Understanding the history of changes in a codebase is important for effective collaboration and maintenance. One powerful tool in Git for this purpose is git-blame. This command helps developers identify who made specific changes to a file, which can be invaluable for debugging, understanding the evolution of code, and attributing contributions. In this guide, we will explore how to use git-blame, its options, and best practices to make the most out of this powerful command.
What is git-blame?
git-blame is a Git command that annotates each line in a file with information about the last commit that modified the line. This information includes the commit hash, the author, the date of the change, and optionally, the line number. By using git-blame, you can track the origin of each line of code, making it easier to understand the history and context of changes.
Why Use git-blame?
- Debugging: When you encounter a bug,
git-blame can help you find out who last modified the relevant lines, providing a starting point for further investigation. - Code Reviews: During code reviews, understanding the history of a piece of code can provide insights into why certain decisions were made.
- Collaboration: Knowing who wrote a particular line of code can help you reach out to the right person for discussions or clarifications.
Syntax:
git blame [options] <file-name>
How to Use git-blame
Let's say in a git repository we have to identify the author details and commit information of a given line of code in a given file of the repository. The same is shown below. The command is illustrated below with help of an example
Step 1: Move to an empty folder and initialize it with an empty git repository.

Step 2: Clone the repository for which you want the information. Here I am cloning a famous repository create-react-app from GitHub. Make sure to change the directory to the cloned repository.
 cloning create-react-app repository from GitHub
cloning create-react-app repository from GitHubStep 3: To get the author name and commit information, execute the git blame command as shown below. Replace the <file-name> option with the relative path of the file from the current directory for which you want details:
git blame <file-name>
Step 4: Here I want details for the file CONTRIBUTING.md which is present in the same directory I am currently at. So, I will execute the below command:
git blame CONTRIBUTING.md
Output:
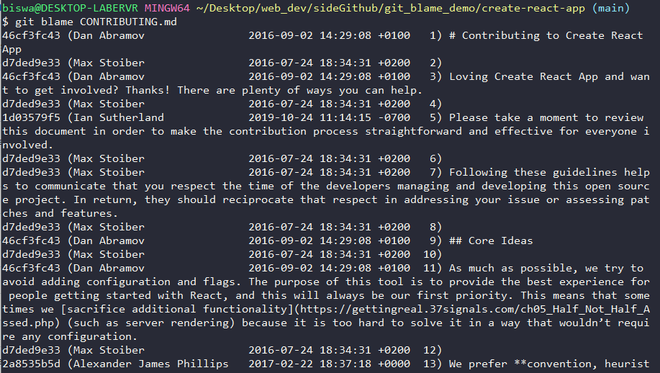 The output of the git blame command on the CONTRIBUTING.md file
The output of the git blame command on the CONTRIBUTING.md fileTip: Observe that the last column of output displays the line number along with the code on that line.
Output study
Let's examine the first line of output:

| Commit Id | Author Name | Timestamp | Code |
|---|
| 46cf3fc43 | Dan Abramov | 2016-09-02 14:29:08 +0100 | # Contributing to Create React App |
- Commit Id: It is the commit Id of the last commit in which this line was modified. In upcoming lines, we will use it to get the details of the commit.
- Author Name: It is the name of the author who last modified the given line of code. We will see how to get the author's email id instead of the author's name.
- Timestamp: It is the date and time when the commit was made expressed in standard notation. We can get the raw timestamp using the -t option as shown below:
git blame -t CONTRIBUTING.md
Output is shown below:
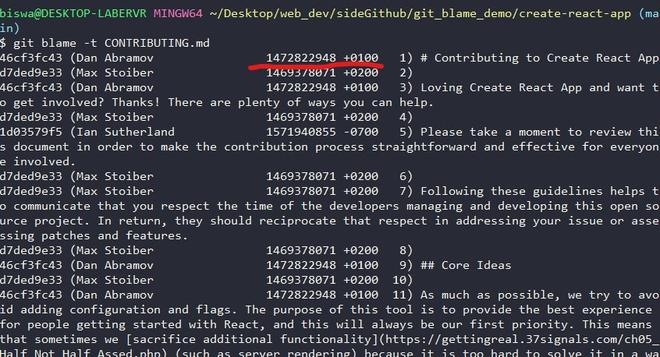 raw timestamp using -t option with the git blame command
raw timestamp using -t option with the git blame commandViewing the commit details: In order to view the commit details, we will execute the git log command with the commit id for which we want the details. So, copy the commit id from the previous output of the git blame command. In my case, I want the commit details for the first line of the CONTRIBUTING.md file, so I will copy the commit id from the previous output of the git blame command. The commit id for that is 46cf3fc43.
Now, execute the below command. Replace <commit-id> with the commit id that you copied just now.
git log -p <commit-id>
In my case the command is below:
git log -p 46cf3fc43
The git log command helps to view the commit history. The -p or --patch option shows the author details and changes (addition or deletion) in the code in the commit of commit id provided.
Options with git blame: Git provides various options with the git blame command for viewing the details of modification in code in a file. Some commonly used options are given below:
To view output for a range of lines
git blame -L start-line,end-line <file-name>
The below command shows output for lines 2 to 5 both inclusive.
git blame -L 2,5 CONTRIBUTING.md
The output is shown below:
 The output of the git blame command for a given range of lines
The output of the git blame command for a given range of linesNote: You will get the same output for command - git blame -L 4,+3 README.md. Here 4,+3 signifies output for 3 lines starting from the fourth line.
To view the author email id
git blame -e CONTRIBUTING.md
The above command will show the author's email id instead of the author's name in the result. The output is shown below:

To view changes not older than the given time
git blame --since=3.months-- CONTRIBUTING.md
The above command is used to view git blame output for commits not older than 3 months for the file CONTRIBUTING.md. The output is shown below:
 The output of the git blame command with commits not older than three months (without removing unrequired commits)
The output of the git blame command with commits not older than three months (without removing unrequired commits)In the above command, we can see that it shows several commits with commit id starting with ^. The caret symbols signify the commits made before the time specified, in our case, it is three months. Hence we need to filter out them from our output. To tackle that we can modify our code as below:
git blame --since=3.months -- CONTRIBUTING.md | grep -v '^\^'
The above code simply filters the output after removing commits starting with the ^ symbol. Hence, the output shows commits not older than three months (from the time the code is executed). The result is shown below:
 The output of the git blame command with commits not older than three months (after removing unrequired commits)
The output of the git blame command with commits not older than three months (after removing unrequired commits)An alternate option to the command line (GUI based): Git hosting sites like - GitHub, Bitbucket, GitLab offer GUI displays for git blame, which gives a clear display of modification history in a file.
Example: GitHub
Step 1: Navigate to the file for which you want to see the modification history and click on the Blame option as shown below.
Step 2: The structure of output is described in the image below :
 labeled picture of blame option on GitHub
labeled picture of blame option on GitHubHence, we saw that git blame is a very useful command in inspecting a repository. It gives a great insight into the commit history and can be used along with other git commands to get desired results.
Similar Reads
How to Undo “git commit –amend"? Git is a powerful tool for version control, helping developers keep track of changes in their code and collaborate effectively. One handy feature is the git commit --amend command, which allows you to modify your most recent commit. In this article, we will see how to Undo “git commit –amend".Unders
5 min read
How to Use Git Shell Commands? Git is a powerful version control system that is important for managing source code in modern software development. While there are many graphical user interfaces (GUIs) available for Git, mastering Git shell commands can significantly enhance your productivity and control over your repositories. Th
3 min read
How to Undo a Commit in Git ? Git offers several ways to backtrack and correct mistakes, making it a powerful tool for developers. In this article, we will explore various methods to undo a commit in Git, ensuring that you can choose the best approach for your specific system.Below are the approaches to Undo a commit in Git:Tabl
3 min read
How to Back Commit in Git? In this article, we are covering how to undo commits in Git. Sometimes, you might make mistakes or realize you need to revert changes you made in a previous commit. Luckily, Git offers a few ways to undo commits. Table of Content Approach 1: Using 'git revert'Approach 2: Using 'git reset' Approach 1
4 min read
How to Check Git Logs? Git is the most popular version control system which records the changes made to our project over time in a special database called a repository. We can look at our project and see who has made what changes when and why and if we screw something up we can easily revert our project back to an earlier
8 min read