Layers in Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
Last Updated : 14 Jun, 2025
In Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), data flows from the input layer to the output layer through one or more hidden layers. Each layer consists of neurons that receive input, process it, and pass the output to the next layer. The layers work together to extract features, transform data, and make predictions.
An Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) consists of three primary types of layers:
- Input Layer
- Hidden Layers
- Output Layer
Each layer is composed of nodes (neurons) that are interconnected. The layers work together to process data through a series of transformations.
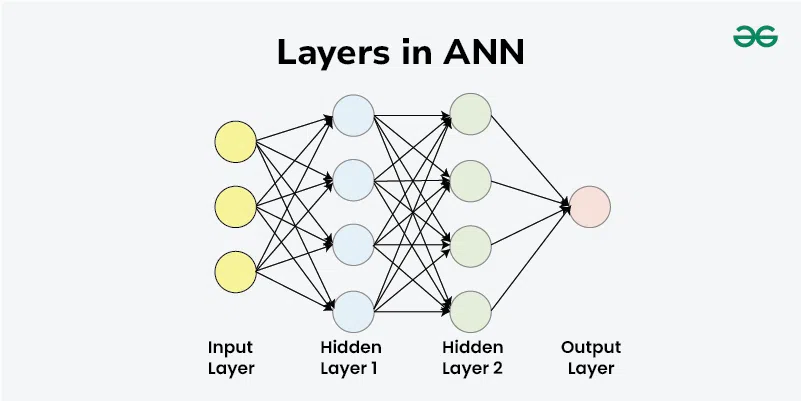 ANN Layers
ANN LayersBasic Layers in ANN
Input layer is the first layer in an ANN and is responsible for receiving the raw input data. This layer's neurons correspond to the features in the input data. For example, in image processing, each neuron might represent a pixel value. The input layer doesn't perform any computations but passes the data to the next layer.
Key Points:
- Role: Receives raw data.
- Function: Passes data to the hidden layers.
- Example: For an image, the input layer would have neurons for each pixel value.
 Input Layer in ANN
Input Layer in ANN2. Hidden Layers
Hidden Layers are the intermediate layers between the input and output layers. They perform most of the computations required by the network. Hidden layers can vary in number and size, depending on the complexity of the task.
Each hidden layer applies a set of weights and biases to the input data, followed by an activation function to introduce non-linearity.
3. Output Layer
Output Layer is the final layer in an ANN. It produces the output predictions. The number of neurons in this layer corresponds to the number of classes in a classification problem or the number of outputs in a regression problem.
The activation function used in the output layer depends on the type of problem:
- Softmax for multi-class classification
- Sigmoid for binary classification
- Linear for regression
For better understanding of the activation functions, Refer to the article - Activation functions in Neural Networks
Types of Hidden Layers in Artificial Neural Networks
Till now we have covered the basic layers: input, hidden, and output. Let’s now dive into the specific types of hidden layers.
1. Dense (Fully Connected) Layer
Dense (Fully Connected) Layer is the most common type of hidden layer in an ANN. Every neuron in a dense layer is connected to every neuron in the previous and subsequent layers. This layer performs a weighted sum of inputs and applies an activation function to introduce non-linearity. The activation function (like ReLU, Sigmoid, or Tanh) helps the network learn complex patterns.
- Role: Learns representations from input data.
- Function: Performs weighted sum and activation.
 Dense (Fully Connected Layer)
Dense (Fully Connected Layer)2. Convolutional Layer
Convolutional layers are used in Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image processing tasks. They apply convolution operations to the input, capturing spatial hierarchies in the data. Convolutional layers use filters to scan across the input and generate feature maps. This helps in detecting edges, textures, and other visual features.
- Role: Extracts spatial features from images.
- Function: Applies convolution using filters.
 Convolutional Layer
Convolutional Layer3. Recurrent Layer
Recurrent layers are used in Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sequence data like time series or natural language. They have connections that loop back, allowing information to persist across time steps. This makes them suitable for tasks where context and temporal dependencies are important.
- Role: Processes sequential data with temporal dependencies.
- Function: Maintains state across time steps.
 Recurrent Layer
Recurrent Layer4. Dropout Layer
Dropout layers are a regularization technique used to prevent overfitting. They randomly drop a fraction of the neurons during training, which forces the network to learn more robust features and reduces dependency on specific neurons. During training, each neuron is retained with a probability p.
- Role: Prevents overfitting.
- Function: Randomly drops neurons during training.
 Dropout Layer
Dropout Layer5. Pooling Layer
Pooling Layer is used to reduce the spatial dimensions of the data, thereby decreasing the computational load and controlling overfitting. Common types of pooling include Max Pooling and Average Pooling.
Use Cases: Dimensionality reduction in CNNs
 Pooling Layer
Pooling Layer6. Batch Normalization Layer
A Batch Normalization Layer normalizes the output of a previous activation layer by subtracting the batch mean and dividing by the batch standard deviation. This helps in accelerating the training process and improving the performance of the network.
Use Cases: Stabilizing and speeding up training
 Batch Normalization
Batch NormalizationUnderstanding the different types of layers in an ANN is essential for designing effective neural networks. Each layer has a specific role, from receiving input data to learning complex patterns and producing predictions. By combining these layers, we can build powerful models capable of solving a wide range of tasks.