Spring Boot JDBC is used to connect the Spring Boot application with JDBC by providing libraries and starter dependencies. Spring Boot JDBC has a level of control over the SQL queries that are being written. Spring Boot JDBC has simplified the work of Spring JDBC by automating the work and steps by using the concept of Auto Configuration. JdbcTemplate, DataSource, NamedParameterJdbcTemplate, etc. all required objects are auto configured, and object creation is done by Spring Boot.
To build an application from scratch, you just need to use JdbcTemplate. As a programmer, you need to auto-wire the JdbcTemplate and perform the database operations like Create, Retrieve, Update, and Delete. Inputs need to be passed by application.properties or application.yml file. In application.properties file, we configure DataSource and connection pooling.
JDBC consists of two parts as depicted below:
- JDBC interfaces: java.sql / javax.sql packages have classes/interfaces of JDBC API.
- JDBC drivers: JDBC Driver allows Java programs to interact with the database.
Spring Boot offers many ways to work with databases (e.g - JdbcTemplate) without the cumbersome effort that JDBC needs. You can use raw JDBC to manually configure the workings.

JDBC Connection Pooling
JDBC Connection pooling is a mechanism which makes a database connection as reusable for more than one client, so burden on a database server will be reduced. A connection pool contains set of pooled connections or reusable connections.
When we use DriverManager or DataSource, the connection opened with a DataSource is a non-reusable. For each client if a new connection is opened, the burden on database server will be increase. So, to reduce the burden on database server, we use connection pooling.
.png)
How Connection Pooling Works
- A server administrator prepares a connection pool with a setoff connection and also a mediator object as a DataSource API to access the pool.
- An administrator stores DataSource object into JNDI (Java Naming Directory Interface).
- Application reads the DataSource from JNDI registry and asks for a connection from a pool.
- A DataSource object takes a connection from a pool and creates a proxy or logical connection to it and then sens the proxy connection to Java.
- When a Java program closes proxy connection, the DataSource will do real connection back to the pool.
To work with a database using Spring Boot, we need to add the following dependencies:
A. JDBC API
Database connectivity API specifies how the client connects and queries a database.
pom.xml Maven Dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
B. MySQL Driver
MySQL JDBC and R2DBC driver to work with the database.
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
After this, we will add datasource properties in application.properties file:
For MySQL database:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:8080/test
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
Project Structure

Implementation of an Application
A. pom.xml (Configuration File)
XML <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.6.3</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>sia</groupId> <artifactId>GFG</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>GFG</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>11</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <excludes> <exclude> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </exclude> </excludes> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
B. Boot of Spring application (GfgApplication.java)
Java // Java Program to Illustrate Boot of Spring Application package gfg; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; // Annotation @SpringBootApplication // Application(Main) Class public class GfgApplication { // Main driver method public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(GfgApplication.class, args); } }
C. Configuration of DataSource (ConfigDataSource.java)
DataSourceBuilder<T> is a useful class to build a DataSource.
- org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder<T>
- public final class DataSourceBuilder<T extends DataSource> extends Object
Methods of DataSourceBuilder<T> Class
|
create() | Creates a new instance of DataSourceBuilder. |
driverClassName(String driverClassName) | Specifies the driver class name which is to be used for building the datasource. |
url(String url) | Specifies the URL which is to be used for building the datasource. |
username(String username) | Specifies the username which is to be used for building the datasource. |
password(String password) | Specifies the password which is to be used for building the datasource. |
build() | Returns a newly built DataSource instance. |
This builder supports the following pooling Datasource implementations.
|
Hikari | com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource |
Tomcat JDBC Pool | org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource |
Apache DBCP2 | org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource |
Oracle UCP | oracle.ucp.jdbc.PoolDataSourceImpl |
Note: The first available pool implementation is used when no type has been explicitly set.

Example:
Java // Java Program Illustrating Configuration of // DataSourceConfiguration of DataSource package gfg; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; // Annotation @Configuration // Class public class ConfigDataSource { @Bean public static DataSource source() { DataSourceBuilder<?> dSB = DataSourceBuilder.create(); dSB.driverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // MySQL specific url with database name dSB.url("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userdetails"); // MySQL username credential dSB.username("user"); // MySQL password credential dSB.password("password"); return dSB.build(); } } Note: Driver class name - 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver' has been deprecated. It would not give error because the driver is automatically loaded and manual loading is not necessary. The new driver class name is 'com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver'.
D. User credentials to be stored in the database (UserDetails.java)
One can add the 'Lombok' library to skip Getter/Setter methods, construct No-Arguments constructor, the constructor for final fields, etc.
Maven-pom.xml dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
Example:
Java // Java Program Illustrating User Credentials to // be Stored in the Database package geek.details; import lombok.Data; // Annotation for Getter/Setter methods @Data public class UserDetails { String user; String userName; String password; }
E. Utility class for connecting and querying the database (JDBC.java)
Password encoding is a must for many security reasons. To use Spring Security, add the following dependency:
Maven - pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Pre-requisites are as follows:
- On adding the above dependency, the login page gets activated by default.
- The default username is - 'user.'
- The password is automatically generated by the Spring Security that gets displayed on the console after booting the application.

Note: Generated password becomes invalid for the next iteration/Running the application as the new password gets generated, but the username remains same.

- For encoding Spring offers many ways like the one - 'BCryptPasswordEncoder'.
- It is an implementation of PasswordEncoder which uses the BCrypt strong hashing algorithm.
- Version, Strength, and SecureRandom instances can be modified.
- org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder
- public class BCryptPasswordEncoder extends java.lang.Object implements PasswordEncoder
Constructors of BCryptPasswordEncoder Class:
|
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( ) | Default constructor. |
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( int strength ) | Strength is the log rounds to use between 4 to 31. Default is 10. |
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( int strength, SecureRandom random ) | The secure random instance to be used. |
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( BCryptVersion version ) | Version of BCrypt - 2a, 2b, 2y. |
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( BCryptVersion version, int strength ) | Bcrypt versions / log rounds. |
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( BCryptVersion version, int strength, SecureRandom random ) | Bcrypt versions / log rounds / Secure Random instance. |
| BCryptPasswordEncoder( BCryptVersion version, SecureRandom random ) | Bcrypt versions / Secure Random instance. |
Methods of BCryptPasswordEncoder Class:
|
encode(CharSequence rawPassword) | Encodes a raw password provided with SHA-1 or greater hash combined with 8-Byte or greater randomly generated salt value. |
matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) | Verifies the stored encoded password matches the submitted encoded raw password. Returns true if matched otherwise false. |
upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) | Returns true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security, else false. The default implementation always returns false. |
Example:
Java // Java Program Illustrating Utility class for Connecting // and Querying the Database package gfg; import geek.details.UserDetails; import java.security.SecureRandom; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; // Annotation to provide logging feature @Slf4j // Class public class JDBC { public int insert(UserDetails user) { DataSource dataSource = null; Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepStatement = null; int result = 0; try { // Get the configured datasourse dataSource = ConfigDataSource.source(); // Attempt for connection to MySQL connection = dataSource.getConnection(); prepStatement = connection.prepareStatement( "insert into user (user,username,password) values (?,?,?)"); prepStatement.setString(1, user.getUser()); prepStatement.setString(2, user.getUserName()); BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder( 10, new SecureRandom()); String encodedPassword = bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode( user.getPassword()); prepStatement.setString(3, encodedPassword); result = prepStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { log.getName(); } return result; } }
F. Controller of Spring Application (JdbcController.java)
Java // Java Program to Illustrate Controller of Spring Application package gfg; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import geek.details.UserDetails; @Controller @RequestMapping("/jdbc") public class JdbcController { @GetMapping public String get(Model model) { // Add object to be bound by user provided details model.addAttribute("obj", new UserDetails()); return "template"; } @PostMapping public String post(@ModelAttribute("obj") UserDetails user, Model model) { JDBC SQL = new JDBC(); int result = SQL.insert(user); if(result == 1) model.addAttribute("message", "Successful JDBC connection and execution of SQL statement"); else model.addAttribute("message", "Query not submitted!"); return "Status"; } } A. template.html: Gets user data and binds it to UserDetails object.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>GFG</title> </head> <body> <h1>Register Geek</h1> <form method="POST" th:action="@{/jdbc}" th:object="${obj}"> <label for="user">User: </label><br/> <input type="text" th:field="*{user}"/><br/> <label for="username">Username: </label><br/> <input type="text" th:field="*{userName}"/><br/> <label for="password">Password: </label><br/> <input type="password" th:field="*{password}"/> <input type="submit" value="Register"/> </form> </body> </html> Output:
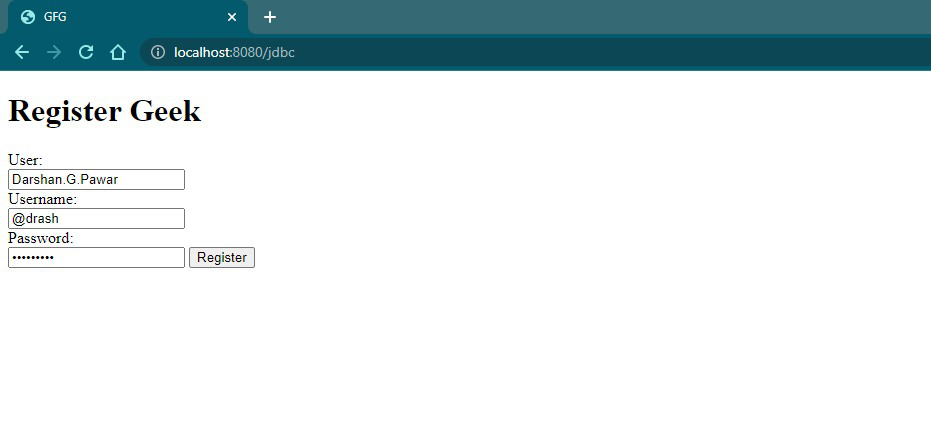 Filling the User details
Filling the User details B. Status.html
Display the message of JDBC operation.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>GFG</title> </head> <body> <h1>STATUS</h1> <h2 th:text="${message}"> <span>message will print here</span> </h2> </body> </html> Output in browser:

C. MySQL Database
Output:
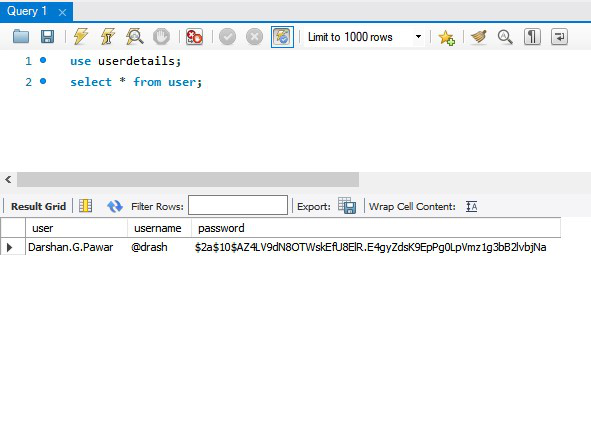
Note: Spring Boot offers many convenient ways of working with data, e.g. Spring Data JPA - which has default implementation of Hibernate. We can use them to make advantage of Java Persistence API (JPA) for object/relational mapping and to avoid cumbersome efforts.
Similar Reads
Spring Boot - Cache Provider The Spring Framework provides support for transparently adding caching to an application. The Cache provider gives authorization to programmers to configure cache explicitly in an application. It incorporates various cache providers such as EhCache, Redis, Guava, Caffeine, etc. It keeps frequently a
6 min read
Spring Boot - AOP Around Advice Aspect-oriented programming(AOP) as the name suggests uses aspects in programming. It can be defined as the breaking of code into different modules, also known as modularisation, where the aspect is the key unit of modularity. Aspects enable the implementation of crosscutting concerns such as transa
6 min read
Spring Boot - Auto-configuration Spring Boot is heavily attracting developers toward it because of three main features as follows: Auto-configuration - such as checking for the dependencies, the presence of certain classes in the classpath, the existence of a bean, or the activation of some property.An opinionated approach to confi
5 min read
Spring Boot - EhCaching EhCache is an open-source and Java-based cache. It is used to boost performance. Its current version is 3. EhCache provides the implementation of the JSR-107 cache manager. Features of EhCache are given below: It is fast, lightweight, Flexible, and Scalable.It allows us to perform Serializable and O
5 min read
Difference Between Spring Boot Starter Web and Spring Boot Starter Tomcat Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read
Spring Boot - Starter Test Spring Boot is built on top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. It is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment, which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and setup.
5 min read
Exception Handling in Spring Boot Exception handling in Spring Boot helps deal with errors and exceptions present in APIs, delivering a robust enterprise application. This article covers various ways in which exceptions can be handled and how to return meaningful error responses to the client in a Spring Boot Project. Key Approaches
8 min read
Spring Boot - Project Deployment Using Tomcat Spring Boot is a microservice-based framework and making a production-ready application in it takes very little time. Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because it’s a rapid production-ready envir
5 min read
Spring Boot - Difference Between AOP and OOP AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming) complements OOP by enabling modularity of cross-cutting concerns. The Key unit of Modularity(breaking of code into different modules) in Aspect-Oriented Programming is Aspect. one of the major advantages of AOP is that it allows developers to concentrate on business
3 min read
Spring Boot - Difference Between AOP and AspectJ Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and se
3 min read