How to Create a Shell Script in linux
Last Updated : 13 Mar, 2024
Shell is an interface of the operating system. It accepts commands from users and interprets them to the operating system. If you want to run a bunch of commands together, you can do so by creating a shell script. Shell scripts are very useful if you need to do a task routinely, like taking a backup. You can list those commands and execute them all with just a single script. Let's see how you can create a shell script and run it on Linux.
Creating a Shell Script
Login to your Linux machine and open the terminal, navigate to the folder where you want to store the shell script. Shell scripts end with the extension ".sh". Let's create our first shell script. Type in
touch script.sh
Now, this script file is not executable by default, we have to give the executable permission to this file. Type in
chmod +x script.sh
Now, we will add some commands to this shell script. Open this shell script with any text editor of your choice (command-line based or GUI based) and add some commands. We will use nano. Type in
nano script.sh
Add the following commands to test this shell script
echo This is my first shell script touch testfile ls echo End of my shell script
Save the changes, and run the shell script by typing in
./script.sh
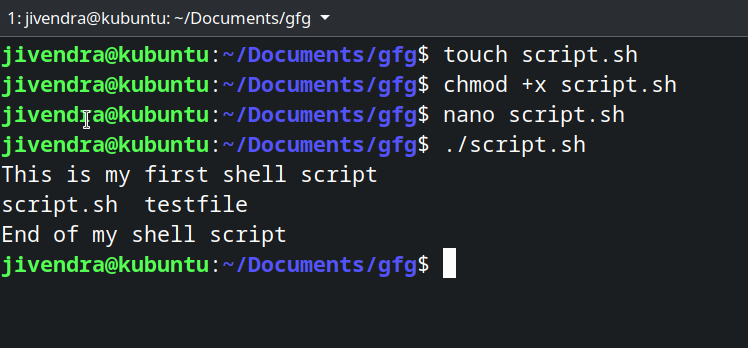 Screenshot of above steps
Screenshot of above steps You can see, it executed all the specified commands.
Comments in the shell script
Any line which starts with "#" in the shell script is treated as a comment and is ignored by the shell during execution, except the shebang line, which we will see later in this article. Let's see an example. A shell script is created with the following content.
# This is a comment echo Testing comments in shell script
 Comments in Shell Script
Comments in Shell Script You can see, the comment gets ignored.
Variables in Shell Script
Yes, Shell scripts support the use of variables, and we need not define a variable's type during its declaration. There are two types of variables:
- System Defined variables
- User-Defined Variables.
System-defined variables, also called environment variables, are generally Capitalised. You can view all the current environment variables using the printenv command. User-Defined variables are set by the user, and they exist only during script execution. You can define a variable by simply typing its name and assigning a value with = sign and access a variable by adding a $ before the variable name. Variables are demonstrated in the following example script.
# Accessing an Environment Variable echo $USER # Creating and accessing User defined Variable variable_name="Geeksforgeeks" echo $variable_name
 Variables in Shell Script
Variables in Shell ScriptDefining the Shell Script interpreter
There are many Shells available in Linux, such as The bourne shell(sh), The Korn Shell(ksh), and GNU Bourne-Again Shell(bash). Scripts written for the sh shell are called shell scripts, and they can be interpreted by both, the ksh and bash shells. ksh and Bash are improved versions of the original sh shell and they have more features than sh. Bash is generally the default shell in most of the Linux Distributions and scripts written specifically for bash shell are called bash scripts.
You can specify which shell the script will use, even if the script is executed from another shell terminal. To do this, add "#!" on top of the script file, followed by the absolute path of the shell of choice. To specify bash as an interpreter, Add the following line on top of the shell script.
#!/bin/bash
This line is called the shebang line.
Note: This will only work if bash is installed on your system.
Comparison Operators
You can compare two variables in shell scripting. We do these comparisons to make decisions, we will see how to do that later in this article, but before that, here is a list of some comparison operators.
Integer comparison
| Operator | Description |
|---|
| -eq | is equal to |
| -ne | is not equal to |
| -gt | is greater than |
| -ge | is greater than or equal to |
| -lt | is less than |
| -le | is less than or equal to |
String Comparison
| Operator | Description |
|---|
| == | is equal to |
| != | is not equal to |
| \< | is less than, in ASCII alphabetical order |
| \> | is greater than, in ASCII alphabetical order |
We add a \ before < and > because they need to be escaped when typed in the [ ] construct. Now, let's see where these are used.
Conditional statements
Conditional statements are used to execute a block of code only when certain conditions are met. Shell scripts support the use of conditional statements. We use comparison operators to check the conditions. Let's see a few conditional statements.
If statement
It checks the condition, and if it is conditioned true, it executes the commands.
Syntax
if [ condition ] then #statements fi
Let's see an example.
#!/bin/sh x=10 y=11 if [ $x -ne $y ] then echo "Not equal" fi
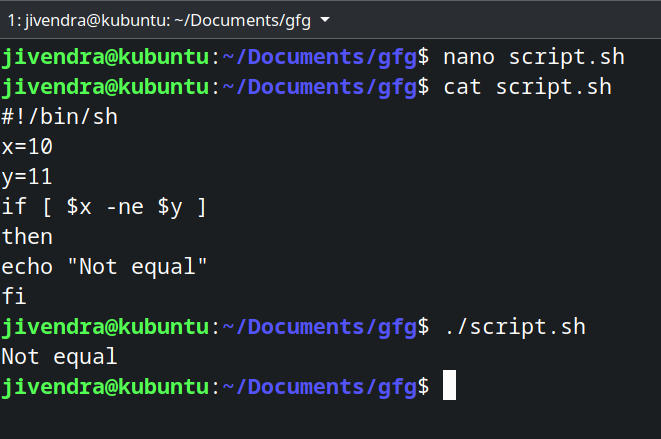 .if statement
.if statementIf-else statement
In an if-else statement, you can specify a set of commands to run if the condition is not met.
Syntax
if [ condition ] then #set of statements if the condition is true else #set of statements if the condition is false fi
Let's see an example
#!/Syntaxbin/sh x=10 y=10 if [ $x -ne $y ] then echo "Not equal" else echo "They are equal" fi
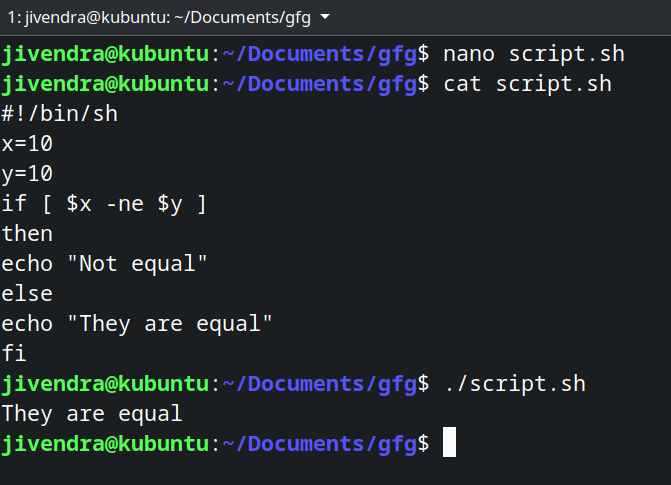 .if-else statement
.if-else statement There are other conditional statements, you can read about them here.
Note: Type a space after [ and before ] while specifying the condition to be checked otherwise you will get an error.
Loops
Using loops, you can a set of commands over and over again, until a certain condition is met. Let's see some of the loops.
While loop
It starts running the specified commands if the condition is true and repeats them until the condition is false.
Syntax
while [ condition ] do #set of statements done
Let's see an example.
#!/bin/sh x=2 while [ $x -lt 6 ] do echo $x x=`expr $x + 1` done
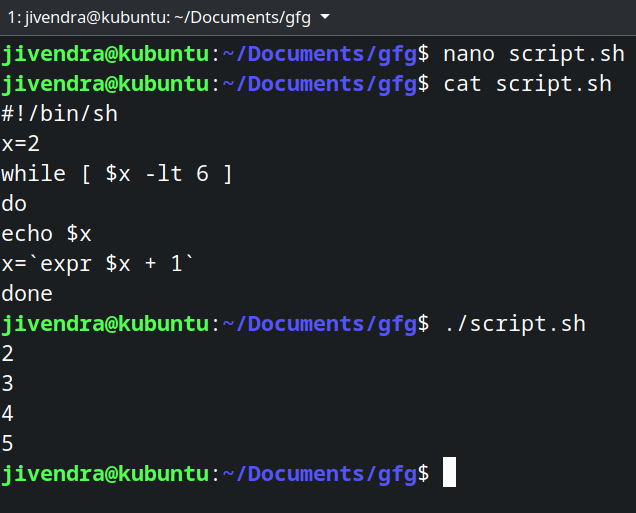 While loop
While loop We enclose an expr statement within ` ` when assigning it to a variable. You can read about expr command here.
For loop
In a for loop, the variable iterates over a list of values and ends when there are no more values to iterate over.
Syntax
for var in val1 val2 val3 do #statements done
Let's see an example.
#!/bin/sh for var in 2 4 5 8 do echo $var done
 for loop
for loop You can read about loops in detail here.
Positional Arguments
Positional arguments are the arguments or values which we pass to the shell script while executing the script. They are accessed by variables $0, $1, $2 ... $9. Beyond that, they are referenced by ${10}, ${11} and so on. $# stores the no of passed arguments and $0 stores the name of the script. Let's see an example to understand all this.
#!/bin/sh echo "No of arguments is $#" echo "Name of the script is $0" echo "First argument is $1" echo "Second argument is $2"
To pass the arguments, just type them in the terminal after the script name as shown below.
 Positional Arguments
Positional ArgumentsStoring the output of commands
You can store the output of commands inside a variable in a shell script. There are two ways to do so.
Syntax
#Syntax 1 var=$(a valid linux command) #Syntax 2 var2=`a valid linux command`
Let's see an example.
#!/bin/sh b=$(pwd) c=`pwd` echo $b echo $c d=$(ls /bin | grep bash) echo $d
 Storing the output of commands
Storing the output of commandsExit Codes of shell commands
Whenever a command ends and returns the control to the parent process, it returns exit codes between 0 and 255. Exit code 0 means the command was successful, and any other exit code means, the command was unsuccessful. You can view the exit code after running any command by accessing the $? variable. See the example below.
 exit code of shell command
exit code of shell command You can manually set an exit code for your shell script. This can be used with conditional statements to convey if the script's purpose was achieved or not.
Example
#!/bin/sh read x if [ $x -ne 10 ] then echo failed exit 1 else echo passed exit 0 fi
 exit code of shell command
exit code of shell command Similar Reads
Introduction to Linux Shell and Shell Scripting If we are using any major operating system, we are indirectly interacting with the shell. While running Ubuntu, Linux Mint, or any other Linux distribution, we are interacting with the shell by using the terminal. In this article we will discuss Linux shells and shell scripting so before understandi
8 min read
Introduction to Shell Scripting
Basic Shell Commands in Linux
Basic Shell Commands in Linux: Complete ListAnyone using Linux should become an expert in the essential shell commands, as they form the backbone of working with the Linux terminal. These commands enable you to navigate the system, manage files, handle processes, and configure settings effectively.The Linux shell serves as an interface for us
5 min read
Linux Directory StructureIn Linux, everything is treated as a file even if it is a normal file, a directory, or even a device such as a printer or keyboard. All the directories and files are stored under one root directory which is represented by a forward slash /. The Linux directory layout follows the Filesystem Hierarchy
6 min read
Input Output Redirection in LinuxIn Linux, whenever an individual runs a command, it can take input, give output, or do both. Redirection helps us redirect these input and output functionalities to the files or folders we want, and we can use special commands or characters to do so. For example, if we run the "date" command, it giv
4 min read
Variables and Data Types
Control Structures
Functions and Script Organization
Input And Output
Command-Line Arguments and Options
Error Handling and Debugging
Regular Expressions