Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration framework that was originally developed by Google. Container orchestration is automation. It can facilitate you to deploy the identical application across different environments like physical machines, virtual machines cloud environments, or perhaps hybrid deployment environments and makes it easier for the management, scaling, and networking of containers.
The original name for Kubernetes (originating from Greek) within Google was Project 7. Within the year 2014, Kubernetes was released for the first time and made open-sourced too after using it to run production workloads at scale for quite a decade. Also, pure open-source Kubernetes is free and might be downloaded from its repository on GitHub.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source platform that is developed for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It will orchestrates containers across a cluster of machines, ensuring high availability and efficient resource utilization. It is initally developed by Google, now Kubernetes is maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It facilitates with simplifying the management of complex microservices architectures, making it a cornerstone of modern cloud-native environments.
What are Kubernetes Containers?
Kubernetes is an container orcherstration platform by which you can automate the deployment of the application , scaling of the application by depending on the traffic. Containers are light in weight which can be portable very easily form one server to the another server very easily following makes ideal for running containerized applications in production.
- Load Balancing
- Service Discovery
- Self-healing
- Horizontal scaling
What Are Containers and Kubernetes and How Do They Work?
Containers are the lightweighted, portable packaged applications that contains all the dependencies it required to run that application providing the consistency across the environments. It simplifies the automation of deployment, scaling, and management of these containerized applications. It works by orchestrating containers across a cluster of machines, providing high availability and efficient resource utilization. Together, containers and Kubernetes enable seamless application development, deployment, and scaling in cloud-native environments.
Containerization Using Kubernetes
Containerization Using Kubernetes is the way of deploying you microservices or monolithic application using container orchestration tool kubernetes. Kubernetes is the best tool to deploy the application in the form of containers because it offers so many features like load balancing, self healing and scaling.
Containerize an application first you need to build the image of the application which can be done by using the docker and it contains all the dependencies required for the application to deploy into the production server after building the image know you need to push the image into the docker-hub registry from where other or kubernetes can pull the image.
Know you need to create the manifest file in the kubernetes to deploy your application in the form of container you can deploy the application by using which kind you want for examples you can use the Deployment.yaml, Demonset.yaml and so on.
Following is the sample manifest file of deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: my-app
image: my-app:latest
Using the kubectl apply command, you can deploy your application to Kubernetes after creating the deployment manifest. The resources required to execute your application, including as pods, kubernetes services, and deployments, will then be created by Kubernetes.
Container Technology
Containerization is OS-based virtualization that creates multiple virtual units in the userspace, known as Containers. Containers share the same host kernel but are isolated from each other through private namespaces and resource control mechanisms at the OS level. Container-based Virtualization provides a different level of abstraction in terms of virtualization and isolation when compared with hypervisors. Hypervisors use a lot of hardware which results in overhead in terms of virtualizing hardware and virtual device drivers. A full operating system (e.g -Linux, Windows) runs on top of this virtualized hardware in each virtual machine instance.
But in contrast, containers implement isolation of processes at the operating system level, thus avoiding such overhead. These containers run on top of the same shared operating system kernel of the underlying host machine and one or more processes can be run within each container. In containers you don’t have to pre-allocate any RAM, it is allocated dynamically during the creation of containers while in VMs you need to first pre-allocate the memory and then create the virtual machine. Containerization has better resource utilization compared to VMs and a short boot-up process. It is the next evolution in virtualization.
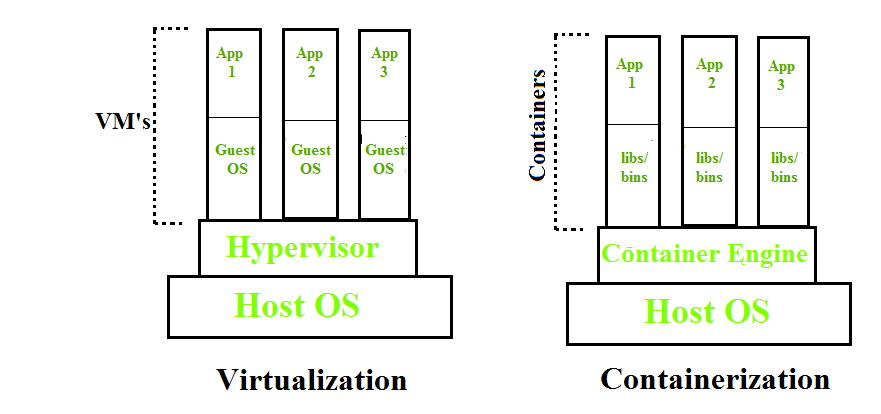
Containers can run virtually anywhere, greatly easy development and deployment: on Linux, Windows, and Mac operating systems; on virtual machines or bare metal, on a developer’s machine or in data centers on-premises; and of course, in the public cloud. Containers virtualize CPU, memory, storage, and network resources at the OS level, providing developers with a sandboxed view of the OS logically isolated from other applications. Docker is the most popular open-source container format available and is supported on Google Cloud Platform and by Google Kubernetes Engine.
What is Docker?
Docker is container management tool that helps in creating and managing the containers. It facilitates the developers to package an application with all its dependencies into a single bundle known as docker image and make it portable to any system that supports docker and facilitates of running the containerized applications seamlessly. It helps the developers for rapid development and prepare for quick production launch.
Container images
Image is an executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application. This image informs how a container should instantiate, determining which software components will run and how. Container is a virtual environment that bundles application code with all the dependencies required to run the application. The application runs quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.
Container registries, which are centralised repositories of container images, are where container images are kept. Docker Hub, Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR), and Google Container Registry (GCR) are a few well-known container registries.
Container Runtimes
Container runtimes are software components responsible for running containers and managing container lifecycle on a host system. They provide the necessary environment for container execution, including resource allocation and isolation. Popular container runtimes include Docker, containerd, CRI-O, and Podman, each offering unique features and optimizations. These runtimes are essential for deploying and managing containerized applications efficiently in various environments.
Kubernetes Pods
A pod is the smallest unit that exists in Kubernetes. It is similar to that of tokens in C or C++ language. A specific pod can have one or more applications. The nature of Pods is ephemeral this means that in any case if a pod fails then Kubernetes can and will automatically create a new replica/ duplicate of the said pod and continue the operation. The pods have the capacity to include one or more containers based on the requirement. The containers can even be Docker containers. The Pods in Kubernetes provide environmental dependencies which include persistent storage volumes which means it is permanent and is available to all pods in the said cluster and even configuration data that is required to run the container within the pod.
Differences Between Docker Images and Docker Containers
The following are the differences between Docker Images and Docker Containers:
| Aspect | Docker Images | Docker Containers |
|---|
| Definition | Blueprint for creating containers | Running instance of a Docker image |
|---|
| State | Static (read-only) | Dynamic (read-write) |
|---|
| Purpose | To provide a consistent environment for applications | To execute applications within a controlled environment |
|---|
| Creation | Built from Dockerfiles or other images | Started from Docker images using the docker run command |
|---|
| Persistence | Does not change; remains the same across instances | Changes and state persist only for the lifecycle of the container |
|---|
Architecture of Kubernetes
The architecture of Kubernetes includes a master node and one or more worker nodes. The below make in clear understanding of the kubernetes architecture.
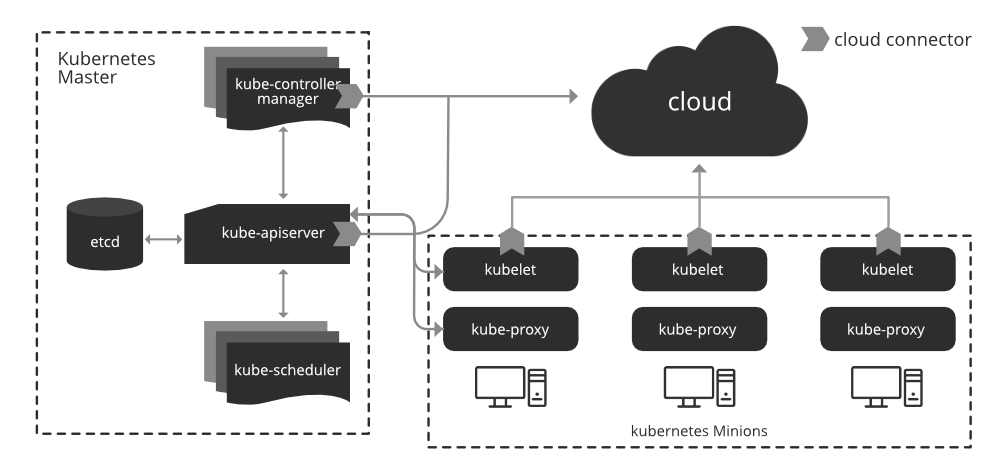
Understanding of Master Node
- Kube-apiserver: a frontend of the cluster that allows you to interact with the Kubernetes API and connects to the etcd database.
- Kube-scheduler: schedules pods on specific nodes supported labels, taints, and tolerations set for pods
- etcd: a database, stores all cluster data which includes job scheduling info, pod details, stage information, etc.
- Kube - controller - manager: manages the current state of the cluster
- cloud - controller - manager: interacts with outside cloud manager
Different optional add-ons: DNS, Dashboard, cluster-level resource monitoring, cluster-level logging
Understanding of Worker Node
We wouldn't get anywhere without Worker Nodes, though. These Worker Nodes are the Nodes where your applications operate. The Worker Nodes communicate back with the Master Node. Communication to a Worker Node is handled by the Kubelet Process.
- kubelet: passes requests to the container engine to ensure that pods are available
- Kube-proxy: runs on every node and uses iptables to provide an interface to connect to Kubernetes components
- container – runtime: take care of actually running container
- network agent: implements a software-defined networking solution
Containers of an application are tightly coupled together in a Pod. By definition, a Pod is the smallest unit that can be scheduled as deployment in Kubernetes. Once Pods have been deployed, and are running, the Kubelet process communicates with the Pods to check on state and health, and therefore the Kube-proxy routes any packets to the Pods from other resources that might be wanting to communicate with them.
Types of kubernetes Containers
The following are the some of the types of containers supported by the kubernetes:
- Docker containers: Docker is the mostly used container runtime and also it is the default container runtime until the kubernetes deprecated docker.
- Podman containers: Podman is the similar to the Docker which is used to run and manage the containers and It is available on Linux and Windows.
- CRI-O containers: CRI-O is a container runtime that is optimized for Kubernetes. It is the default container runtime for Red Hat OpenShift.
- Containerd containers: Containerd in simple terms is a container runtime that is, Containerd is a software responsible for running and managing containers on a host system.
Along with LXC and rkt, Kubernetes also supports various container runtimes. These container runtimes are not as popular, though, as the ones mentioned above.
How to Install Kubernetes? A Step-By-Step Guide
In this section, we will learn how to install Kubernetes on the Linux platform. So, follow the given steps for installing the Kubernetes:
Step 1: First of all, we have to update our apt-get repository.
sudo apt-get update

Step 2: Install apt transport HTTPS. This is basically used to make repositories while HTTPS.
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
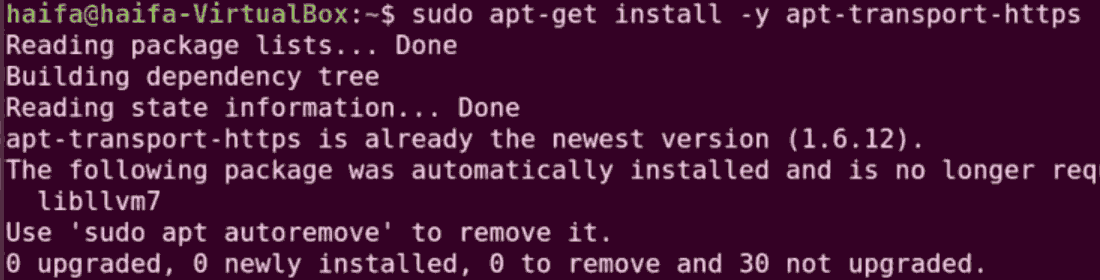
Step 3: Install the docker dependency
sudo apt install docker.io

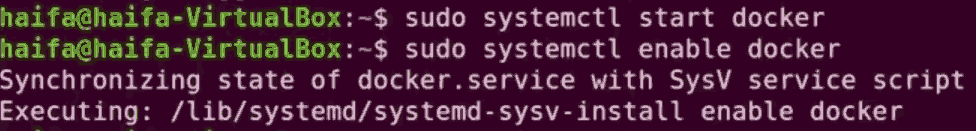
Step 4: After installing the docker we have to start and enable the docker.
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
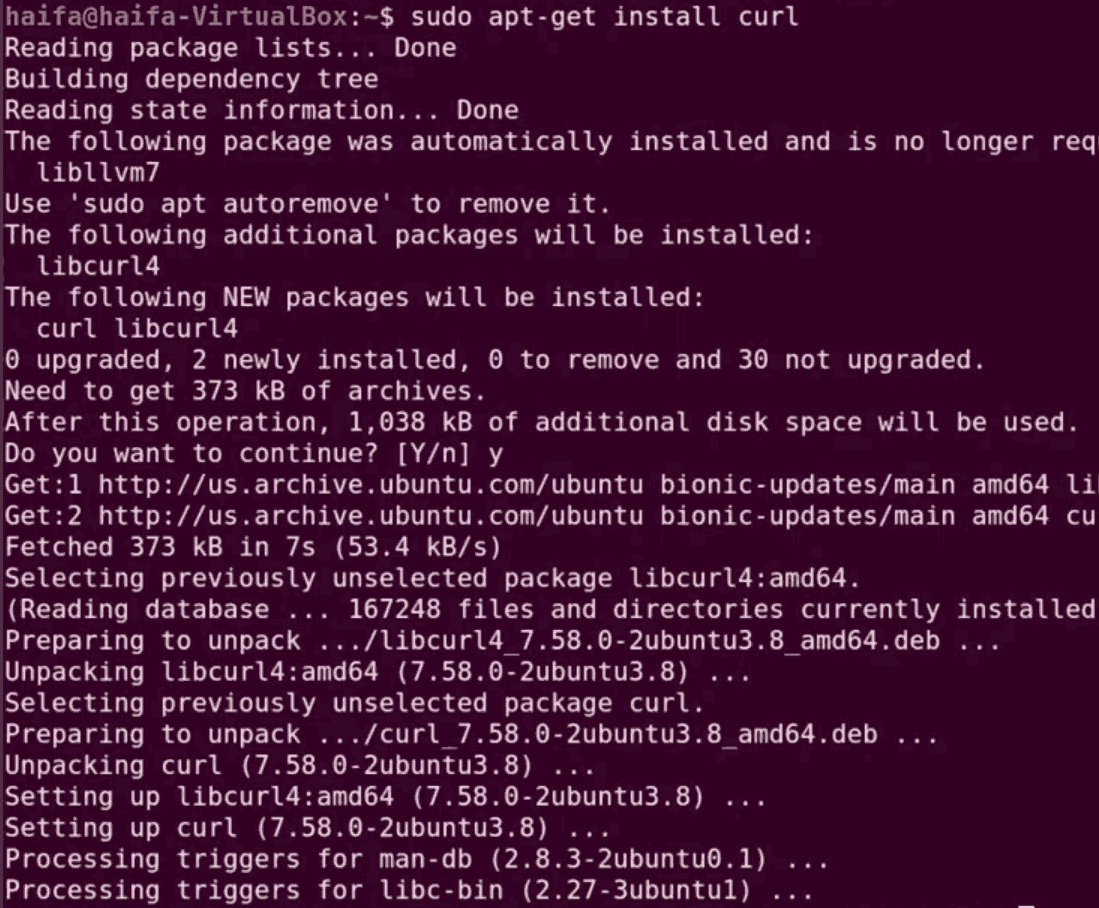
Step 5: We have to install the necessary components for Kubernetes. Before that, we have to install the curl command because the curl command is used to send the data using URL syntax. Let’s install the curl command by:
sudo apt-get install curl
Step 6: Download an add key for Kubernetes installation from a URL.
sudo curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add

Step 7: We have to add a repository in a certain location.
echo “deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main” | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
Step 8: Now check for any updates available.
sudo apt-get update

Step 9: Now we are going to install Kubernetes components.
sudo apt-get install -y kubectl kubeadm kubelet kubernetes-cni docker.io

Step 10: We have to initialize the master node and to do this we have to first use a swapoff command to disable the swapping on other devices.
sudo swapoff -a
Step 11: Go ahead with the initialization.
sudo kubeadm init

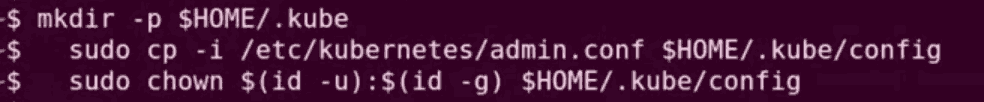
Step 12: To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
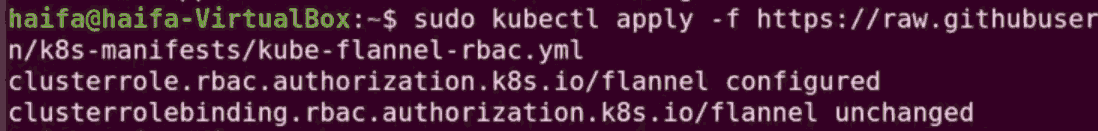
Step 13: To deploy paths, use the following command:
sudo kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/k8s-manifests/kube-flannel-rbac.yml
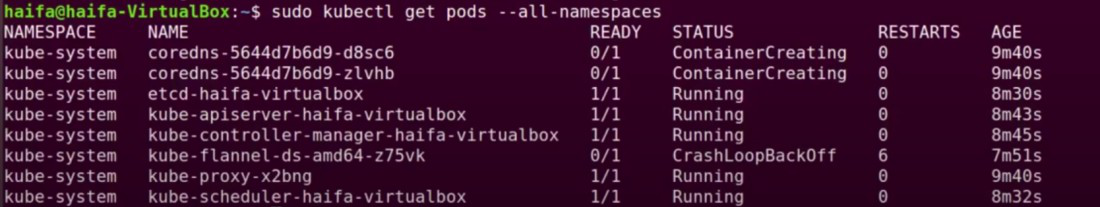
Step 14: To see all the pods you have, use the command:
sudo kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
Docker Container vs Kubernetes
The following are the differences between Docker Container and Kubernetes:
| Aspect | Docker Containers | Kubernetes |
|---|
| Definition | Container management tool for building, running, and managing containers | Container orchestration platform for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications |
|---|
| Purpose | To package applications with their dependencies into containers | To orchestrate and manage containerized applications across a cluster of machines |
|---|
| Deployment | Uses Docker CLI or Docker Compose for managing individual containers or multi-container applications | Uses kubectl and manifests (YAML files) for managing containers at scale within clusters |
|---|
| Scaling | Manual scaling using Docker CLI commands or Docker Compose | Automated scaling using Kubernetes controllers like Deployments and StatefulSets |
|---|
| Networking | Docker networking for linking containers within the same host or network | Advanced networking with built-in service discovery and load balancing |
|---|
Differences Between Kubernetes Ingress vs Kubernetes Services
The following are the differences between kubernetes Ingress and Kubernetes Services:
| Aspect | Kubernetes Ingress | Kubernetes Services |
|---|
| Definition | Manages external access to services within a cluster | Exposes a set of pods as a network service |
|---|
| Purpose | Provides HTTP and HTTPS routing to services based on host and path | Facilitates internal and external connectivity for pods |
|---|
| Routing | Supports advanced routing (e.g., URL-based routing, SSL termination) | Basic routing, mainly for internal communication within the cluster |
|---|
| Configuration | Requires an Ingress Controller and Ingress resources | Defined using Service resources (ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer) |
|---|
| Load Balancing | Provides application layer (L7) load balancing | Provides network layer (L4) load balancing |
|---|
Features of Kubernetes Containers
The following are the various features or characteristics of Kubernetes:
- Multi-Host Container Scheduling: Done by Kube-scheduler, it assigns containers, also referred to as pods in Kubernetes to nodes at runtime. It accounts for resources, quality of service, and policies before scheduling.
- Scalability and availability: The Kubernetes master is often deployed during a highly available configuration. Multi-region deployments are available as well.
- Flexibility and modularization: Kubernetes includes a plug-and-play architecture that permits you to increase it when you need to. There are specific add-ons from network drivers, service discovery, container runtime, visualization, and command. If there are tasks that you need to perform for your environment specifically, you’ll be able to create an add-on to suit your needs.
- Registration: New worker nodes can register themselves with the Kubernetes master node.
- Service discovery: Service discovery allows for automatic detection of new services and endpoints via DNS or environment variables.
- Persistent storage: It is a much-requested feature when working with containers. Pods can use persistent volumes to store data and therefore the data is retained across pod restarts and crashes.
- Maintenance: When it involves Kubernetes maintenance and upgrades, Kubernetes features are always backward compatible for some versions. All APIs are versioned and when upgrading or running maintenance on the host, you’ll unschedule the host so that no deployments can happen thereon. Once you're done, you’ll simply turn the host back on and schedule deployments or jobs.
- Logging and Monitoring: In terms of logging and monitoring, application monitoring or health checks are also built-in, TCP, HTTP, or container exact health checks are available out of the box. There are also health checks to give you the status of the nodes and failures monitored by the node controller. Kubernetes status can also be monitored via add-ons like Metrics Server, cAdvisor, and Prometheus. And lastly, you can use the built-in logging frameworks or if you choose, you can bring your own.
- Secrets Management: Sensitive data is a first-class citizen in Kubernetes. Secrets mounted to data volumes or environment variables. They’re also specific to a single namespace so aren't shared across all applications.
Advantages Of Kubernetes Containers
The following are the advantages of kubernetes containers:
- Scalability: Kubernetes allows for easy scaling of applications by increasing or decreasing the number of replicas of a particular service.
- High availability: Kubernetes provides features such as self-healing and automatic failover, which help ensure that applications remain available even in the event of a node failure.
- Portability: Kubernetes is designed to be platform-agnostic, which means that applications can be deployed on any infrastructure, whether it be on-premises, in the cloud, or at the edge.
- Automation: Kubernetes automates many of the tasks associated with deploying and managing applications, such as rolling updates, service discovery, and load balancing.
- Flexibility: Kubernetes allows for the use of multiple orchestration patterns, such as blue-green deployment, canary releases, and A/B testing, which gives developers more flexibility in how they deploy their applications.
Benefits of Kubernetes Containers
The following are the benefits of Kubernetes Containers:
- Complexity: Kubernetes can be complex to set up and manage, especially for organizations that are new to container orchestration.
- Steep learning curve: There is a steep learning curve for understanding how to use Kubernetes effectively, and for troubleshooting issues that may arise.
- Limited native support for certain technologies: Kubernetes does not natively support certain technologies, such as Windows containers, which can create challenges for organizations that use these technologies.
- Networking complexity: Kubernetes networking can be complex, especially when working with multiple clusters or when trying to integrate with existing network infrastructure.
- Higher resource requirements: running a Kubernetes cluster can consume more resources than running a traditional application, which can make it more expensive to operate.
Similar Reads
Kubernetes Tutorial Kubernetes is an open-source container management platform that automates the deployment, management, and scaling of container-based applications in different kinds of environments like physical, virtual, and cloud-native computing foundations. In this Kubernetes Tutorial, you are going to learn all
8 min read
Introduction to Kubernetes
Installation and Setup
Application Deployment
What are Kubernetes Containers?Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration framework that was originally developed by Google. Container orchestration is automation. It can facilitate you to deploy the identical application across different environments like physical machines, virtual machines cloud environments, or perha
15 min read
Kubernetes - Introduction to Container OrchestrationIn this article, we will look into Container Orchestration in Kubernetes. But first, let's explore the trends that gave rise to containers, the need for container orchestration, and how that it has created the space for Kubernetes to rise to dominance and growth. The growth of technology into every
4 min read
Kubernetes - ImagesPre-requisite:- Kubernetes A container image is used to represent binary data that is being used to encapsulate an application and all its software dependencies. Container images can be represented as executable software bundles that run standalone and make very defined assumptions about their runti
3 min read
Kubernetes - JobsPre-requisite: Kubernetes In the Kubernetes world, jobs are considered an object to act as a supervisor or controllers of a task. The Kubernetes job will create a pod, monitor the task, and recreate another one if that pod fails for some reason. Upon completion of the task, it will terminate the pod
4 min read
Kubernetes - Labels & SelectorsAn open-source container management platform called Kubernetes automates the deployment, scaling, descaling, and load balancing of containers (also called a container orchestration tool). It was created by Google in Golang and has a sizable community as a result of that. Google eventually donated it
5 min read
Kubernetes - NamespacesKubernetes Namespace is a mechanism that enables you to organize resources. It is like a virtual cluster inside the cluster. A namespace isolates the resources from the resources of other namespaces. For example, You need to have different names for deployments/services in a namespace but you can ha
9 min read
Kubernetes - NodeKubernetes Nodes are the Worker or master machines where the actual work happens. Each Kubernetes node has the services required to execute Pods and is controlled by the Control Plane. Each Kubernetes Node can have multiple pods and pods have containers running inside them. 3 processes in every Node
13 min read
Kubernetes - NodePort ServiceNodePort service in Kubernetes is a service that is used to expose the application to the internet from where the end-users can access it. If you create a NodePort Service Kubernetes will assign the port within the range of (30000-32767). The application can be accessed by end-users using the node's
5 min read
Kubernetes - ClusterIP vs NodePort vs LoadBalancerThree main service types are used in Kubernetes networking: ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer. Each has a specific function in controlling external access and service-to-service communication. Comprehending their distinctions is essential for efficiently coordinating applications. This article e
7 min read
Kubernetes - ServicesSoftware deployment, scaling, and management are all automated using Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration system. K8s is another name for Kubernetes. Kubernetes was initially developed by Google and is now managed by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. Despite the fact that it now s
3 min read
Kubernetes Pods: How to Create and Manage ThemKubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system mainly used for automated software deployment, management, and scaling. Kubernetes is also known as K8s. Kubernetes was originally developed by Google, but it is now being maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. It was original
13 min read
How to Run Shell Commands in Kubernetes Pods or ContainersIn Kubernetes, we create pods by adding an extra layer of information on containers. This Kubernetes in short is known as K8s, an open-source container orchestration tool developed by Google. It is used to orchestrate the containers for bringing Agility in software deployment through scaling, and ma
6 min read
Kubernetes - Creating Multiple Container in a PodPre-requisite:- Kubernetes Kubernetes is a container management tool and it automates container deployment, load balancing, and container scaling. It is open-source and developed by Google in 2014 and written in Golang. All cloud providers adopt Kubernetes. It is scheduled runs and manages isolated
3 min read
Kubernetes - Replication ControllerWith the help of the open-source container orchestration technology Kubernetes, software deployment, scalability, and management are mostly automated. Another name for Kubernetes is K8s. Google created Kubernetes, which is now overseen by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. Even though it now wor
7 min read
Kuberneters - Difference Between Replicaset and Replication ControllerPre-requisite: Kubernetes Kubernetes is also known as K8s is an open-source container orchestration tool developed by google which is used for automating software deployment, scaling, and management. Currently, it is being maintained by the cloud native computing foundation(CNCF). K8s has two versio
4 min read
What is Kubernetes Deployment?Kubernetes is an open-source Container Management tool that automates container deployment, container scaling, descaling, and container load balancing (also called as container orchestration tool). It is written in Golang and has a huge community because it was first developed by Google and later do
10 min read
Configmaps
Kubernetes - ConfigMapsKubernetes allows you to run and manage applications in containers. However, when you need to update configurations like usernames, passwords, or URLs without modifying the application code, ConfigMaps provide an efficient solution. ConfigMaps separate application configuration from the application
10 min read
Kubernetes - Create Config Map From FilesPre-requisite: Kubernetes While creating a manifest file in Kubernetes, we can define environment variables. However, when you have a lot of manifest files, it will become difficult to manage the environment data stored in various manifest files. To overcome this issue, we can manage environment dat
3 min read
Kubernetes - Create ConfigMap From YAML FileA ConfigMap is a dictionary consisting of non-confidential data. Its primary role is to keep the configuration separate from the container image. ConfigMap can be created in different ways. This article will cover the declarative approach to creating ConfigMap from the YAML file. Example: apiVersion
1 min read
Kubernetes - Config Map From DirectoryPre-requisite:- Kubernetes Software deployment, scalability, and administration are mostly automated using Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration framework. K8s is another name for Kubernetes. Kubernetes was initially developed by Google and is now managed by the Cloud Native Computing F
2 min read
Kubernetes - Injecting ConfigMap as FilesPre-requisite:- Kubernetes The automated deployment, scaling, and administration of software using a system called Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration tool. K8s is another name for Kubernetes. Kubernetes was initially developed by Google and is now managed by the Cloud Native Computin
3 min read
Kubernetes - Injecting ConfigMap in PodsPre-requisite: Kubernetes Leveraging the open-source container orchestration engine Kubernetes to automate the deployment, scalability, and management of applications. Another name for Kubernetes is K8s. Google originally created Kubernetes, which is currently overseen by the Cloud Native Computing
3 min read
Scaling and Updating Applications
Kubernetes - Service DNS An open-source container orchestration system called Kubernetes is primarily employed for the automated deployment, scaling, and management of software. Another name for Kubernetes is K8s. Initially created by Google, Kubernetes is currently maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. Altho
11 min read
Additional Topics
What is Kubernetes API ?Complete GuideKubernetes API is an application that serves Kubernetes functionality through a RESTful interface and stores the state of the cluster via HTTP. Users can directly interact with the Kubernetes API or via tools like kubectl. It supports retrieving, creating, updating, and deleting primary resources vi
14 min read
Kubernetes - Taint and TolerationA pod is a group of one or more containers and is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. A node is a representation of a single machine in a cluster (we can simply view these machines as a set of CPU and RAM). A node can be a virtual machine, a physical machine in a data center hosted on a clou
6 min read
Kubernetes Resource Model (KRM) and How to Make Use of YAML?Here we will explain how YAML can simplify system management and automation of most processes so that Kubernetes is a convenient working system. Basic Kubernetes Models: KRM and Everything-as-CodeAccording to Kubernetes co-founder Brian Grant, Kubernetes is very convenient thanks to the Kubernetes R
6 min read
Installing Private Git Server on K8s Cluster with Gitea and AKSIn this article, we are going to install a self-hosted Gitea server on top of Azure Kubernetes Service with Helm and set up a git repo. Having a private Git server might be beneficial these days. Gitea is a community-managed Git-compatible lightweight code hosting solution written in Go. It is publi
4 min read
Enable Remote Debugging For Java Application Deployed in Kubernetes EnvironmentDuring Development, developers have to debug their applications to resolve code problems. In order to debug a java application which is deployed on remote machine in a Kubernetes cluster, first developer has to do some steps to enable its application ready for debugging. Below are the manual steps t
2 min read
How to Enable JMX For Java Application Running in the Kubernetes Cluster?Many times we want to monitor our application's CPU utilization, background thread behavior, and most importantly memory consumptions for tasks that deal with loads for data (500MB - 1GB) or much more data. Such monitoring helps to find which operation is causing heavy CPU or Memory utilization and
3 min read