HTML | DOM Style alignContent Property
Last Updated : 10 Aug, 2022
The DOM Style alignContent property is used to align the items of a flexible container when they do not use all available space on the cross-axis.
Syntax:
- To get the alignContent Property
object.style.alignContent
- To set the alignContent Property
object.style.alignContent = "stretch | center | flex-start | flex-end | space-between | space-around | initial | inherit"
Property Values:
- stretch: This is used to stretch the items to fit the container.
- center: This is used to center the items in the container.
- flex-start: This is used to position the items at the beginning of the container.
- flex-end: This is used to position the items at the end of the container.
- space-between: This is used to position the items with even space between the lines. The first item is at the first line and the last item at the last line. The other items are spaced in between.
- space-around: This is used to position the items with equal space around them.
- initial: This is used to set this property to its default value.
- inherit: This inherits the property from its parent.
Return Values: It returns a string value which representing the align-content property of an element.
Example-1: Using the stretch value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title>DOM Style alignContent property</title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; /* setting to space-around to observe the effect of 'stretch'*/ align-content: space-around; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "stretch"</p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "stretch"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Example-2: Using the center value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "center"</p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "center"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Example-3: Using the flex-start value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "flex-start"</p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "flex-start"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Example-4: Using the flex-end value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b> DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "flex-end" </p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "flex-end"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Example-5: Using the space-between value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "space-between" </p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "space-between"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Example-6: Using the space-around value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "space-around" </p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "space-around"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Example-7: Using the initial value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; /* setting to space-around to observe the effect of 'initial' */ align-content: space-around; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "initial" </p> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "initial"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:
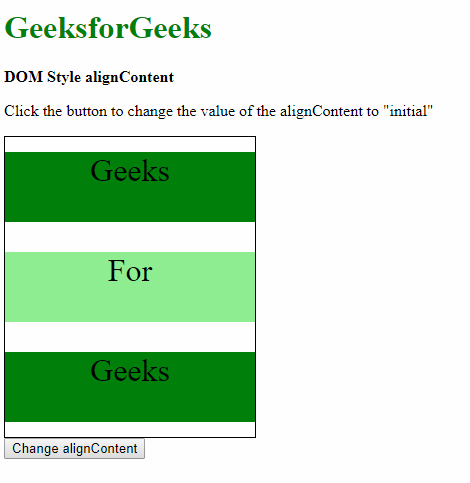
- After clicking the button:

Example-8: Using the inherit value.
HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <title> DOM Style alignContent property </title> <head> <style> #parent { /* Set the align-content of parent to observe effect of 'inherit' */ align-content: flex-end; } .main { width: 250px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid; display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; } .main div { width: 250px; height: 70px; font-size: 2rem; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="color: green"> GeeksforGeeks </h1> <b>DOM Style alignContent</b> <p>Click the button to change the value of the alignContent to "inherit" </p> <div id="parent"> <div class="main"> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> <div style="background-color:lightgreen;"> For </div> <div style="background-color:green;"> Geeks </div> </div> </div> <button onclick="changeAlign()"> Change alignContent </button> <script> function changeAlign() { document.querySelector('.main').style.alignContent = "inherit"; } </script> </body> </html> Output:
- Before clicking the button:

- After clicking the button:

Supported Browsers: The browser supported by alignContent property are listed below:
- Google Chrome 29.0 and above
- Edge 12.0 and above
- Internet Explorer 11.0 and above
- Firefox 28.0 and above
- Opera 12.1 and above
- Safari 9.0 and above