How to Push Git Branch to Remote?
Last Updated : 16 Feb, 2022
Git is the most popular version control system which records the changes made to our project over time in a special database called a repository. We can look at our project and see who has made what changes when and why and if we screw something up we can easily revert our project back to an earlier state. In this article, we will see the essential commands for pushing a git branch to a remotely hosted repository or project you can say and what is the core meaning of these commands.
Key Terminologies are as follows:
- init: It is basically a part of a git command with which we initialize git in a non-git repository.
- status: It is also a part of a command with which we can see the current state of any git repository.
- log: It is a record of all the commits done in the repository.
- commit: A commit is a snapshot of the git repository at one point in time.
- commit id: It is a 40 character hexadecimal value and it’s a unique identifier that git generates every time we make a commit to our repository.
So let us begin and see how to push a git branch to a remotely hosted repository as stepwise justified below as follows:
Git init
So before we will start pushing a branch directly, we need to create a local repository in our local system to push to the remotely hosted repository. First of all, we need to initialize git in an existing directory in our local system. For that purpose, we use the below command,
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 ~ (master) $ cd "E:\git pushing"
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing $ git status fatal: not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .git
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing $ git init Initialized empty Git repository in E:/git pushing/.git/
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git status On branch main
No commits yet
nothing to commit (create/copy files and use "git add" to track)
Here we can see, first of all, we ran a command "cd <path to the directory". By default, you will be on your C drive but here we are working on a directory that is there in the E drive, so we have to run that command which is basically the command to change the directory.
Then you can see, we tried to run a git command "git status" with which we can see the current state of any git repository. But as it is a non-git repository it is giving us an error "not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .git". So to resolve this issue we have to initialize git in the directory first.
For that purpose, we ran the "git init" command with which we initialize git in a non-git repository. then the git stated to us that it initialized an empty git repository in the current directory and then if we run any git command it will not gonna throw this kind of error (as you can see in the next "git status" command).
git status
So "git status" command is basically the command to know the current state of any existing git repository. In the previous explanation, you saw that by running the command "git status" we get this information from git:
- We are on the default main branch ("On branch main")
- There are no commits yet to be done
- Finally, no files to add to the staging area.
Now we will create a file named "hello_world.cpp" in the directory and then if we run "git status" we will get something like this
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git status On branch main No commits yet Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) hello_world.cpp nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
so basically it is saying that you have a change in the directory that you created a file named "hello_world.cpp" and currently it is untracked.
git add
So to track any change in an existing git repository we have to add it to the staging area and we can commit that change to push all the commits or you can say changes to a remotely hosted repository. For that, we ran the command "git add ."
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git add . Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git status On branch main No commits yet Changes to be committed: (use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage) new file: hello_world.cpp
now we added the changes to the staging area and let's commit those changes.
git commit
To commit all changes which are there in the staging area we have a command "git commit -m "a commit message".
Note: You can only commit those changes which were already staged means which were already there in the staging area.
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git commit -m "created hello_wprld.cpp" [main (root-commit) bb198fb] created hello_wprld.cpp 1 file changed, 8 insertions(+) create mode 100644 hello_world.cpp
Now we have to add a remote origin to tell git that whenever we want to push or pull anything for this current repository you have to do the operations from that remote origin only. So, let's do that
git add origin
To add a remote origin to an existing local repository first of all you have to create a repository in your GitHub account.
Step 1: First of all simply go to the repositories section in your GitHub account and create a new repo by simply clicking on new button
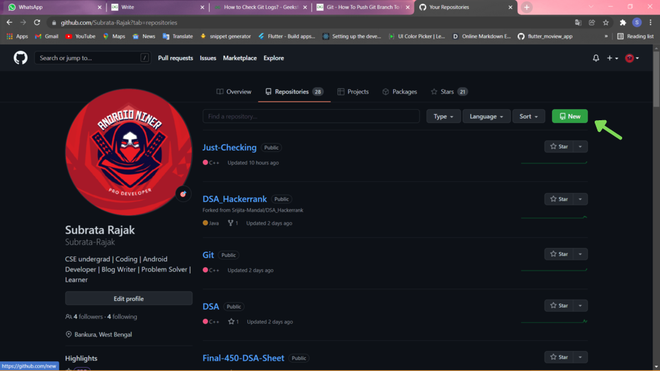 Creating repo in my github account
Creating repo in my github account Step 2: Then Give a nice name to your repo which you just created and create the repo
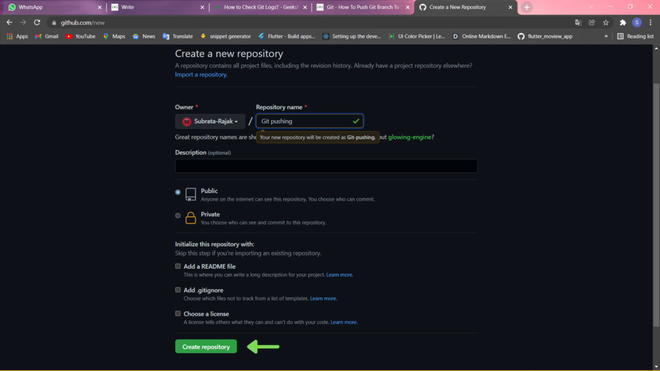 Create a new repo by clicking on create repository button
Create a new repo by clicking on create repository button Step 3: Then simply copy the URL to the repo to add as origin in your local directory
Step 4: Run the command "git remote add origin <the URL to the github repo>"
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git remote add origin https://github.com/Subrata-Rajak/Git-pushing.git Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git remote -v origin https://github.com/Subrata-Rajak/Git-pushing.git (fetch) origin https://github.com/Subrata-Rajak/Git-pushing.git (push)
After executing the command you can simply check whether your remote origin is defined or not by the "git remote -v" command.
Step 6: Finally Git push
To push the branch or you can say to push the changes in the branch to the Github repo you have to run this command "git push origin <the branch name>" in our case the branch name is "main".
Personal@LAPTOP-SKVEHBA2 MINGW64 /e/git pushing (main) $ git push origin main Enumerating objects: 3, done. Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. Delta compression using up to 8 threads Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 327 bytes | 327.00 KiB/s, done. Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 To https://github.com/Subrata-Rajak/Git-pushing.git * [new branch] main -> main
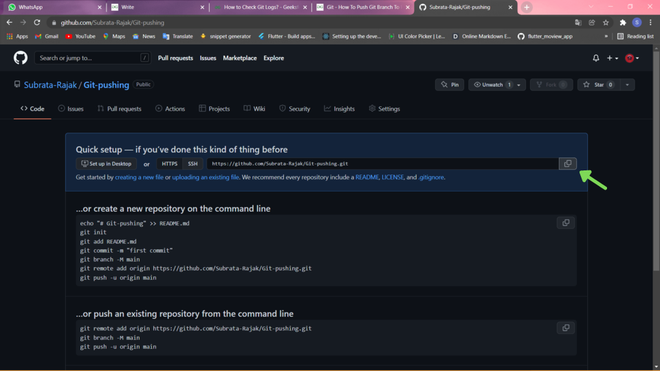
After pushing the changes the repo will look like and this is how you can push a branch to a remotely hosted GitHub repository.
 The repo after pushing changes
The repo after pushing changes