Inventory Management System in Java
Last Updated : 09 Jun, 2025
An inventory management system is very important for businesses to keep track of their stocks, manage orders, and maintain an accurate record. With the help of this project, the user can add, remove, and view items in the inventory. Also beginners can learn important concepts like classes, generics, and handling user input.
In this article, we are going to build a simple inventory management system in Java. This system helps us perform important tasks like adding, removing, and viewing items in the inventory. The implementation will be divided into multiple classes for better code organization and understanding.
Working of the Inventory System
Here is how the inventory management system is going to work:
- The user can add items by giving details like item name, quantity, and price.
- The user can remove items from the inventory by telling the item's name.
- The user can also view all items in the inventory.
- The system displays the inventory status after each operation.
Project Structure
The image below demonstrates the project structure.
We will organize the code into these parts which are listed below:
- Item Class: This class represents an item with all the attributes like name, quantity and price.
- Inventory Class: This class handles all the inventory operations like adding, removing and viewing items.
- InventorySystem Class: This is the main class that runs the system and takes input from the user.
Let's now try to implement the code.
Java Inventory Management System Project Implementation
1. Item Class
This class represents all the inventory item. It includes attributes like name, quantity and price of the item.
Item.java:
Java package com.inventory; public class Item { private String name; private int quantity; private double price; // Constructor public Item(String name, int quantity, double price) { this.name = name; this.quantity = quantity; this.price = price; } // Getter and setter methods public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getQuantity() { return quantity; } public void setQuantity(int quantity) { this.quantity = quantity; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Item{name='" + name + "', quantity=" + quantity + ", price=" + price + "}"; } }
2. Inventory Class
This class manages the list of items in the inventory. It allows us to add, remove and view items.
Inventory.java:
Java package com.inventory; import java.util.*; public class Inventory<T> { private List<T> items; public Inventory() { items = new ArrayList<>(); } // Add an item to the inventory public void addItem(T item) { try { items.add(item); System.out.println("Item added successfully: " + item); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Error adding item: " + e.getMessage()); } } // Remove an item from the inventory public void removeItem(T item) { try { if (!items.contains(item)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Item not found in inventory."); } items.remove(item); System.out.println("Item removed successfully: " + item); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Error removing item: " + e.getMessage()); } } // View all items in the inventory public void viewItems() { if (items.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Inventory is empty."); } else { System.out.println("Inventory items:"); for (T item : items) { System.out.println(item); } } } // Getter method for items public List<T> getItems() { return items; } }
3. InventorySystem
This class is the entry point of the application. The main task of this class is to interact with the user, take inputs and perform actions like adding, removing, and viewing items in the inventory.
InventorySystem.java:
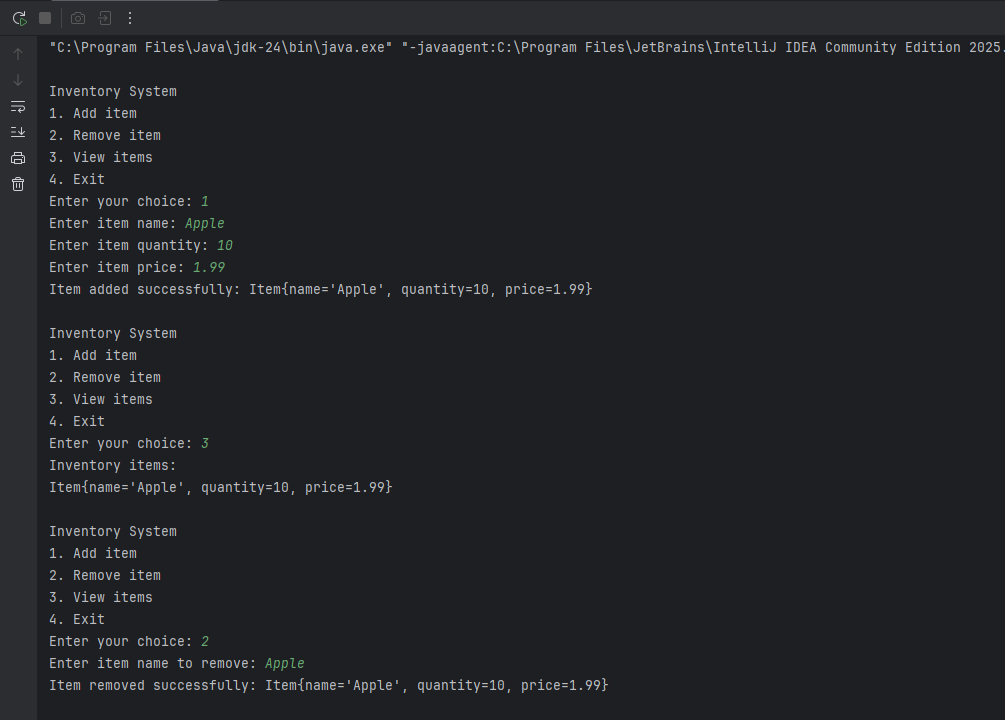
Java package com.inventory; import java.util.Scanner; public class InventorySystem { public static void main(String[] args) { Inventory<Item> inventory = new Inventory<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean exit = false; while (!exit) { System.out.println("\nInventory System"); System.out.println("1. Add item"); System.out.println("2. Remove item"); System.out.println("3. View items"); System.out.println("4. Exit"); System.out.print("Enter your choice: "); int choice = scanner.nextInt(); scanner.nextLine(); // consume the newline switch (choice) { case 1: // Add an item System.out.print("Enter item name: "); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.print("Enter item quantity: "); int quantity = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter item price: "); double price = scanner.nextDouble(); scanner.nextLine(); // consume the newline Item newItem = new Item(name, quantity, price); inventory.addItem(newItem); break; case 2: // Remove an item System.out.print("Enter item name to remove: "); String itemNameToRemove = scanner.nextLine(); Item itemToRemove = null; // Search for the item using the getter method for items for (Item item : inventory.getItems()) { if (item.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(itemNameToRemove)) { itemToRemove = item; break; } } if (itemToRemove != null) { inventory.removeItem(itemToRemove); } else { System.out.println("Item not found in inventory."); } break; case 3: // View items inventory.viewItems(); break; case 4: // Exit exit = true; System.out.println("Exiting Inventory System."); break; default: System.out.println("Invalid choice. Please try again."); } } scanner.close(); } } Output:
How to Run the Project in IntelliJ IDEA?
To run the project on IntelliJ IDEA we just need to follow these steps which are listed below:
- Open IntelliJ IDEA and create a new Java project.
- Start creating the packages and the structure must be look like this:
- Item.java
- Inventory.java
- InventorySystem.java
- Create the classes in the correct packages
- Save all the files.
- Run the main class

Similar Reads
Inventory Management System using Spring Boot Inventory Management System plays an important role in Business for tracking the Inventory, and It is used for tracking and movement of goods. In this article, we have provided some basic functionality for the Inventory Management System like an Analysis report of goods, adding new Products to the S
15 min read
JUnit - Inventory Stock Testing as a Maven Project The quality of the software is very important. Though Unit tests and integration tests are done in the manual testing way, we cannot expect all kinds of scenarios to test. Hence as a testing mechanism, we can test a software code or project by means of JUnit. In this article let us see how to do tes
4 min read
Java.util Package in Java Java.util PackageIt contains the collections framework, legacy collection classes, event model, date and time facilities, internationalization, and miscellaneous utility classes (a string tokenizer, a random-number generator, and a bit array).Following are the Important Classes in Java.util package
4 min read
Java Fundamentals Coding Practice Problems Understanding Java fundamentals is the first step to becoming a proficient Java programmer. This collection of Java basic coding practice problems covers essential topics such as input/output operations, arithmetic and logical operators, type conversion, conditional statements, loops, and more. Thes
1 min read
What is Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE)? In today's world of large-scale applications, businesses need secure, scalable, and efficient software solutions. Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) now known as Jakarta EE provides a powerful framework for building enterprise-level applications. JEE has become the backbone of many banking, e-commerc
6 min read