We can understand these formulas with the help of the example discussed below,
Example: In a class of 40 students, 18 like Mathematics, 16 like Science, and 10 like both Mathematics and Science. Then find the students who like either Mathematics or Science.
Solution:
Let A be the set of students who like Mathematics and B be the set of students who like Science, then
n(A) = 18,
n(B) = 16, and
n(A ⋂ B) = 10
Now to find the number of students who like either Mathematics or Science i.e. n(A U B) we use the above formula.
n(A U B) = n(A) + n(B) – n (A ⋂ B)
⇒ n(A U B) = 18 + 16 - 10
⇒ n(A U B) = 24
Uses and Applications of Venn Diagram
Venn diagrams have various use cases such as solving various problems and representing the data in an easy-to-understand format. Various applications of Venn Diagrams are:
- The relation between various sets and their operations can be easily achieved using Venn diagrams.
- They are used for explaining large data sets in a very easy way.
- They are used for logic building and finding the solution to complex data problems.
- They are used to solve problems based on various analogies.
- Analysts use Venn diagrams to represent complex data in easily understandable ways, etc.
Related Article on Venn Diagram:
Solved Example Problems on Venn Diagram
Example 1: Set A= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and U= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}. Represent A' or Ac on the Venn diagram.
Solution:
Venn Diagram for A'

Example 2: In a Group of people, 50 people either speak Hindi or English, 10 prefer speaking both Hindi and English, 20 prefer only English. How many people prefer speaking Hindi? Explain both by formula and by Venn diagram.
Solution:
According to formula,
n(H∪E) = n(H) + n(E) - n(H∩E)
Both English and Hindi speakers, n(H∩E) = 10
English speakers, n(E)= 20
Either Hindi or English, n(H∪E)= 50
50= 20+ n(H) - 10
n(H)= 50 - 10
n(H)= 40
From Venn Diagram,

Example 3: In a Class, Students like to play these games- Football, Cricket, and Volleyball. 5 students Play all 3 games, 20 play Football, 30 play Volleyball, and 40 play Cricket. 10 play both cricket and volleyball, 12 play both football and cricket, 9 play both football and volleyball. How many students are present in the class?
Solution:
n(F∪ C∪ V)= n(F)+ n(C)+ n(V) - n(F∩C) - n(F∩V) - n(C∩V)+ n(F∩ C∩ V)
n(F∪ C∪ V)= 20+ 30+ 40- 10-12-9+5
n(F∪ C∪ V)= 64
There are 64 Students in the class.
Example 4: Represent the above information with the help of a Venn diagram showing the amount of data present in each set.
Solution:
Above information should look something like this on Venn diagram,

Example 5: Below given Venn diagram has all the sufficient information required to show the data of all the sets possible. Observe the diagram carefully then answer the following.

- What is the value of n(A∩ B∩ C)?
- What is the value of n(C)?
- What is the value of n(B ∩ A)?
- What is the value of n(A∪ B∪ C)?
- What is the value of n(B')?
Solution:
Observing the Venn diagram, the above questions can be easily answered,
1. n(A ∩ B∩ C) = 5
2. n(C) = 15 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 30
3. n( B∩A) = 5 + 5 = 10
4. n(A∪ B∪ C) = 15+ 20 + 10 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 65
5. n(B') = U - n(B) = 100 - (20 + 5 + 5 + 5) = 100 - 35 = 65
➣ Suggested Article: Venn Diagrams on Reasoning
Venn Diagrams Practice Questions
Question 1: Consider two sets, A and B, where A represents fruits and B represents vegetables. Set A contains apples, bananas, and grapes, while set B contains carrots, lettuce, and apples. Draw a Venn diagram to represent these sets. How many items are only in the fruit category?
Question 2: In a small neighborhood, 10 households have dogs, 7 have cats, and 3 households have both dogs and cats. How many households have at least one kind of pet? Draw a Venn diagram to represent this situation.
Question 3: In a sports club, 120 members play tennis, 150 play badminton, and 50 play both tennis and badminton. How many members play either tennis or badminton? Create a Venn diagram to help you answer.
Question 4: In a class of 30 students, 18 students play basketball, 12 students play football, and 8 students play both basketball and football. How many students do not play either basketball or football?
Question 5: A survey of 100 people was conducted to find their preferences for three types of movies: Action, Comedy, and Drama. The survey results showed:
- 45 people like Action movies.
- 50 people like Comedy movies.
- 60 people like Drama movies.
- 25 people like both Action and Comedy.
- 30 people like both Comedy and Drama.
- 20 people like both Drama and Action.
- 10 people like all three types of movies.
How many people like exactly two types of movies?
Conclusion
Venn diagrams, created by English logician John Venn in the 1880s. Venn diagrams are a powerful tool for visualizing the relationships between different sets, making complex concepts more accessible and easier to understand. Using overlapping circles within a rectangle (the universal set), they illustrate how sets intersect, differ, and relate, with each circle representing a different set. Overlapping regions show common elements, while non-overlapping areas highlight unique element. Venn diagrams are applied across various fields for problem-solving, data presentation, and logical reasoning, making them a versatile tool for educators, students, and professionals alike.
Similar Reads
Set Theory Set theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with collections of objects, called sets. A set is simply a collection of distinct elements, such as numbers, letters, or even everyday objects, that share a common property or rule.Example of SetsSome examples of sets include:A set of fruits: {apple,
3 min read
Set Theory Formulas In mathematics, a set is simply a collection of well-defined individual objects that form a group. A set can contain any group of items, such as a set of numbers, a day of the week, or a vehicle. Each element of the set is called an element of the set.Example: A = { 2, 4, 6, 8 }. A is a set and 2, 4
8 min read
Representation of Set
Types of Set
Types Of SetsIn mathematics, a set is defined as a well-defined collection of distinct elements that share a common property. These elements— like numbers, letters, or even other sets are listed in curly brackets "{ }" and represented by capital letters. For example, a set can include days of the week. The diffe
13 min read
Empty SetEmpty Sets are sets with no items or elements in them. They are also called null sets. The symbol (phi) ∅represents the empty set and is written as ∅ = { }. It is also known as a void set or a null set. When compared to other sets, empty sets are seen to be distinctive.Empty sets are used to simplif
10 min read
Disjoint SetsDisjoint Sets are one of the types of many pair of sets, which are used in Set Theory, other than this other types are equivalent sets, equal sets, etc. Set Theory is the branch of mathematics that deals with the collection of objects and generalized various properties for these collections of objec
8 min read
Finite SetsFinite set is a collection of finite, well-defined elements. For better understanding, imagine you have a bunch of your favourite toys or snacks. You know exactly how many you have, that's the idea of a finite set in math. A finite set is a way to discuss collections of things you can count. In this
10 min read
Universal SetsUniversal Set is a set that has all the elements associated with a given set, without any repetition. Suppose we have two sets P = {1, 3, 5} and Q = {2, 4, 6} then the universal set of P and Q is U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. We generally use U to denote universal sets. Universal Set is a type of set that
6 min read
Subsets in MathsSubsets in Maths are a core concept in the study of Set Theory. It can be defined as a group of elements, objects, or members enclosed in curly braces, such as {x, y, z} is called a Set, where each member of the set is unique and is taken from another set called the Parent Set.This article explores
12 min read
Operation on Sets
Set OperationsA set is simply a collection of distinct objects. These objects can be numbers, letters, or even people—anything! We denote a set using curly brackets.For example: A = {1, 2, 3}Set Operations can be defined as the operations performed on two or more sets to obtain a single set containing a combinati
10 min read
Union of SetsUnion of two sets means finding a set containing all the values in both sets. It is denoted using the symbol '∪' and is read as the union. Example 1:If A = {1, 3. 5. 7} and B = {1, 2, 3} then A∪B is read as A union B and its value is,A∪B = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7}Example 2:If A = {1, 3. 5.7} and B = {2, 4} t
12 min read
Intersection of SetsIntersection of Sets is the operation in set theory and is applied between two or more sets. It result in the output as all the elements which are common in all the sets under consideration. For example, The  intersection of sets A and B is the set of all elements which are common to both A and B.In
11 min read
Difference of SetsDifference of Sets is the operation defined on sets, just like we can perform arithmetic operations on numbers in mathematics. Other than the difference, we can also perform the union and intersection of sets for any given set. These operations have a lot of important applications in mathematical pr
10 min read
Complement of a SetIn mathematics, a set is a collection or grouping of well-defined objects. All such objects, when grouped in a set, are called elements. Sets are represented by capital letter symbols, and the elements are placed together in a curly bracket {}.For example, if W is the set of whole numbers, then W =
10 min read
Cartesian Product of Sets The term 'product' mathematically refers to the result obtained when two or more values are multiplied together. For example, 45 is the product of 9 and 5.To understand the Cartesian product of sets, one must first be familiar with basic set operations such as union and intersection, which are appli
7 min read
Application of Set
De Morgan's Law - Theorem, Proofs, Formula & ExamplesDe Morgan's law is the law that gives the relation between union, intersection, and complements in set theory. In Boolean algebra, it gives the relation between AND, OR, and complements of the variable, and in logic, it gives the relation between AND, OR, or Negation of the statement. With the help
13 min read