Introduction to Dynamic Programming on Trees
Last Updated : 04 Dec, 2024
Dynamic Programming is a technique to solve problems by breaking them down into overlapping sub-problems which follows the optimal substructure. There are various problems using DP like subset sum, knapsack, coin change etc. DP can also be applied to trees to solve some specific problems.
Given a binary tree with n nodes and n-1 edges, calculate the maximum sum of the node values from the root to any of the leaves without re-visiting any node.
Examples:
Input:
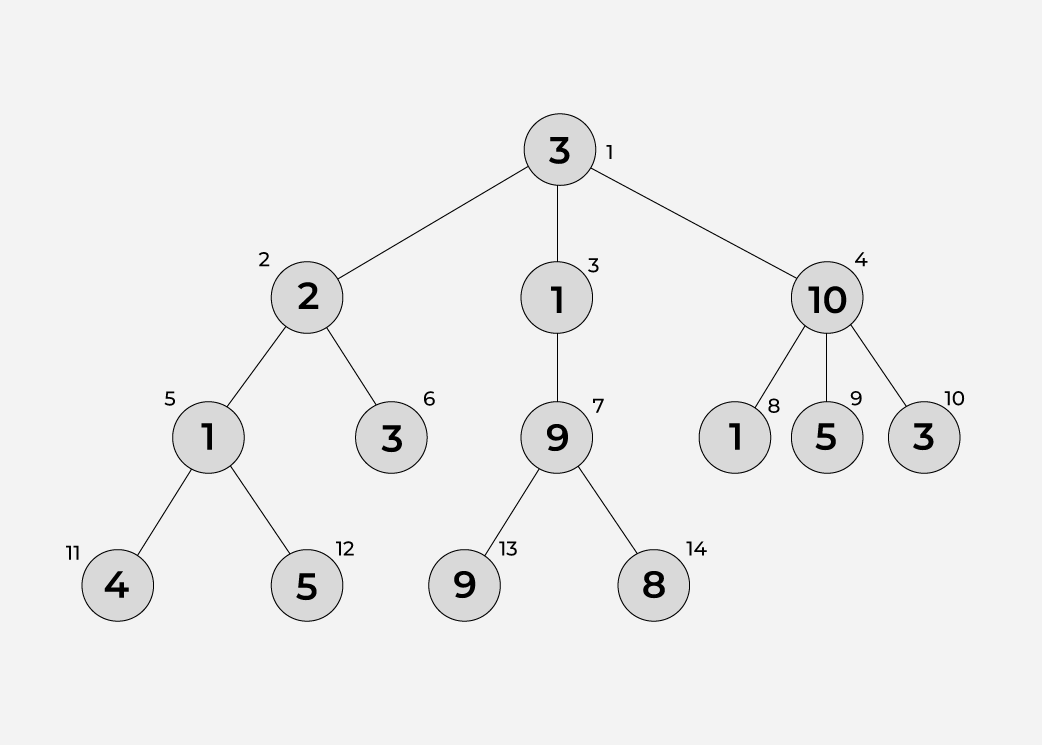
Output: 22
Explanation: Given above is a diagram of a tree with n = 14 nodes and n-1 = 13 edges.The below shows all the paths from root to leaves:
- 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 4: sum of all node values = 10
- 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 5: sum of all node values = 11
- 3 -> 2 -> 3: sum of all node values = 8
- 3 -> 1 -> 9 -> 9: sum of all node values = 22
- 3 -> 1 -> 9 -> 8 : sum of all node values = 21
- 3 -> 10 -> 1: sum of all node values = 14
- 3 -> 10 -> 5 : sum of all node values = 18
- 3 -> 10 -> 3 : sum of all node values = 16
The answer is 22, as Path 4 has the maximum sum of values of nodes in its path from a root to leaves.
The greedy approach fails in this case. Starting from the root and take 3 from the first level, 10 from the next level and 5 from the third level greedily. Result is path -7 if after following the greedy approach, hence do not apply greedy approach over here.
Using Recursion - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
For the recursive approach, the task is to calculate the maximum sum from the root to any leaf node. At each node, there are two cases:
- Add the value of the current node to the currentSum and proceed to its left and right children recursively.
- If the node is a leaf (both left and right children are null), compare the currentSum with the maxSum. Update maxSum if currentSum is greater.
Mathematically, the recurrence relation can be expressed as:
- maxSumPath(node) = node->data + max(maxSumPath(node->left), maxSumPath(node->right))
Base Case:
If the current node is nullptr, return from the recursion (no addition to the sum is possible).
C++ // C++ code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion. #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Helper function to find maximum sum path void maxSumPath(Node *node, int currentSum, int &maxSum) { if (node == nullptr) { return; } // Add current node's data to the path sum currentSum += node->data; // Check if leaf node is reached, update maxSum if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) { if (currentSum > maxSum) { maxSum = currentSum; } } else { // Recurse for left and right subtrees maxSumPath(node->left, currentSum, maxSum); maxSumPath(node->right, currentSum, maxSum); } } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf int maxRootToLeafSum(Node *root) { int maxSum = 0; maxSumPath(root, 0, maxSum); return maxSum; } int main() { // Harcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // /\ / // 4 5 6 Node *root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(3); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->left = new Node(6); cout << maxRootToLeafSum(root) << endl; return 0; } // Java code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion. import java.util.*; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { static void maxSumPath(Node node, int currentSum, int[] maxSum) { if (node == null) { return; } // Add current node's data to the path sum currentSum += node.data; // Check if leaf node is reached, update maxSum if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { if (currentSum > maxSum[0]) { maxSum[0] = currentSum; } } else { // Recurse for left and right subtrees maxSumPath(node.left, currentSum, maxSum); maxSumPath(node.right, currentSum, maxSum); } } // Function to get the maximum sum from // root to any leaf static int maxRootToLeafSum(Node root) { int[] maxSum = {0}; maxSumPath(root, 0, maxSum); return maxSum[0]; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // /\ / // 4 5 6 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); System.out.print(maxRootToLeafSum(root)); } } # Python code to calculate the maximum sum from root # to leaf node using recursion. class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Helper function to find maximum sum path def max_sum_path(node, current_sum, max_sum): if node is None: return # Add current node's data to the path sum current_sum += node.data # Check if leaf node is reached, update max_sum if node.left is None and node.right is None: max_sum[0] = max(max_sum[0], current_sum) else: # Recurse for left and right subtrees max_sum_path(node.left, current_sum, max_sum) max_sum_path(node.right, current_sum, max_sum) # Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf def max_root_to_leaf_sum(root): max_sum = [0] max_sum_path(root, 0, max_sum) return max_sum[0] if __name__ == "__main__": # Hardcoded binary tree # 1 # / \ # 2 3 # / \ / # 4 5 6 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.left = Node(6) print(max_root_to_leaf_sum(root))
// C# code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion. using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Helper function to find maximum sum path static void MaxSumPath(Node node, int currentSum, int[] maxSum) { if (node == null) { return; } // Add current node's data to the path sum currentSum += node.data; // Check if leaf node is reached, update maxSum if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { if (currentSum > maxSum[0]) { maxSum[0] = currentSum; } } else { // Recurse for left and right subtrees MaxSumPath(node.left, currentSum, maxSum); MaxSumPath(node.right, currentSum, maxSum); } } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf static int MaxRootToLeafSum(Node root) { int[] maxSum = {0}; MaxSumPath(root, 0, maxSum); return maxSum[0]; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ / // 4 5 6 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); Console.WriteLine(MaxRootToLeafSum(root)); } } // JavaScript code to calculate the maximum sum // from root to leaf node using recursion. class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Helper function to find the maximum sum path function maxSumPath(node, currentSum, maxSum) { if (node === null) { return; } // Add current node's data to the path sum currentSum += node.data; // Check if leaf node is reached, update maxSum if (node.left === null && node.right === null) { if (currentSum > maxSum[0]) { maxSum[0] = currentSum; } } else { // Recurse for left and right subtrees maxSumPath(node.left, currentSum, maxSum); maxSumPath(node.right, currentSum, maxSum); } } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf function maxRootToLeafSum(root) { let maxSum = [0]; maxSumPath(root, 0, maxSum); return maxSum[0]; } // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ / // 4 5 6 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); console.log(maxRootToLeafSum(root)); Using Top-Down DP (Memoization) - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
1. Optimal Substructure: The solution to the maximum sum problem can be derived from the optimal solutions of smaller subproblems. At any given node, the maximum path sum is the sum of the node’s value and the maximum of the sums obtained from its left and right children.
2. Overlapping Subproblems: The maximum sum for a node may be recomputed multiple times. Using a memoization table we:
- Check if the result for a node exists.If not, compute and store it.
- This avoids redundant calculations and ensures each node is processed once.
Memoization Condition: If the result for the current node is already stored in the memoization table:
- if memo[node] exists, return memo[node]

C++ // C++ code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion and memoization. #include <iostream> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Helper function to find maximum sum path with memoization int maxSumPath(Node *node, unordered_map<Node*, int> &memo) { if (node == nullptr) { return 0; } // Check if the result is already in memo if (memo.find(node) != memo.end()) { return memo[node]; } // If it's a leaf node, the maximum sum is its own data if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) { return memo[node] = node->data; } // Recurse for left and right subtrees and // choose the maximum path int leftSum = maxSumPath(node->left, memo); int rightSum = maxSumPath(node->right, memo); // Store the computed result in memo memo[node] = node->data + max(leftSum, rightSum); return memo[node]; } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf int maxRootToLeafSum(Node *root) { unordered_map<Node*, int> memo; return maxSumPath(root, memo); } int main() { // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // /\ / // 4 5 6 Node *root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(3); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->left = new Node(6); cout << maxRootToLeafSum(root) << endl; return 0; } // Java code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion and memoization. import java.util.HashMap; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Helper function to find maximum sum path with memoization static int maxSumPath(Node node, HashMap<Node, Integer> memo) { if (node == null) { return 0; } // Check if the result is already in memo if (memo.containsKey(node)) { return memo.get(node); } // If it's a leaf node, the maximum sum is its own data if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { memo.put(node, node.data); return node.data; } // Recurse for left and right subtrees and // choose the maximum path int leftSum = maxSumPath(node.left, memo); int rightSum = maxSumPath(node.right, memo); // Store the computed result in memo int result = node.data + Math.max(leftSum, rightSum); memo.put(node, result); return result; } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf static int maxRootToLeafSum(Node root) { HashMap<Node, Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return maxSumPath(root, memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // /\ / // 4 5 6 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); System.out.print(maxRootToLeafSum(root)); } } # Python code to calculate the maximum sum from root # to leaf node recursion and memoization. class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # Helper function to find maximum sum # path with memoization def max_sum_path(node, memo): if node is None: return 0 # Check if the result is already in memo if node in memo: return memo[node] # If it's a leaf node, the maximum sum # is its own data if node.left is None and node.right is None: memo[node] = node.data return memo[node] # Recurse for left and right subtrees and # choose the maximum path left_sum = max_sum_path(node.left, memo) right_sum = max_sum_path(node.right, memo) # Store the computed result in memo memo[node] = node.data + max(left_sum, right_sum) return memo[node] # Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf def max_root_to_leaf_sum(root): memo = {} return max_sum_path(root, memo) if __name__ == "__main__": # Hardcoded binary tree # 1 # / \ # 2 3 # /\ / # 4 5 6 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.left = Node(6) print(max_root_to_leaf_sum(root)) // C# code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion and memoization. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Helper function to find maximum sum path with memoization static int MaxSumPath(Node node, Dictionary<Node, int> memo) { if (node == null) { return 0; } // Check if the result is already in memo if (memo.ContainsKey(node)) { return memo[node]; } // If it's a leaf node, the maximum sum is its own data if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { memo[node] = node.data; return node.data; } // Recurse for left and right subtrees and choose the maximum path int leftSum = MaxSumPath(node.left, memo); int rightSum = MaxSumPath(node.right, memo); // Store the computed result in memo int result = node.data + Math.Max(leftSum, rightSum); memo[node] = result; return result; } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf static int MaxRootToLeafSum(Node root) { Dictionary<Node, int> memo = new Dictionary<Node, int>(); return MaxSumPath(root, memo); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // /\ / // 4 5 6 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); Console.WriteLine(MaxRootToLeafSum(root)); } } // JavaScript code to calculate the maximum sum from root // to leaf node using recursion and memoization. class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Helper function to find maximum sum // path with memoization function maxSumPath(node, memo) { if (node === null) { return 0; } // Check if the result is already in memo if (memo.has(node)) { return memo.get(node); } // If it's a leaf node, the maximum sum is its own data if (node.left === null && node.right === null) { memo.set(node, node.data); return node.data; } // Recurse for left and right subtrees and // choose the maximum path const leftSum = maxSumPath(node.left, memo); const rightSum = maxSumPath(node.right, memo); // Store the computed result in memo const result = node.data + Math.max(leftSum, rightSum); memo.set(node, result); return result; } // Function to get the maximum sum from root to any leaf function maxRootToLeafSum(root) { const memo = new Map(); return maxSumPath(root, memo); } // Hardcoded binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // /\ / // 4 5 6 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); console.log(maxRootToLeafSum(root));