Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a branch of machine learning that focuses on how agents can learn to make decisions through trial and error to maximize cumulative rewards. RL allows machines to learn by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback based on their actions. This feedback comes in the form of rewards or penalties.
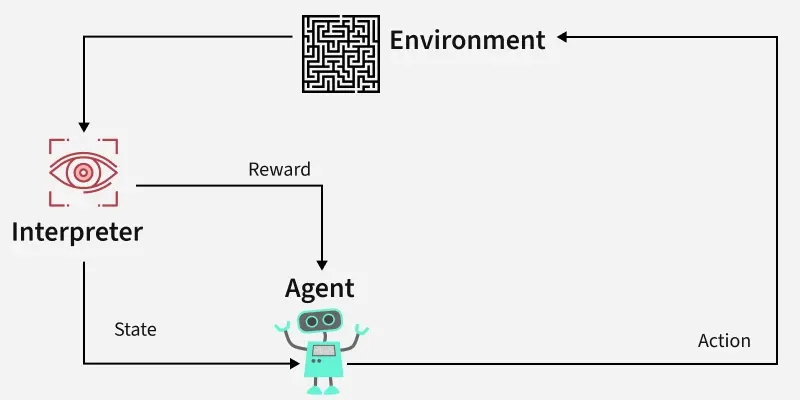
Reinforcement Learning revolves around the idea that an agent (the learner or decision-maker) interacts with an environment to achieve a goal. The agent performs actions and receives feedback to optimize its decision-making over time.
- Agent: The decision-maker that performs actions.
- Environment: The world or system in which the agent operates.
- State: The situation or condition the agent is currently in.
- Action: The possible moves or decisions the agent can make.
- Reward: The feedback or result from the environment based on the agent’s action.
How Reinforcement Learning Works?
The RL process involves an agent performing actions in an environment, receiving rewards or penalties based on those actions, and adjusting its behavior accordingly. This loop helps the agent improve its decision-making over time to maximize the cumulative reward.
Here’s a breakdown of RL components:
- Policy: A strategy that the agent uses to determine the next action based on the current state.
- Reward Function: A function that provides feedback on the actions taken, guiding the agent towards its goal.
- Value Function: Estimates the future cumulative rewards the agent will receive from a given state.
- Model of the Environment: A representation of the environment that predicts future states and rewards, aiding in planning.
Reinforcement Learning Example: Navigating a Maze
Imagine a robot navigating a maze to reach a diamond while avoiding fire hazards. The goal is to find the optimal path with the least number of hazards while maximizing the reward:
- Each time the robot moves correctly, it receives a reward.
- If the robot takes the wrong path, it loses points.
The robot learns by exploring different paths in the maze. By trying various moves, it evaluates the rewards and penalties for each path. Over time, the robot determines the best route by selecting the actions that lead to the highest cumulative reward.

The robot's learning process can be summarized as follows:
- Exploration: The robot starts by exploring all possible paths in the maze, taking different actions at each step (e.g., move left, right, up, or down).
- Feedback: After each move, the robot receives feedback from the environment:
- A positive reward for moving closer to the diamond.
- A penalty for moving into a fire hazard.
- Adjusting Behavior: Based on this feedback, the robot adjusts its behavior to maximize the cumulative reward, favoring paths that avoid hazards and bring it closer to the diamond.
- Optimal Path: Eventually, the robot discovers the optimal path with the least number of hazards and the highest reward by selecting the right actions based on past experiences.
Types of Reinforcements in RL
1. Positive Reinforcement
Positive Reinforcement is defined as when an event, occurs due to a particular behavior, increases the strength and the frequency of the behavior. In other words, it has a positive effect on behavior.
- Advantages: Maximizes performance, helps sustain change over time.
- Disadvantages: Overuse can lead to excess states that may reduce effectiveness.
2. Negative Reinforcement
Negative Reinforcement is defined as strengthening of behavior because a negative condition is stopped or avoided.
- Advantages: Increases behavior frequency, ensures a minimum performance standard.
- Disadvantages: It may only encourage just enough action to avoid penalties.
CartPole in OpenAI Gym
One of the classic RL problems is the CartPole environment in OpenAI Gym, where the goal is to balance a pole on a cart. The agent can either push the cart left or right to prevent the pole from falling over.
- State space: Describes the four key variables (position, velocity, angle, angular velocity) of the cart-pole system.
- Action space: Discrete actions—either move the cart left or right.
- Reward: The agent earns 1 point for each step the pole remains balanced.
Python import gym import numpy as np import warnings # Suppress specific deprecation warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=DeprecationWarning) # Load the environment with render mode specified env = gym.make('CartPole-v1', render_mode="human") # Initialize the environment to get the initial state state = env.reset() # Print the state space and action space print("State space:", env.observation_space) print("Action space:", env.action_space) # Run a few steps in the environment with random actions for _ in range(10): env.render() # Render the environment for visualization action = env.action_space.sample() # Take a random action # Take a step in the environment step_result = env.step(action) # Check the number of values returned and unpack accordingly if len(step_result) == 4: next_state, reward, done, info = step_result terminated = False else: next_state, reward, done, truncated, info = step_result terminated = done or truncated print(f"Action: {action}, Reward: {reward}, Next State: {next_state}, Done: {done}, Info: {info}") if terminated: state = env.reset() # Reset the environment if the episode is finished env.close() # Close the environment when done Output:

Application of Reinforcement Learning
- Robotics: RL is used to automate tasks in structured environments such as manufacturing, where robots learn to optimize movements and improve efficiency.
- Game Playing: Advanced RL algorithms have been used to develop strategies for complex games like chess, Go, and video games, outperforming human players in many instances.
- Industrial Control: RL helps in real-time adjustments and optimization of industrial operations, such as refining processes in the oil and gas industry.
- Personalized Training Systems: RL enables the customization of instructional content based on an individual's learning patterns, improving engagement and effectiveness.
Advantages of Reinforcement Learning
- Solving Complex Problems: RL is capable of solving highly complex problems that cannot be addressed by conventional techniques.
- Error Correction: The model continuously learns from its environment and can correct errors that occur during the training process.
- Direct Interaction with the Environment: RL agents learn from real-time interactions with their environment, allowing adaptive learning.
- Handling Non-Deterministic Environments: RL is effective in environments where outcomes are uncertain or change over time, making it highly useful for real-world applications.
Disadvantages of Reinforcement Learning
- Not Suitable for Simple Problems: RL is often an overkill for straightforward tasks where simpler algorithms would be more efficient.
- High Computational Requirements: Training RL models requires a significant amount of data and computational power, making it resource-intensive.
- Dependency on Reward Function: The effectiveness of RL depends heavily on the design of the reward function. Poorly designed rewards can lead to suboptimal or undesired behaviors.
- Difficulty in Debugging and Interpretation: Understanding why an RL agent makes certain decisions can be challenging, making debugging and troubleshooting complex
Reinforcement Learning is a powerful technique for decision-making and optimization in dynamic environments. However, the complexity of RL necessitates careful design of reward functions and substantial computational resources. By understanding its principles and applications, RL can be leveraged to solve intricate real-world problems and drive advancements across various industries.
Similar Reads
Artificial Intelligence Tutorial | AI Tutorial Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines which helps in allowing them to think and act like humans. It involves creating algorithms and systems that can perform tasks which requiring human abilities such as visual perception, speech recognition, decisio
5 min read
What is Artificial Intelligence(AI)? Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the technology that allows machines and computers to replicate human intelligence. It enables systems to perform tasks that require human-like decision-making, such as learning from data, identifying patterns, making informed choices and solving complex problem
13 min read
History of AI The term Artificial Intelligence (AI) is already widely used in everything from smartphones to self-driving cars. AI has come a long way from science fiction stories to practical uses. Yet What is artificial intelligence and how did it go from being an idea in science fiction to a technology that re
7 min read
Types of AI
Agents in AI An AI agent is a software program that can interact with its surroundings, gather information, and use that information to complete tasks on its own to achieve goals set by humans.For instance, an AI agent on an online shopping platform can recommend products, answer customer questions, and process
9 min read
Problem Solving in AI
Search Algorithms in AIArtificial Intelligence is the study of building agents that act rationally. Most of the time, these agents perform some kind of search algorithm in the background in order to achieve their tasks. A search problem consists of: A State Space. Set of all possible states where you can be.A Start State.
10 min read
Uninformed Search Algorithms in AIUninformed search algorithms is also known as blind search algorithms, are a class of search algorithms that do not use any domain-specific knowledge about the problem being solved. Uninformed search algorithms rely on the information provided in the problem definition, such as the initial state, ac
8 min read
Informed Search Algorithms in Artificial IntelligenceInformed search algorithms, also known as heuristic search algorithms, are an essential component of Artificial Intelligence (AI). These algorithms use domain-specific knowledge to improve the efficiency of the search process, leading to faster and more optimal solutions compared to uninformed searc
10 min read
Local Search Algorithm in Artificial IntelligenceLocal search algorithms are essential tools in artificial intelligence and optimization, employed to find high-quality solutions in large and complex problem spaces. Key algorithms include Hill-Climbing Search, Simulated Annealing, Local Beam Search, Genetic Algorithms, and Tabu Search. Each of thes
4 min read
Adversarial Search Algorithms in Artificial Intelligence (AI)Adversarial search algorithms are the backbone of strategic decision-making in artificial intelligence, it enables the agents to navigate competitive scenarios effectively. This article offers concise yet comprehensive advantages of these algorithms from their foundational principles to practical ap
15+ min read
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) in Artificial IntelligenceA Constraint Satisfaction Problem is a mathematical problem where the solution must meet a number of constraints. In CSP the objective is to assign values to variables such that all the constraints are satisfied. Many AI applications use CSPs to solve decision-making problems that involve managing o
10 min read
Knowledge, Reasoning and Planning in AI
How do knowledge representation and reasoning techniques support intelligent systems?In artificial intelligence (AI), knowledge representation and reasoning (KR&R) stands as a fundamental pillar, crucial for enabling machines to emulate complex decision-making and problem-solving abilities akin to those of humans. This article explores the intricate relationship between KR&R
5 min read
First-Order Logic in Artificial IntelligenceFirst-order logic (FOL) is also known as predicate logic. It is a foundational framework used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. In artificial intelligence (AI), FOL is important for knowledge representation, automated reasoning, and NLP.FOL extends propositional logic by
3 min read
Types of Reasoning in Artificial IntelligenceIn today's tech-driven world, machines are being designed to mimic human intelligence and actions. One key aspect of this is reasoning, a logical process that enables machines to conclude, make predictions, and solve problems just like humans. Artificial Intelligence (AI) employs various types of re
6 min read
What is the Role of Planning in Artificial Intelligence?Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the future, playing a pivotal role in domains like intelligent robotics, self-driving cars, and smart cities. At the heart of AI systems’ ability to perform tasks autonomously is AI planning, which is critical in guiding AI systems to make informed decisions
7 min read
Representing Knowledge in an Uncertain Domain in AIArtificial Intelligence (AI) systems often operate in environments where uncertainty is a fundamental aspect. Representing and reasoning about knowledge in such uncertain domains is crucial for building robust and intelligent systems. This article explores the various methods and techniques used in
6 min read
Learning in AI
Supervised Machine LearningSupervised machine learning is a fundamental approach for machine learning and artificial intelligence. It involves training a model using labeled data, where each input comes with a corresponding correct output. The process is like a teacher guiding a student—hence the term "supervised" learning. I
12 min read
What is Unsupervised Learning?Unsupervised learning is a branch of machine learning that deals with unlabeled data. Unlike supervised learning, where the data is labeled with a specific category or outcome, unsupervised learning algorithms are tasked with finding patterns and relationships within the data without any prior knowl
8 min read
Semi-Supervised Learning in MLToday's Machine Learning algorithms can be broadly classified into three categories, Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. Casting Reinforced Learning aside, the primary two categories of Machine Learning problems are Supervised and Unsupervised Learning. The basic
4 min read
Reinforcement LearningReinforcement Learning (RL) is a branch of machine learning that focuses on how agents can learn to make decisions through trial and error to maximize cumulative rewards. RL allows machines to learn by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback based on their actions. This feedback comes
6 min read
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)In this article, we will learn a major type of machine learning model which is Self-Supervised Learning Algorithms. Usage of these algorithms has increased widely in the past times as the sizes of the model have increased up to billions of parameters and hence require a huge corpus of data to train
8 min read
Introduction to Deep LearningDeep Learning is transforming the way machines understand, learn and interact with complex data. Deep learning mimics neural networks of the human brain, it enables computers to autonomously uncover patterns and make informed decisions from vast amounts of unstructured data. How Deep Learning Works?
7 min read
Natural Language Processing (NLP) - OverviewNatural Language Processing (NLP) is a field that combines computer science, artificial intelligence and language studies. It helps computers understand, process and create human language in a way that makes sense and is useful. With the growing amount of text data from social media, websites and ot
9 min read
Computer Vision TutorialComputer Vision is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to interpret and extract information from images and videos, similar to human perception. It involves developing algorithms to process visual data and derive meaningful insights.Why Learn Computer Vision?High Demand i
8 min read
Artificial Intelligence in RoboticsArtificial Intelligence (AI) in robotics is one of the most groundbreaking technological advancements, revolutionizing how robots perform tasks. What was once a futuristic concept from space operas, the idea of "artificial intelligence robots" is now a reality, shaping industries globally. Unlike ea
10 min read
Generative AI