Introduction to Sockets.IO in NodeJS
Last Updated : 17 Feb, 2025
Socket.IO is a popular library that is used for building real-time web applications. It allows your website and server to talk to each other instantly, making things like live chat and instant updates possible.
- Socket.IO makes it easy to manage WebSocket connections and events.
- It works even with older browsers that don't fully support WebSockets.
Why Use Socket.IO?
Many web applications use a client-server setup, where clients (like web browsers) request things from servers. Traditional web communication often uses HTTP, which can be slow for real-time updates and only allows one message at a time. Socket.IO solves this problem.
- Socket.IO enables instant, two-way communication between clients and servers.
- It's more efficient than traditional HTTP for real-time applications.
Features of Socket.IO
Socket.IO, built on top of Engine.IO, offers several important features that make it a robust choice for real-time web applications:
- Reliability: Maintains connections even when faced with network obstacles like proxies, load balancers, firewalls, and antivirus software.
- Automatic Reconnection: The client automatically attempts to reconnect to the server if the connection is lost.
- Disconnection Detection: Provides mechanisms for both the client and server to detect when the other party has disconnected.
- Multiplexing: Allows multiple communication channels to operate over a single connection, improving efficiency.
- Binary Streaming: Supports the transmission of binary data, such as ArrayBuffers and Blobs.
How Socket.IO Works?
Socket.IO consists of two main components
- Server-side (Node.js): Listens for incoming connections and handles events.
- Client-side (Browser/Frontend): Connects to the server and sends/receives messages.
How Communication Happens
- A client connects to the Socket.IO server.
- The server acknowledges the connection.
- Both parties can send and receive messages using events.
- If the connection is lost, Socket.IO automatically tries to reconnect.
Installing and Setting Up Socket.IO
Required for Installation of Sockets.IO
1. Server-side: Install the Socket.IO server library using npm
npm install --save socket.io
2. Client-side: The Socket.IO client library is usually served directly from your Node.js server. You typically include it in your HTML like this
<script src="/socket.io/socket.io.js"></script>
Alternatively, for use in a Node.js client (less common), you can install it via:
npm install --save socket.io-client
Example
This example demonstrates a simple upvote button using Socket.IO to show real-time communication.
1. Project Setup: Create a project directory and initialize it with npm:
npm init -y
This creates a package.json file.
2. Install Express.js: Install Express.js, a web framework for Node.js:
npm install --save [email protected]
3. Create index.js: Create the main application file:
JavaScript var app = require('express')(); var http = require('http').createServer(app); const PORT = 3000; app.get('/', function(req, res) { res.send('Hello World'); }); http.listen(PORT, function() { console.log('listening on *:' + PORT); }); In this example
- This code sets up a basic Express app that listens on port 3000 and sends "Hello World" to the client.

4. Serving HTML: Serve HTML File: Modify index.js to serve an HTML file
JavaScript app.get('/', function(req, res) { res.sendFile(__dirname + '/public/index.html'); });
5. Create index.html: Create the public directory and add index.html
html <html> <head> <title>SocketIO Upvote</title> <style> .container { width: 80%; margin: 1rem auto; } .text-justify { text-align: justify; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <p class="text-justify">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet...</p> </div> <div class="container"> <center> <button id="upvote-btn">Upvote</button> <p id="upvote-count">0 Upvotes</p> </center> </div> </body> </html> This HTML sets up the basic layout with an upvote button and a counter display.

6. Integrating Socket.IO: For installing server side module, run the following command,
$ npm install --save socket.io
Modify index.js
JavaScript var io = require('socket.io')(http); // ... (rest of the code) io.on('connection', function(socket) { console.log("a user has connected!"); }); - This initializes Socket.IO and listens for client connections.
7. Add Client-Side Socket.IO: Add the following script to your index.html before the closing </body> tag:
<script src="/socket.io/socket.io.js"></script>
<script>
var socket = io();
</script>
- This includes the Socket.IO client library and establishes a connection to the server.
Restart the project again from the console and try opening the localhost on multiple tabs and browsers. Each of them will act as a unique client connection. The log message will print every time a connection is established between the client and the server.
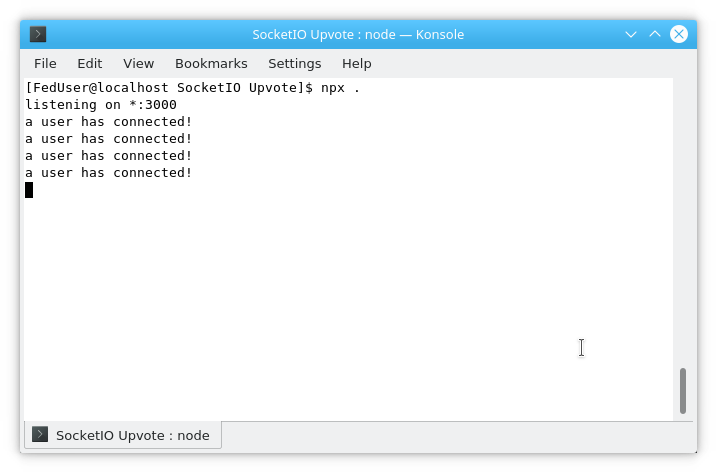
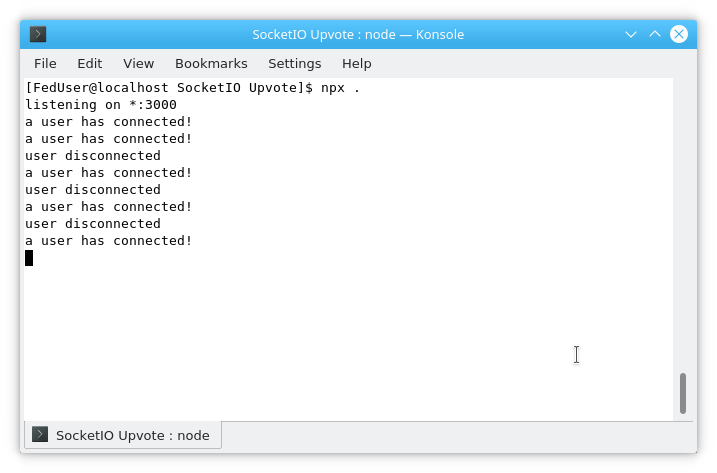
8. Handle Disconnections: Add a disconnect handler to index.js:
io.on('connection', function(socket) {
// ...
socket.on('disconnect', function() {
console.log('user disconnected');
});
});- This logs when a user disconnects (closes the tab, refreshes, etc.).
Emitting events
Add an event listener to the upvote button in index.html:
JavaScript var socket = io(); var btn = document.getElementById("upvote-btn"); var upvote_val = false; btn.addEventListener("click", function(e) { e.preventDefault(); upvote_val = upvote_val ? false : true; socket.emit("upvote-event", upvote_val); }); - This code emits an upvote-event when the button is clicked.
Listen for Upvote Event (Server-Side): Add a listener in index.js:
io.on('connection', function(socket) {
// ...
socket.on('upvote-event', function(upvote_flag) {
console.log('upvote: ' + upvote_flag);
});
});- This logs the upvote-event data on the server.

Broadcasting Upvotes
Broadcast Upvote Count (Server-Side): Update index.js to broadcast the upvote count:
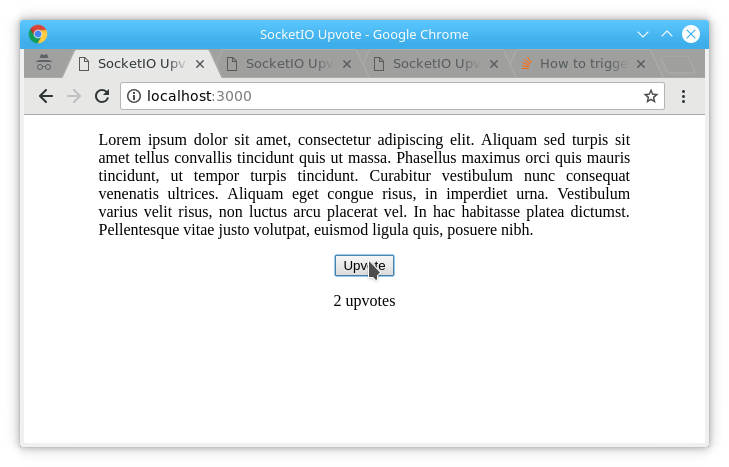
JavaScript let upvote_count = 0; io.on('connection', function(socket) { // ... socket.on('upvote-event', function(upvote_flag) { upvote_count += upvote_flag ? 1 : -1; let f_str = upvote_count + (upvote_count == 1 ? ' upvote' : ' upvotes'); io.emit('update-upvotes', f_str); }); }); - This code increments/decrements the upvote count and broadcasts it to all connected clients.
Update Upvote Count (Client-Side): Update index.html to receive the broadcast:
<script>
// ...
socket.on('update-upvotes', function(f_str) {
document.getElementById('upvote-count').innerHTML = f_str;
});
</script>
This updates the upvote count display on all clients.
Getting this example: Find complete code for this example on Github here.
Best Practices for Using Socket.IO
- Handle disconnections gracefully: Clean up resources when clients disconnect.
- Implement reconnection logic: Allow clients to automatically reconnect if the connection drops.
- Use acknowledgements: Ensure messages are delivered reliably.
- Sanitize user input: Prevent security vulnerabilities.
Similar Reads
NodeJS Introduction NodeJS is a runtime environment for executing JavaScript outside the browser, built on the V8 JavaScript engine. It enables server-side development, supports asynchronous, event-driven programming, and efficiently handles scalable network applications. NodeJS is single-threaded, utilizing an event l
5 min read
How to Create a Chat App Using socket.io in NodeJS? Socket.io is a JavaScript library that enables real-time, bidirectional, event-based communication between the client and server. It works on top of WebSocket but provides additional features like automatic reconnection, broadcasting, and fallback options.What We Are Going to Create?In this article,
5 min read
How to Manage Users in Socket.io in Node.js ? Socket.IO is a library that enables real-time, bidirectional, and event-based communication between the browser and the server. Managing users in Socket.io and Node.js typically involves handling user connections, disconnections, and broadcasting messages to specific users or groups of usersPrerequi
9 min read
What is REST API in NodeJS? NodeJS is an ideal choice for developers who aim to build fast and efficient web applications with RESTful APIs. It is widely adopted in web development due to its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, making it suitable for handling numerous simultaneous requests efficiently.But what makes NodeJ
7 min read
Servers, streams and sockets in Node Node.js Server Node.js is a javascript framework for writing Server-side applications. A Node.js server provides the mechanisms for connecting to a service and sending/receiving data. It achieves this through TCP or UDP connections. Developers can hence create their own server and test their app dep
5 min read