Loops in R (for, while, repeat)
Last Updated : 07 Jun, 2025
Loops are fundamental constructs in programming that allow repetitive execution of code blocks. In R loops are primarily used for iterating over elements of a vector, performing calculations and automating repetitive tasks. In this article we will learn about different types of loops in R.
1. For Loop in R
The for loop is used when we know the exact number of iterations required. It iterates over a sequence such as a vector, list or numeric range.
Syntax:
for (value in sequence)
{
statement
}
For Loop Flow Diagram:

Example 1: Program to display numbers from 1 to 5 using for loop.
Here, for loop is iterated over a sequence having numbers from 1 to 5. In each iteration each item of the sequence is displayed.
R for (val in 1: 5) { print(val) } Output:
[1] 1
[1] 2
[1] 3
[1] 4
[1] 5
Example 2: Program to display days of the week.
In this program initially all the days (strings) of the week are assigned to the vector week. Then for loop is used to iterate over each string in a week. In each iteration, each day of the week is displayed.
R week <- c('Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday') for (day in week) { print(day) } Output:
[1] "Sunday"
[1] "Monday"
[1] "Tuesday"
[1] "Wednesday"
[1] "Thursday"
[1] "Friday"
[1] "Saturday"
Example 3: For-Loop on a List
In this example we have a list of five numbers in this case. The seq_along() function is used to create a list of indices to loop through and double brackets [[]] are used to retrieve the current element during each loop iteration. We print a message showing the element we're dealing with inside the loop followed by the value of that element.
R my_list <- list(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) for (i in seq_along(my_list)) { current_element <- my_list[[i]] print(paste("The current element is:", current_element)) } Output
[1] "The current element is: 1"
[1] "The current element is: 2"
[1] "The current element is: 3"
[1] "The current element is: 4"
[1] "The current element is: 5"
Example 4: For-Loop on a Matrix
In this the integers in a 3x3 matrix range from 1 to 9. We cycle through the matrix's rows and columns using two for-loops, each of which uses the [i, j] notation to retrieve the current member. We output a message showing the element we're dealing with inside the loop, followed by the value of that element.
R my_matrix <- matrix(1:9, nrow = 3) for (i in seq_len(nrow(my_matrix))) { for (j in seq_len(ncol(my_matrix))) { current_element <- my_matrix[i, j] print(paste("The current element is:", current_element)) } } Output
[1] "The current element is: 1"
[1] "The current element is: 4"
[1] "The current element is: 7"
[1] "The current element is: 2"
[1] "The current element is: 5"
[1] "The current element is: 8"
[1] "The current element is: 3"
[1] "The current element is: 6"
[1] "The current element is: 9"
Example 5: For-Loop on a Data Frame
In this example we have a data frame with some sample information on the names, ages and genders of persons. The data frame's rows are iterated using a for-loop and each time the loop iterates, the current row is accessed using the [i] notation. We print a message within the loop stating the row we are presently working with, followed by the contents of that row.
R my_dataframe <- data.frame( Name = c("Joy", "Juliya", "Boby", "Marry"), Age = c(40, 25, 19, 55), Gender = c("M", "F", "M", "F") ) for (i in seq_len(nrow(my_dataframe))) { current_row <- my_dataframe[i, ] print(paste("The current row is:", toString(current_row))) } Output
[1] "The current row is: Joy, 40, M"
[1] "The current row is: Juliya, 25, F"
[1] "The current row is: Boby, 19, M"
[1] "The current row is: Marry, 55, F"
2. While Loop in R
The while loop runs as long as a specified condition holds TRUE. It is useful when the number of iterations is unknown beforehand.
Syntax:
while ( condition )
{
statement
}
While loop Flow Diagram:
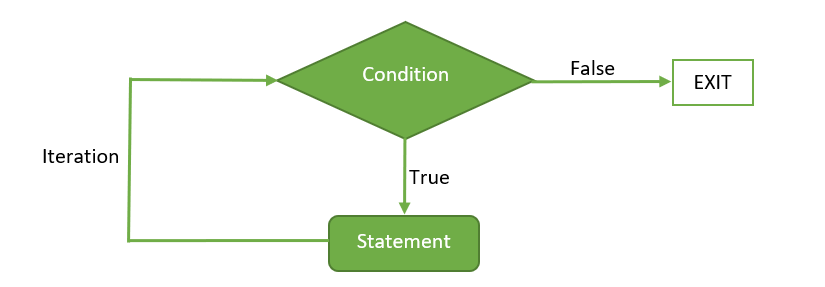
Example 1: Program to display numbers from 1 to 5 using a while loop in R.
In this example initially the variable value is initialized to 1. In each iteration of the while loop the condition is checked and the value of val is displayed and then it is incremented until it becomes 5 and the condition becomes false the loop is terminated.
R val = 1 while (val <= 5) { print(val) val = val + 1 } Output:
[1] 1
[1] 2
[1] 3
[1] 4
[1] 5
Example 2: Program to calculate the factorial of a number.
In this example at first the variable "n" is assigned to 5 whose factorial is going to be calculated, then variable i and factorial are assigned to 1, i will be used for iterating over the loop and factorial will be used for calculating the factorial. In each iteration of the loop, the condition is checked i.e. i should be less than or equal to 5 and after that factorial is multiplied with the value of i, then i is incremented. When i becomes 5 the loop is terminated and the factorial of 5 i.e. 120 is displayed beyond the scope of the loop.
R n <- 5 factorial <- 1 i <- 1 while (i <= n) { factorial = factorial * i i = i + 1 } print(factorial) Output:
[1] 120
3. Repeat Loop in R
The repeat loop executes indefinitely until explicitly stopped using the break statement. To terminate the repeat loop we use a jump statement that is the break keyword.
Syntax:
repeat
{
statement
if( condition )
{
break
}
}
Repeat loop Flow Diagram:

Example 1: Display numbers from 1 to 5 using a repeat loop in R.
Here the variable val is initialized to 1, then in each iteration of the repeat loop the value of val is displayed and then it is incremented until it becomes greater than 5. If the value of val becomes greater than 5 then a break statement is used to terminate the loop.
R val = 1 repeat { print(val) val = val + 1 if(val > 5) { break } } Output:
[1] 1
[1] 2
[1] 3
[1] 4
[1] 5
Example 2: Display a statement five times.
Here initially the variable i is initialized with 0 then in each iteration of the repeat loop after printing "Geeks 4 geeks!" the value of i is incremented till it becomes 5 and the condition in the if statement becomes true then the break statement is executed to terminate the repeat loop.
R i <- 0 repeat { print("Geeks 4 geeks!") i = i + 1 if (i == 5) { break } } Output:
[1] "Geeks 4 geeks!"
[1] "Geeks 4 geeks!"
[1] "Geeks 4 geeks!"
[1] "Geeks 4 geeks!"
[1] "Geeks 4 geeks!"
We explored three types of loops in R which are for, while and repeat with practical examples. Each loop serves a unique purpose allowing efficient iteration and automation of repetitive tasks.
Similar Reads
For loop in R For loop in R Programming Language is useful to iterate over the elements of a list, data frame, vector, matrix, or any other object. It means the for loop can be used to execute a group of statements repeatedly depending upon the number of elements in the object. It is an entry-controlled loop, in
5 min read
R - Repeat loop Repeat loop in R is used to iterate over a block of code multiple number of times. And also it executes the same code again and again until a break statement is found. Repeat loop, unlike other loops, doesn't use a condition to exit the loop instead it looks for a break statement that executes if a
2 min read
How To Use A For Loop In R For loops in R is a fundamental programming construct that allows you to repeat a block of code a specified number of times or for a given range of elements. They are essential for automating repetitive tasks, manipulating data, and performing various computational operations. The basic syntax of a
3 min read
For loop in Programming For loop is one of the most widely used loops in Programming and is used to execute a set of statements repetitively. We can use for loop to iterate over a sequence of elements, perform a set of tasks a fixed number of times. In this article, we will learn about the basics of For loop, its syntax al
11 min read
R - while loop While loop in R programming language is used when the exact number of iterations of a loop is not known beforehand. It executes the same code again and again until a stop condition is met. While loop checks for the condition to be true or false n+1 times rather than n times. This is because the whil
5 min read