Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)
Last Updated : 13 Dec, 2023
In this article, we will learn a major type of machine learning model which is Self-Supervised Learning Algorithms. Usage of these algorithms has increased widely in the past times as the sizes of the model have increased up to billions of parameters and hence require a huge corpus of data to train the same.
What is Self-Supervised Learning?
Self-supervised learning is a deep learning methodology where a model is pre-trained using unlabelled data and the data labels are generated automatically, which are further used in subsequent iterations as ground truths. The fundamental idea for self-supervised learning is to create supervisory signals by making sense of the unlabeled data provided to it in an unsupervised fashion on the first iteration. Then, the model uses the high-confidence data labels among those generated to train the model in subsequent iterations like the supervised learning model via backpropagation. The only difference is, the data labels used as ground truths in every iteration are changed.
 Self-supervised learning
Self-supervised learningThere are some popular learning techniques other than Self-Supervised Learning Algorithms as well:
Supervised Learning
In these types of machine learning algorithms, we have labeled data that we have some independent features and a target variable for the same which determines from which class it belongs.
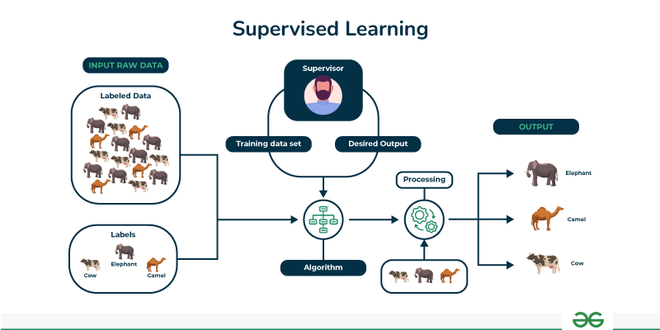 Supervised learning
Supervised learningUnsupervised Learning
In these algorithms, we have raw data without labels. The main task of the machine learning model is to identify the patterns present in the data at hand. This technique is also sometimes used to label the data because this technique is fast and efficient in terms of time and money.
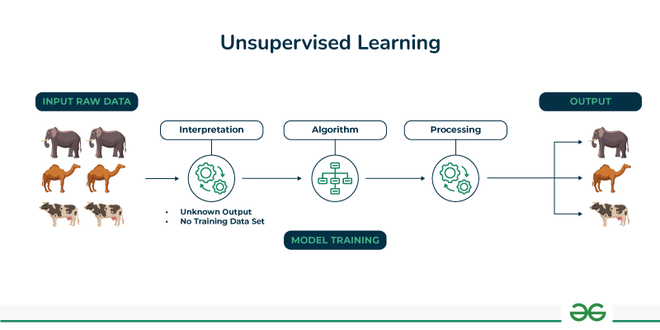 Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learningSemi-Supervised Learning
Semi-Supervised or Semi Unsupervised? You are right this is a mixture of supervised and unsupervised machine-learning algorithms. We have a subset of the dataset labeled and its complement is unlabeled.
 Semi-Supervised learning
Semi-Supervised learningReinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is the science of decision-making. It is about learning the optimal behavior in an environment to obtain the maximum reward. In RL, the data is accumulated from machine learning systems that use a trial-and-error method. Data is not part of the input that we would find in supervised or unsupervised machine learning.
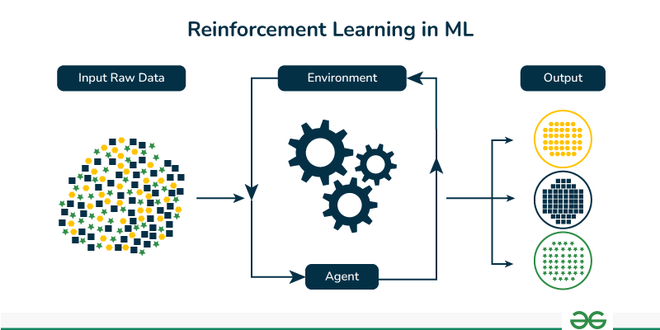 Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learningHow to train a Self-Supervised Learning Model in ML
- Select a property of the data to predict: To predict the next word in a sentence, the orientation of an object in an image, or the speaker of an audio clip.
- Define a loss function: The loss function measures the model's performance on the task of predicting the property of the data. It should be designed to encourage the model to learn useful features and representations of the data that are relevant to the task.
- Train the model: The model is trained on a large dataset by minimizing the loss function. This is typically done using an optimization algorithm, such as stochastic gradient descent (SGD) or Adam.
- Fine-tune the model: Once the model has been trained, it can be fine-tuned on a specific task by adding a few labeled examples and fine-tuning the model's weights using supervised learning techniques. This allows the model to learn task-specific features and further improve its performance on the target task.
Application of SSL in Computer Vision
Image and video recognition: Self-supervised learning has been used to improve the performance of image and video recognition tasks, such as object recognition, image classification, and video classification. For example, a self-supervised learning model might be trained to predict the location of an object in an image given the surrounding pixels to classify a video as depicting a particular action.
Application of SSL in Natural Language Processing
- Language understanding: Self-supervised learning has been used to improve the performance of natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as machine translation, language modeling, and text classification. For example, a self-supervised learning model might be trained to predict the next word in a sentence given the previous words, or to classify a sentence as positive or negative.
- Speech recognition: Self-supervised learning has been used to improve the performance of speech recognition tasks, such as transcribing audio recordings into text. For example, a self-supervised learning model might be trained to predict the speaker of an audio clip based on the characteristics of their voice.
Self-Supervised Learning Techniques
- Pretext tasks: Pretext tasks are auxiliary tasks designed to solve using the inherent structure of the data, but are also related to the main task. For example, the model might be trained on a pretext task of predicting the rotation of an image, with the goal of improving performance on the main task of image classification.
- Contrastive learning: Contrastive Learning is a self-supervised learning technique that involves training a model to distinguish between a noisy version of the data to a clean version. The model is trained to distinguish between the two, with the goal of learning a robust representation of noise.
Advantages of Self-Supervised Learning
- Reduced Reliance on Labeled Data: One of the main benefits of self-supervised learning is that it allows a model to learn useful features and representations of the data without the need for large amounts of labeled data. This can be particularly useful in situations where it is expensive or time-consuming to obtain labeled data, or where there is a limited amount of labeled data available.
- Improved Generalization: Self-supervised learning can improve the generalization performance of a model, meaning that it is able to make more accurate predictions on unseen data. This is because self-supervised learning allows a model to learn from the inherent structure of the data, rather than just memorizing specific examples.
- Transfer Learning: Self-supervised learning can be useful for transfer learning, which involves using a model trained on one task to improve performance on a related task. By learning useful features and representations of the data through self-supervised learning, a model can be more easily adapted to new tasks and environments.
- Scalability: Self-supervised learning can be more scalable than supervised learning, as it allows a model to learn from a larger dataset without the need for human annotation. This can be particularly useful in situations where the amount of data is too large to be labeled by humans.
Limitations of Self-Supervised Learning
- Quality of supervision signal: One of the main limitations of self-supervised learning is that the quality of the supervision signal can be lower than in supervised learning. This is because the supervision signal is derived from the data itself, rather than being explicitly provided by a human annotator. As a result, the supervision signal may be noisy or incomplete, which can lead to lower performance on the task.
- Limited to certain types of tasks: Self-supervised learning may not be as effective for tasks where the data is more complex or unstructured.
- The complexity of training: Some self-supervised learning techniques can be more complex to implement and train than supervised learning techniques. For example, contrastive learning and unsupervised representation learning can be more challenging to implement and tune than supervised learning methods.
Differences between Supervised, Unsupervised, and Self-Supervised Learning
Now let's look at the differences between the three most common machine learning algorithms categories in brief.
Supervised | Unsupervised | Self-Supervised |
| Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where the model is trained on labeled data, meaning that the input data is accompanied by its corresponding correct output. | Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where the model is trained on unlabeled data, meaning that the input data does not have a corresponding correct output. | Self-supervised learning is a type of machine learning that falls between supervised and unsupervised learning. It is a form of unsupervised learning where the model is trained on unlabeled data, but the goal is to learn a specific task or representation of the data that can be used in a downstream supervised learning task. |
| The goal of supervised learning is to learn a mapping from input data to the correct output. | The goal of unsupervised learning is to learn patterns or structures in the input data without the guidance of a labeled output. | In self-supervised learning, the model learns to predict certain properties of the input data, such as a missing piece or its rotation angle. This learned representation can then be used to initialize a supervised learning model, providing a good starting point for fine-tuning on a smaller labeled dataset. |
| Common examples of supervised learning include image classification, object detection, and Natural Language Processing tasks. | Common examples of unsupervised learning include clustering, dimensionality reduction, and anomaly detection. | A common example of self-supervised learning is the task of image representation learning, sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. |
Overall, self-supervised learning has the potential to improve the performance and efficiency of machine learning systems greatly and is an active area in the research field.
Similar Reads
Artificial Intelligence Tutorial | AI Tutorial Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines which helps in allowing them to think and act like humans. It involves creating algorithms and systems that can perform tasks which requiring human abilities such as visual perception, speech recognition, decisio
5 min read
What is Artificial Intelligence(AI)? Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the technology that allows machines and computers to replicate human intelligence. It enables systems to perform tasks that require human-like decision-making, such as learning from data, identifying patterns, making informed choices and solving complex problem
13 min read
History of AI The term Artificial Intelligence (AI) is already widely used in everything from smartphones to self-driving cars. AI has come a long way from science fiction stories to practical uses. Yet What is artificial intelligence and how did it go from being an idea in science fiction to a technology that re
7 min read
Types of AI
Agents in AI An AI agent is a software program that can interact with its surroundings, gather information, and use that information to complete tasks on its own to achieve goals set by humans.For instance, an AI agent on an online shopping platform can recommend products, answer customer questions, and process
9 min read
Problem Solving in AI
Search Algorithms in AIArtificial Intelligence is the study of building agents that act rationally. Most of the time, these agents perform some kind of search algorithm in the background in order to achieve their tasks. A search problem consists of: A State Space. Set of all possible states where you can be.A Start State.
10 min read
Uninformed Search Algorithms in AIUninformed search algorithms is also known as blind search algorithms, are a class of search algorithms that do not use any domain-specific knowledge about the problem being solved. Uninformed search algorithms rely on the information provided in the problem definition, such as the initial state, ac
8 min read
Informed Search Algorithms in Artificial IntelligenceInformed search algorithms, also known as heuristic search algorithms, are an essential component of Artificial Intelligence (AI). These algorithms use domain-specific knowledge to improve the efficiency of the search process, leading to faster and more optimal solutions compared to uninformed searc
10 min read
Local Search Algorithm in Artificial IntelligenceLocal search algorithms are essential tools in artificial intelligence and optimization, employed to find high-quality solutions in large and complex problem spaces. Key algorithms include Hill-Climbing Search, Simulated Annealing, Local Beam Search, Genetic Algorithms, and Tabu Search. Each of thes
4 min read
Adversarial Search Algorithms in Artificial Intelligence (AI)Adversarial search algorithms are the backbone of strategic decision-making in artificial intelligence, it enables the agents to navigate competitive scenarios effectively. This article offers concise yet comprehensive advantages of these algorithms from their foundational principles to practical ap
15+ min read
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) in Artificial IntelligenceA Constraint Satisfaction Problem is a mathematical problem where the solution must meet a number of constraints. In CSP the objective is to assign values to variables such that all the constraints are satisfied. Many AI applications use CSPs to solve decision-making problems that involve managing o
10 min read
Knowledge, Reasoning and Planning in AI
How do knowledge representation and reasoning techniques support intelligent systems?In artificial intelligence (AI), knowledge representation and reasoning (KR&R) stands as a fundamental pillar, crucial for enabling machines to emulate complex decision-making and problem-solving abilities akin to those of humans. This article explores the intricate relationship between KR&R
5 min read
First-Order Logic in Artificial IntelligenceFirst-order logic (FOL) is also known as predicate logic. It is a foundational framework used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. In artificial intelligence (AI), FOL is important for knowledge representation, automated reasoning, and NLP.FOL extends propositional logic by
3 min read
Types of Reasoning in Artificial IntelligenceIn today's tech-driven world, machines are being designed to mimic human intelligence and actions. One key aspect of this is reasoning, a logical process that enables machines to conclude, make predictions, and solve problems just like humans. Artificial Intelligence (AI) employs various types of re
6 min read
What is the Role of Planning in Artificial Intelligence?Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the future, playing a pivotal role in domains like intelligent robotics, self-driving cars, and smart cities. At the heart of AI systems’ ability to perform tasks autonomously is AI planning, which is critical in guiding AI systems to make informed decisions
7 min read
Representing Knowledge in an Uncertain Domain in AIArtificial Intelligence (AI) systems often operate in environments where uncertainty is a fundamental aspect. Representing and reasoning about knowledge in such uncertain domains is crucial for building robust and intelligent systems. This article explores the various methods and techniques used in
6 min read
Learning in AI
Supervised Machine LearningSupervised machine learning is a fundamental approach for machine learning and artificial intelligence. It involves training a model using labeled data, where each input comes with a corresponding correct output. The process is like a teacher guiding a student—hence the term "supervised" learning. I
12 min read
What is Unsupervised Learning?Unsupervised learning is a branch of machine learning that deals with unlabeled data. Unlike supervised learning, where the data is labeled with a specific category or outcome, unsupervised learning algorithms are tasked with finding patterns and relationships within the data without any prior knowl
8 min read
Semi-Supervised Learning in MLToday's Machine Learning algorithms can be broadly classified into three categories, Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. Casting Reinforced Learning aside, the primary two categories of Machine Learning problems are Supervised and Unsupervised Learning. The basic
4 min read
Reinforcement LearningReinforcement Learning (RL) is a branch of machine learning that focuses on how agents can learn to make decisions through trial and error to maximize cumulative rewards. RL allows machines to learn by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback based on their actions. This feedback comes
6 min read
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL)In this article, we will learn a major type of machine learning model which is Self-Supervised Learning Algorithms. Usage of these algorithms has increased widely in the past times as the sizes of the model have increased up to billions of parameters and hence require a huge corpus of data to train
8 min read
Introduction to Deep LearningDeep Learning is transforming the way machines understand, learn and interact with complex data. Deep learning mimics neural networks of the human brain, it enables computers to autonomously uncover patterns and make informed decisions from vast amounts of unstructured data. How Deep Learning Works?
7 min read
Natural Language Processing (NLP) - OverviewNatural Language Processing (NLP) is a field that combines computer science, artificial intelligence and language studies. It helps computers understand, process and create human language in a way that makes sense and is useful. With the growing amount of text data from social media, websites and ot
9 min read
Computer Vision TutorialComputer Vision is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to interpret and extract information from images and videos, similar to human perception. It involves developing algorithms to process visual data and derive meaningful insights.Why Learn Computer Vision?High Demand i
8 min read
Artificial Intelligence in RoboticsArtificial Intelligence (AI) in robotics is one of the most groundbreaking technological advancements, revolutionizing how robots perform tasks. What was once a futuristic concept from space operas, the idea of "artificial intelligence robots" is now a reality, shaping industries globally. Unlike ea
10 min read
Generative AI