In Linux, most of the operations are performed on files. And to handle these files Linux has directories also known as folders which are maintained in a tree-like structure. Though, these directories are also a type of file themselves. Linux has 3 types of files:
- Regular Files: It is the common file type in Linux. it includes files like - text files, images, binary files, etc. Such files can be created using the touch command. They consist of the majority of files in the Linux/UNIX system. The regular file contains ASCII or Human Readable text, executable program binaries, program data and much more.
- Directories: Windows call these directories as folders. These are the files that store the list of file names and the related information. The root directory(/) is the base of the system, /home/ is the default location for user's home directories, /bin for Essential User Binaries, /boot – Static Boot Files, etc. We could create new directories with mkdir command.
- Special Files: Represents a real physical device such as a printer which is used for IO operations. Device or special files are used for device Input/Output(I/O) on UNIX and Linux systems. You can see them in a file system like an ordinary directory or file.
In Unix systems, there are two types of special files for each device, i.e. character special files and block special files. For more details, read the article
Unix file system.
1. Files Listing
To perform Files listings or to list files and directories
ls command is used
$ls

All your files and directories in the current directory would be listed and each type of file would be displayed with a different color. Like in the output directories are displayed with dark blue color.
$ls -l
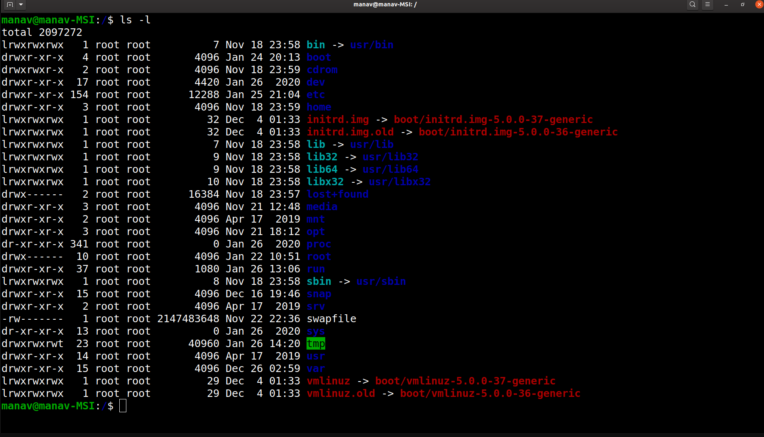
It returns the detailed listing of the files and directories in the current directory. The command gives os the owner of the file and even which file could be managed by which user or group and which user/group has the right to access or execute which file.
2. Creating Files
touch command can be used to create a new file. It will create and open a new blank file if the file with a filename does not exist. And in case the file already exists then the file will not be affected.
$touch filename

3. Displaying File Contents
cat command can be used to display the contents of a file. This command will display the contents of the 'filename' file. And if the output is very large then we could use more or less to fit the output on the terminal screen otherwise the content of the whole file is displayed at once.
$cat filename

4. Copying a File
cp command could be used to create the copy of a file. It will create the new file in destination with the same name and content as that of the file 'filename'.
$cp source/filename destination/

5. Moving a File
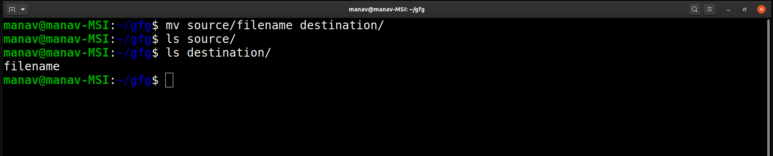
mv command could be used to move a file from source to destination. It will remove the file filename from the source folder and would be creating a file with the same name and content in the destination folder.
$mv source/filename destination/
6. Renaming a File
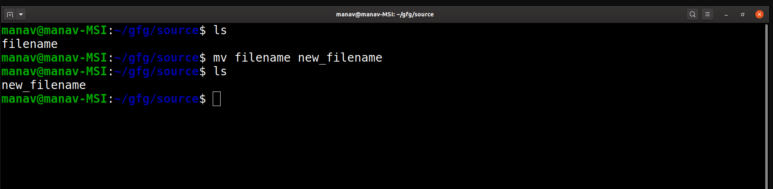
mv command could be used to rename a file. It will rename the filename to new_filename or in other words, it will remove the filename file and would be creating a new file with the new_filename with the same content and name as that of the filename file.
$mv filename new_filename
7. Deleting a File
rm command could be used to delete a file. It will remove the filename file from the directory.
$rm filename

Similar Reads
Kali Linux - File Management In Kali Linux, most of the operations are performed on files. And to handle these files Kali Linux has directories also known as folders which are maintained in a tree-like structure. Though, these directories are also a type of file themselves. Kali Linux has 3 basic types of files: Regular Files:
4 min read
How to Open a File in Linux​ In Linux, a file is a fundamental unit of storage, representing everything from documents and images to system logs and program data. Unlike traditional operating systems, Linux treats almost everything—files, directories, devices, and processes—as a file. Whether you're accessing a simple text docu
6 min read
How to Run a File in Linux The command line is one of the most powerful tools in Linux. It allows you to execute commands, manage files, and automate tasks all from a single terminal window. One common task you'll often need to do is run a file, whether it’s a script, a compiled program, or even a text file. In this article,
6 min read
Linux File System A file system is a structured method of storing and managing data—including files, directories, and metadata—on your machine. Think of it like a library. If thousands of books were scattered around, finding one would be hard. But in an organized structure, like labeled shelves, locating a book becom
12 min read
How to Rename File in Linux | rename Command Changing the names of files in Linux is something we often do, and the "rename" command is like a helpful friend for this job. This guide is like a journey to becoming really good at renaming files on Linux, showing you how handy and useful the "rename" command can be. Whether you're just starting o
8 min read