In Java, the EnumSet is a specialized set implementation for use with enum types. It is a part of java.util package and provides a highly optimized set for storing enum constants. The EnumSet is one of the specialized implementations of the Set interface for use with the enumeration type.
Example: This example demonstrates how to create an EnumSet and print its elements
Java // Creating an EnumSet import java.util.EnumSet; enum Student { Geek1, Geek2, Geek3, Geek4, Geek5 } public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create an EnumSet containing specific elements EnumSet<Student> e = EnumSet.of(Student.Geek1, Student.Geek2, Student.Geek3); System.out.println("EnumSet: " + e); } } OutputEnumSet: [Geek1, Geek2, Geek3]
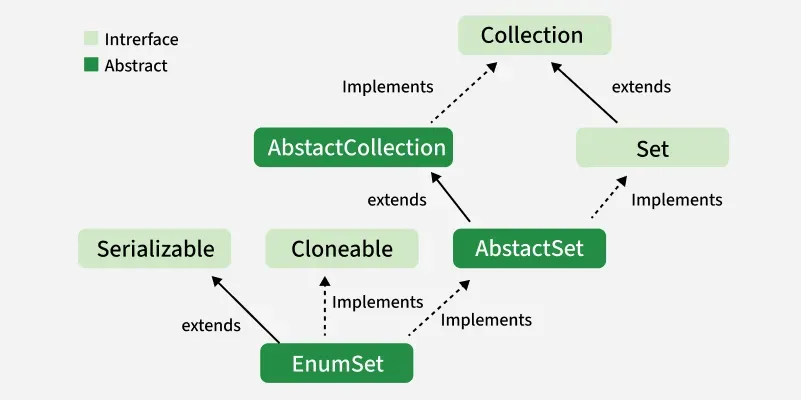
Hierarchy of EnumSet
The Hierarchy of EnumSet is as follows:

Here, E is the type of elements stored.
Declaration of EnumSet
In Java, the declaration of EnumSet can be done as:
EnumSet<Type> name = EnumSet.of(Element1, Element2, Element3);
- Parameter: EnumSet.of() take one or more enum constants as arguments and specifying which enum values to include in the set.
- Return Type: It returns a set containing the specified enum constants
Methods
Method | Action Performed |
|---|
| allOf(Class<E> elementType) | Creates an enum set containing all of the elements in the specified element type. |
| clone() | Returns a copy of this set. |
| complementOf(EnumSet<E> s) | Creates an enum set with the same element type as the specified enum set, initially containing all the elements of this type that are not contained in the specified set. |
| copyOf(Collection<E> c) | Creates an enum set initialized from the specified collection. |
| copyOf(EnumSet<E> s) | Creates an enum set with the same element type as the specified enum set, initially containing the same elements (if any). |
| noneOf(Class<E> elementType) | Creates an empty enum set with the specified element type. |
| of(E e) | Creates an enum set initially containing the specified element. |
| of(E e1, E e2) | Creates an enum set initially containing the specified elements. |
| of(E first, E… rest) | Creates an enum set initially containing the specified elements. |
| of(E e1, E e2, E e3) | Creates an enum set initially containing the specified elements. |
| of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4) | Creates an enum set initially containing the specified elements. |
| of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5) | Creates an enum set initially containing the specified elements. |
| range(E from, E to) | Creates an enum set initially containing all of the elements in the range defined by the two specified endpoints. |
Example: This example demonstrates how to create and manipulate EnumSet using methods like of(), complementOf(), allOf() and range() with enum constants.
Java // Java Program to demonstrate the Working // of EnumSet and its functions import java.util.EnumSet; // Enum enum e { CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ, MCQ }; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a set EnumSet<e> s1, s2, s3, s4; // Adding elements s1 = EnumSet.of(e.QUIZ, e.CONTRIBUTE, e.LEARN, e.CODE); s2 = EnumSet.complementOf(s1); s3 = EnumSet.allOf(e.class); s4 = EnumSet.range(e.CODE, e.CONTRIBUTE); // Printing corresponding elements in Sets System.out.println("Set 1: " + s1); System.out.println("Set 2: " + s2); System.out.println("Set 3: " + s3); System.out.println("Set 4: " + s4); } } OutputSet 1: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ] Set 2: [MCQ] Set 3: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ, MCQ] Set 4: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE]
Creating a EnumSet
In Java, EnumSet is an abstract class, we can not directly create an instance of it. Instead it provides static factory methods to create instances. There are two different internal implementations of EnumSet which are listed below:
- RegularEnumSet: It uses a single long object to store the elements of the EnumSet. Each bit in the long value represents an enum constant. The size of a long is 64 bits, RegularEnumSet can store up to 64 enum values.
- JumboEnumSet: It uses an array of long values to store the elements of the EnumSet. The key difference is that JumboEnumSet allows atoring more than 63 values by using multiple long elements to represent a larger set of enum constants.
Note: These are package-private and backed by a bit vector.
Factory Method for EnumSet Creation
Implementation of Internal Logic
If the number of elements (universe.length) is less than or equal to 64, RegularEnumSet is used otherwise JumboEnumSet is used for larger enum types.
if (universe.length <= 64)
return new RegularEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
else
return new JumboEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
Example: This example demonstrates how to create an EnumSet using the EnumSet.allOf() method and print sites contents.
Java // Java Program to demonstrates the // working of EnumSet.allOf() method import java.util.*; class Geeks { // Enum enum Game { CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating an EnumSet using allOf() EnumSet<Game> g = EnumSet.allOf(Game.class); // Printing EnumSet elements to the console System.out.println("EnumSet: " + g); } } OutputEnumSet: [CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS]
Performing Various Operations on EnumSet
1. Adding Elements: We can use add() and addAll() to insert elements to an EnumSet.
Example: This example demonstrates how to add elements to an EnumSet using both add() and addAll() method.
Java // Java program to demonstrate the // working of both add and addAll() method import java.util.EnumSet; class Geeks { // Enum enum Game { CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating an EnumSet // using allOf() EnumSet<Game> g1 = EnumSet.allOf(Game.class); // Creating an EnumSet // using noneOf() EnumSet<Game> g2 = EnumSet.noneOf(Game.class); // Using add() method g2.add(Game.HOCKEY); // Printing the elements to the console System.out.println("EnumSet Using add(): " + g2); // Using addAll() method g2.addAll(g1); // Printing the elements to the console System.out.println("EnumSet Using addAll(): " + g2); } } OutputEnumSet Using add(): [HOCKEY] EnumSet Using addAll(): [CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS]
2. Accessing Elements: We can access the EnumSet using the iterator() method.
Example: This example demonstrates how to use the iterator() method to iterate over the elements of an EnumSet.
Java // Java program to demonstrates the // working of iterator() method import java.util.EnumSet; import java.util.Iterator; class Geeks { // Enum enum Game { CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating an EnumSet using allOf() EnumSet<Game> g = EnumSet.allOf(Game.class); // Creating an iterator on games Iterator<Game> i = g.iterator(); System.out.print("EnumSet: "); while (i.hasNext()) { // Iterating and printing elements to // the console using next() method System.out.print(i.next()); System.out.print(", "); } } } OutputEnumSet: CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS,
3. Removing Elements: We can use the remove() and removeAll() to remove elements from an EnumSet.
Example: This example, demonstrates the use of remove() to remove a single element and removeAll() to remove all elements from an EnumSet.
Java // Java program to demonstrates the working // of both remove() and removeAll() Method import java.util.EnumSet; class Geeks { // Enum enum Game { CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating EnumSet using allOf() EnumSet<Game> g = EnumSet.allOf(Game.class); // Printing the EnumSet System.out.println("EnumSet: " + g); // Using remove() boolean b = g.remove(Game.CRICKET); System.out.println("Is CRICKET removed? " + b); // Using removeAll() and storing the boolean result boolean b2 = g.removeAll(g); System.out.println("Are all elements removed? " + b2); } } OutputEnumSet: [CRICKET, HOCKEY, TENNIS] Is CRICKET removed? true Are all elements removed? true
Some other methods of classes or interfaces are defined below that somehow helps us to get a better understanding of AbstractSet Class as follows:
Methods Declared in Class java.util.AbstractSet
Method | Description |
|---|
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this set for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this set. |
| removeAll(Collection<?> c) | Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
Methods Declared in Interface java.util.Collection
Method | Description |
|---|
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> generator) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array. |
Methods Declared in Interface java.lang.Iterable
Method | Description |
|---|
| forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
Methods Declared in Interface java.util.Set
Method | Description |
|---|
| add(E e) | Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present (optional operation). |
| addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present (optional operation). |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this set (optional operation). |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this set contains the specified element. |
| containsAll(Collection<?> c) | Returns true if this set contains all of the elements of the specified collection. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this set contains no elements. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this set. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes the specified element from this set if it is present (optional operation). |
| retainAll(Collection<?> c) | Retains only the elements in this set that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| size() | Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality). |
| spliterator() | Creates a Spliterator over the elements in this set. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array |
Methods Declared in Class java.util.AbstractCollection
Method | Description |
|---|
| add(E e) | Ensures that this collection contains the specified element (optional operation). |
| addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation). |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this collection (optional operation). |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this collection contains the specified element. |
| containsAll(Collection<?> c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements contained in this collection. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes a single instance of the specified element from this collection, if it is present (optional operation). |
| retainAll(Collection<?> c) | Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this collection. |
Similar Reads
EnumSet in Java In Java, the EnumSet is a specialized set implementation for use with enum types. It is a part of java.util package and provides a highly optimized set for storing enum constants. The EnumSet is one of the specialized implementations of the Set interface for use with the enumeration type.It extends
9 min read
EnumSet allof() Method in Java The Java.util.EnumSet.allOf(Class elementType) in Java is used to create an enum set that will be used to contain all of the elements in the specified elementType. Syntax: public static > EnumSet allOf(Class elementType) Parameters: The method accepts one parameter elementType of element type and re
2 min read
EnumSet clone() Method in Java The Java.util.EnumSet.clone() method in Java is used to return a shallow copy of the existing or this set. Syntax: Enum_Set_2 = Enum_Set_1.clone() Parameters: The method does not take any parameters. Return Value: The method does not return any value. Below programs illustrate the working of Java.ut
2 min read
EnumSet complementOf() Method in Java The java.util.EnumSet.complementOf(Enum_Set) method is used to create an EnumSet containing elements of the same type as that of the specified Enum_Set, with the values present in the enum but other than those contained in the specified Enum_Set. Syntax: New_Enum_Set = EnumSet.complementOf(Enum_Set)
2 min read
EnumSet copyOf() Method in Java The java.util.EnumSet.copyOf(Collection collect) method in Java is used to copy all of the contents from a collection to a new enum set. At first, the collection is made out of the elements of the enum and then a new enum set is created, which is the copy of the collection. Syntax: New_Enum_Set = En
3 min read
Java EnumSet noneOf() Method The EnumSet.noneOf() method is a part of java.util package. This method is used to create an empty EnumSet for a given enum type. Suppose we create a set with no elements first, but that will only hold the enum constants of a particular enum class. In this article, we are going to learn about the En
2 min read
EnumSet of() Method in Java The java.util.EnumSet.of(E ele1, E ele2, E ele3, ...) method in Java is used to create an enum set initially containing the specified elements in the parameters. When multiple items are added at the same time the elements are pushed down the set as the new elements are added. When different elements
5 min read
Java EnumSet range() Method The EnumSet.range() method is a part of the java.util package. This method is used to create an EnumSet that contains all enum constants between the specified start and end points, and it should be inclusive. It easily creates a subset of enum constants within a specified range.Syntax of EnumSet ran
2 min read