LinkedHashSet in Java implements the Set interface of the Collection Framework. It combines the functionality of a HashSet with a LinkedList to maintain the insertion order of elements.
- Stores unique elements only.
- Maintains insertion order.
- Provides faster iteration compared to HashSet.
- Allows null elements.
Example:
Java import java.util.LinkedHashSet; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a LinkedHashSet of Strings LinkedHashSet<String> lh = new LinkedHashSet<>(); System.out.println("" + lh); } } Hierarchy of LinkedHashSet
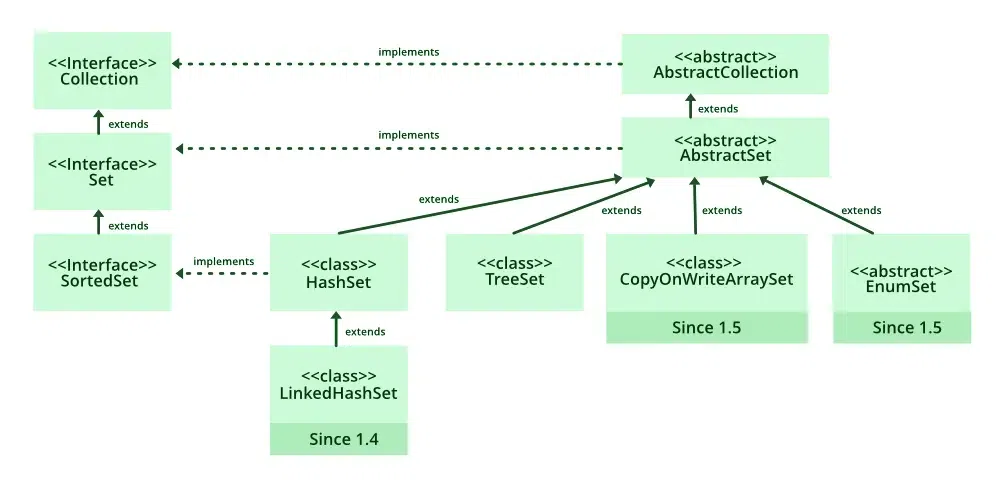
Declaring a LinkedHashSet
public class LinkedHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
where, E is the type of elements maintained by this set.
The LinkedHashSet is an ordered version of HashSet that maintains a doubly-linked List across all elements. When the iteration order is needed to be maintained this class is used. When iterating through a HashSet the order is unpredictable, while a LinkedHashSet lets us iterate through the elements in the order in which they were inserted. When cycling through LinkedHashSet using an iterator, the elements will be returned in the order in which they were inserted.
Constructors of LinkedHashSet Class
1. LinkedHashSet(): This constructor is used to create an empty LinkedHashSet with the default capacity i.e. 16 and load factor 0.75.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>();
2. LinkedHashSet(Collection C): Used in initializing the HashSet with the elements of the collection C.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(Collection c);
3. LinkedHashSet(int size): Used to initialize the size of the LinkedHashSet with the integer mentioned in the parameter.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(int size);
4. LinkedHashSet(int capacity, float fillRatio): Can be used to initialize both the capacity and the fill ratio, also called the load capacity of the LinkedHashSet with the arguments mentioned in the parameter. When the number of elements exceeds the capacity of the hash set is multiplied with the fill ratio thus expanding the capacity of the LinkedHashSet.
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(int capacity, int fillRatio);
Methods of LinkedHashSet
Here are some commonly used methods in LinkedHashSet:
Method | Description |
|---|
| spliterator() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this set. |
Methods Declared in java.util.AbstractSet Class
Method | Description |
|---|
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this set for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this set. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
Methods Declared in java.util.AbstractCollection Class
Method | Description |
|---|
| addAll?(Collection<? extends E> c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation). |
| containsAll?(Collection<?> c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| retainAll?(Collection<?> c) | Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection. |
| toArray?(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this collection. |
Methods Declared in java.util.Collection Interface
Method | Description |
|---|
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
Methods Declared in java.util.HashSet Class
Method | Description |
|---|
| add(E e) | Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this set. |
| clone() | Returns a shallow copy of this HashSet instance: the elements themselves are not cloned. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this set contains the specified element. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this set contains no elements. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this set. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes the specified element from this set if it is present. |
| size() | Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality). |
Methods declared in java.lang.Iterable Interface
Method | Description |
|---|
forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
Methods Declared in java.util.Set Interface
| Method | Description |
|---|
| add(element) | This method is used to add a specific element to the set. The function adds the element only if the specified element is not already present in the set else the function returns False if the element is already present in the Set. |
| addAll(Collection c) | This method is used to append all of the elements from the mentioned collection to the existing set. The elements are added randomly without following any specific order. |
| clear() | This method is used to remove all the elements from the set but not delete the set. The reference for the set still exists. |
| contains(element) | This method is used to check whether a specific element is present in the Set or not. |
| containsAll(Collection c) | This method is used to check whether the set contains all the elements present in the given collection or not. This method returns true if the set contains all the elements and returns false if any of the elements are missing. |
| hashCode() | This method is used to get the hashCode value for this instance of the Set. It returns an integer value which is the hashCode value for this instance of the Set. |
| isEmpty() | This method is used to check whether the set is empty or not. |
| iterator() | This method is used to return the iterator of the set. The elements from the set are returned in random order. |
| remove(element) | This method is used to remove the given element from the set. This method returns True if the specified element is present in the Set otherwise it returns False. |
| removeAll(collection) | This method is used to remove all the elements from the collection which are present in the set. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| retainAll(collection) | This method is used to retain all the elements from the set which are mentioned in the given collection. This method returns true if this set changed as a result of the call. |
| size() | This method is used to get the size of the set. This returns an integer value which signifies the number of elements. |
| toArray() | This method is used to form an array of the same elements as that of the Set. |
| toArray?(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
Performing Various Operations on LinkedHashSet
Let’s see how to perform a few frequently used operations on the LinkedHashSet.
1. Adding Elements in LinkedHashSet
In order to add an element to the LinkedHashSet, we can use the add() method. This is different from HashSet because in HashSet, the insertion order is not retained but is retained in the LinkedHashSet.
Example:
Java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating an empty LinkedHashSet LinkedHashSet<String> lh = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); // Adding elements to above Set // using add() method lh.add("Geek"); lh.add("For"); lh.add("Geeks"); System.out.println("LinkedHashSet : " + lh); } } OutputLinkedHashSet : [Geek, For, Geeks]
2. Removing Elements in LinkedHashSet
The values can be removed from the LinkedHashSet using the remove() method.
Example:
Java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating an empty LinekdhashSet of string type LinkedHashSet<String> lh = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); // Adding elements to above Set // using add() method lh.add("Geek"); lh.add("For"); lh.add("Geeks"); lh.add("A"); lh.add("B"); lh.add("Z"); System.out.println("" + lh); // Removing the element from above Set lh.remove("B"); // Again removing the element System.out.println("After removing element " + lh); // Returning false if the element is not present System.out.println(lh.remove("AC")); } } Output[Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z] After removing element [Geek, For, Geeks, A, Z] false
3. Iterating through the LinkedHashSet
Iterate through the elements of LinkedHashSet using the iterator() method. The most famous one is to use the enhanced for loop.
Example:
Java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Instantiate an object of Set // Since LinkedHashSet implements Set // Set points to LinkedHashSet Set<String> lh = new LinkedHashSet<String>(); lh.add("Geek"); lh.add("For"); lh.add("Geeks"); lh.add("A"); lh.add("B"); lh.add("Z"); // Iterating though the LinkedHashSet // using iterators Iterator itr = lh.iterator(); while (itr.hasNext()) System.out.print(itr.next() + ", "); System.out.println(); // Using enhanced for loop for iteration for (String s : lh) System.out.print(s + ", "); System.out.println(); } } OutputGeek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z, Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z,
Advantages of LinkedHashSet
- It maintains insertion order.
- It allows quick insertion, deletion, and lookup of elements.
- It is useful for caching applications where insertion order is important.
Disadvantages of LinkedHashSet
- It takes higher memory as compared to HashSet due to the linked list for maintaining insertion order.
- This is slightly slower operations compared to HashSet because of the linked structure.
LinkedHashMap vs LinkedHashSet
| Categories | LinkedHashMap | LinkedHashSet |
|---|
| Operation | Usd to store key-value pairs. | Used to store collection of things |
| Duplicates | Take unique an no duplicate keys but can takeduplicate values | Stores no duplicate element |
| Implements | HashMap | HashSet |
| Example | Map<String, Integer> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>(); | Set<String> lhs = new LinkedhashSet<String>(); |
Note: Keeping the insertion order in both LinkedHashmap and LinkedHashset have additional associated costs, both in terms of spending additional CPU cycles and needing more memory. If you do not need the insertion order maintained, it is recommended to use the lighter-weight HashSet and HashMap instead.
Similar Reads
Java Collection Tutorial Java Collection Framework is unlikely any group of individual objects which are represented as a single unit be it of any type is known as the collection of objects. Earlier in Java, there was no such thing defined which holds true for it so there arises a need in the next versions of any such conce
15+ min read
Collection Interface in Java The Collection interface in Java is a core member of the Java Collections Framework located in the java.util package. It is one of the root interfaces of the Java Collection Hierarchy. The Collection interface is not directly implemented by any class. Instead, it is implemented indirectly through it
6 min read
List Interface
Java List InterfaceThe List Interface in Java extends the Collection Interface and is a part of the java.util package. It is used to store the ordered collections of elements. In a Java List, we can organize and manage the data sequentially. Key Features:Maintained the order of elements in which they are added.Allows
15+ min read
ArrayList in JavaJava ArrayList is a part of the collections framework and it is a class of java.util package. It provides us with dynamic-sized arrays in Java. The main advantage of ArrayList is that, unlike normal arrays, we don't need to mention the size when creating ArrayList. It automatically adjusts its capac
9 min read
LinkedList in JavaLinked List is a part of the Collection framework present in java.util package. This class is an implementation of the LinkedList data structure, which is a linear data structure where the elements are not stored in contiguous locations, and every element is a separate object with a data part and an
12 min read
Vector Class in JavaThe Vector class in Java implements a growable array of objects. Vectors were legacy classes, but now it is fully compatible with collections. It comes under java.util package and implement the List interface.Key Features of Vector:It expands as elements are added.Vector class is synchronized in nat
12 min read
Stack Class in JavaThe Java Collection framework provides a Stack class, which implements a Stack data structure. The class is based on the basic principle of LIFO (last-in-first-out). Besides the basic push and pop operations, the class also provides three more functions, such as empty, search, and peek. The Stack cl
11 min read
AbstractList in Java with ExamplesThe AbstractList class in Java is a part of the Java Collection Framework and implements the Collection interface and the AbstractCollection class. AbstractList class provides a skeletal implementation of the List interface to minimize the effort required to implement this interface backed by a Rand
7 min read
AbstractSequentialList in Java with ExamplesThe AbstractSequentialList class in Java is a part of the Java Collection Framework and implements the Collection interface and the AbstractCollection class. This class provides a skeletal implementation of the List interface to minimize the effort required to implement this interface backed by a "s
7 min read
Set Interface
Queue Interface
Deque Interface
Map Interface