java.lang.Character Class Methods | Set 1
Last Updated : 10 Jan, 2025
java.lang.Character Class wraps the value of a primitive data type char to an object of datatype Character. This object contains a single field having the data type char. This class provides several methods regarding character manipulations like converting them from lowercase to uppercase. Character Class is based on Unicode Standards to provide character information.
Class Declaration
public final class Character
extends Object
implements Serializable, Comparable
Character Class Methods
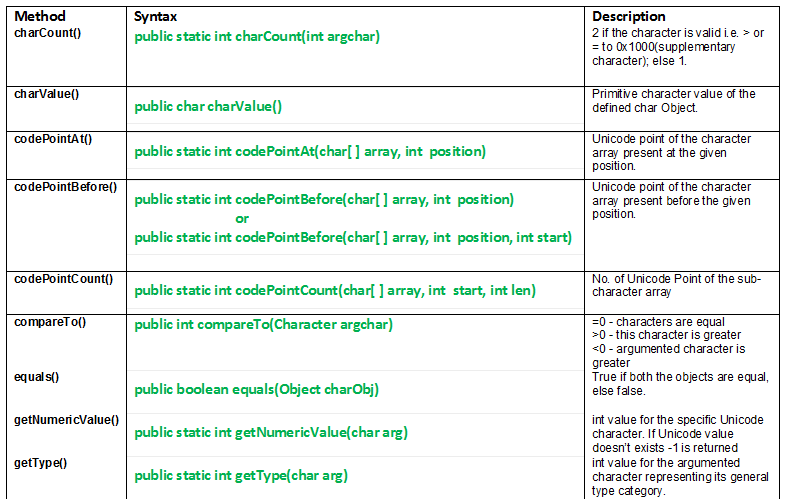
1. charCount()
java.lang.charCount() method uses Unicode point to return the number of char values to represent the argument char values. A Unicode code point is used for character values in the range between U+0000 and U+10FFFF and for 16-bit char values that are code units of the UTF-16 encoding.
Syntax:
public static int charCount(int argchar)
- Parameters: argchar: Unicode point of the character to be counted.
- Return: 2 if the character is valid i.e. > or = to 0X1000 (supplementary character); else 1
2. charValue()
The charValue() method returns primitive char value of defined Character Object.
Syntax:
public char charValue()
Return Value: The primitive char value of the specified Character object.
3. codePointAt()
The codePointAt(char[ ] array, int position) method returns Unicode Point of the character array present at the argumented position.
Syntax:
public static int codePointAt(char[] array, int position)
Parameters:
- array: The character array.
- position: The index of the character whose Unicode code point you need.
Return Value: The Unicode point of the character at the specified position
Examples Using charCount(), charValue(), and codePointAt() Methods:
JAVA // Java program explaining Character class methods // charCount(), charValue(), codePointat() import java.lang.Character; public class Geeks { public static void check(int ele) { // Checking for geek if (ele == 2) System.out.println("Valid Character geek"); else System.out.println("Invalid Character geek"); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Use of charCount() method int geek = 0x9999, geek1 = 0x10000, geek2 = 0x10001; int c = Character.charCount(geek); int c1 = Character.charCount(geek1); int c2 = Character.charCount(geek2); check(c); check(c1); check(c2); System.out.println(); // Character object m Character m; // Assigning value g to m; m = new Character('g'); char gfg; // Use of charValue() method gfg = m.charValue(); System.out.println("Primitive value of gfg : "+ gfg); System.out.println(); // Use of codePointAt() char[] arg = new char[] { 'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's' }; int val, val1, position = 3; val = Character.codePointAt(arg, position); val1 = Character.codePointAt(arg, 0); System.out.println("Unicode code point at " + position + " : " + val); System.out.println("Unicode code point at 0 : " + val1); } } OutputInvalid Character geek Valid Character geek Valid Character geek Primitive value of gfg : g Unicode code point at 3 : 107 Unicode code point at 0 : 103
4. codePointBefore()
The codePointBefore(char[ ] array, int position) method returns Unicode Point of the character array present before the argumented position.
Syntax:
public static int codePointBefore(char[] array, int position)
or
public static int codePointBefore(char[] array, int position, int start)
Parameters:
- array: The character array.
- position: The index of the character whose preceding Unicode point is needed.
- start: The start index of the character array (optional).
Return Value: The Unicode point of the character before the specified position.
5. codePointCount()
The codePointCount() method returns number of Unicode Point of the sub-character array.
Syntax:
public static int codePointCount(char[] array, int start, int len)
Parameters:
- array: The character array.
- start: The starting index of the sub-array.
- len: The length of the sub-array.
Return Value: The number of Unicode code points in the sub-array.
Exceptions:
6. compareTo()
The compareTo(Character argChar) method compares given character with argumented character.
Syntax:
public int compareTo(Character argChar)
Parameters: argChar: character to be compared with.
Return Values:
- = 0: if both characters are equal
- > 0: if given this character is greater
- < 0: if argumented character is greater
Examples Using codePointBefore(), codePointCount(), and compareTo() Methods:
JAVA // Java program explaining Character class methods // codePointBefore(), codePointCount(), compareTo() import java.lang.Character; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Use of codePointBefore() char[] arg = new char[] { 'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's' }; int position = 4; int val = Character.codePointBefore(arg, position); int val1 = Character.codePointBefore(arg, 1); int val2 = Character.codePointBefore(arg, 3, 1); System.out.println( "Unicode code point before " + position + " : " + val ); System.out.println( "Unicode code point before 1 : " + val1 ); System.out.println( "Unicode code point before 3" +" to 1 : " + val2); System.out.println(); // Use of codePointCount() int count = Character.codePointCount(arg, 1,3 ); System.out.println("No. of Unicode points : " + count); System.out.println(); // Use of compareTo() Character g1 = new Character('g'); Character g2 = new Character('o'); int check = g1.compareTo(g2); System.out.println("g1 < g2 : " + check); int check1 = g2.compareTo(g1); System.out.println("g2 > g1 : " + check1); int check2 = g2.compareTo(g2); System.out.println("g2 = g2 : " + check2); } } OutputUnicode code point before 4 : 107 Unicode code point before 1 : 103 Unicode code point before 3 to 1 : 101 No. of Unicode points : 3 g1 < g2 : -8 g2 > g1 : 8 g2 = g2 : 0
7. equals()
The equals() method compares the present char object with the argumented char object.
Syntax:
public boolean equals(Object charObj)
- Parameter: charObj: char object to compare with.
- Returns: true if both the objects are equal, else false.
8. getNumericValue()
The getNumericValue(char arg) method returns int value for the specific Unicode character. A - Z value ranges u0041 to u005A a -z value ranges u0061 to u007A
Syntax:
public static int getNumericValue(char arg)
- Parameters: arg: The char whose numeric value is to be retrieved.
- Return Value: The integer value of the specified Unicode character. If the character does not have a numeric value, -1 is returned.
9. getType()
The getType(char arg) method identifies the general type of character A - Z value ranges u0041 to u005A a -z value ranges u0061 to u007A.
Syntax:
public static int getType(char arg)
- Parameter: arg: The char whose type category is to be identified.
- Return Value: An integer value representing the character's general type.
Example: Using equals(), getNumericValue(), and getType() Methods:
JAVA // Java program explaining Character class methods // equals(), getNumericValue(), getType() import java.lang.Character; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Use of equals() method Character g1 = new Character('g'); Character g2 = new Character('O'); boolean check = g1.equals(g2); boolean check1 = g1.equals(g1); System.out.println("Are g and o equal?: " + check); System.out.println("Are g and g equal?: " + check1); System.out.println(); // Use of getNumericValue() method int c = Character.getNumericValue(g1); int c1 = Character.getNumericValue(g2); System.out.println("Int value for g: " + c); System.out.println("Int value for A: " + c1); System.out.println(); // Use of getType() method Character g3 = new Character('$'); Character g4 = new Character('6'); int r1 = Character.getType(g1); int r2 = Character.getType(g2); int r3 = Character.getType(g3); int r4 = Character.getType(g4); System.out.println("Type for lowercase: " + r1); System.out.println("Type for uppercase: " + r2); System.out.println("Type for currency: " + r3); System.out.println("Type for numeric: " + r4); } } OutputAre g and o equal?: false Are g and g equal?: true Int value for g: 16 Int value for A: 24 Type for lowercase: 2 Type for uppercase: 1 Type for currency: 26 Type for numeric: 9