How to Initialize and Compare Strings in Java?
Last Updated : 19 Jun, 2024
String is one of the most basic data types and it is widely used in storing and manipulating pieces of text. One of the fundamental features of strings in Java is their immutability that is once a string is created, it will never be changed. Immutability creates two general ways of initialization with strings in Java using the String Pool.
This article will cover those methods, including examples and explanations.
Syntax of String Declaration:
Before initializing a string, we have to declare it. For that, we can follow the following syntax:
String str;
Different Ways to Initialize Strings in Java
- Initialize String Using Literals (Direct Initialization)
- Initialize String Using new keyword (Object Initialization)
- Initialization using NULL values
Before we moving forward, let us understand the String Pool Concept in Java from the below diagram.
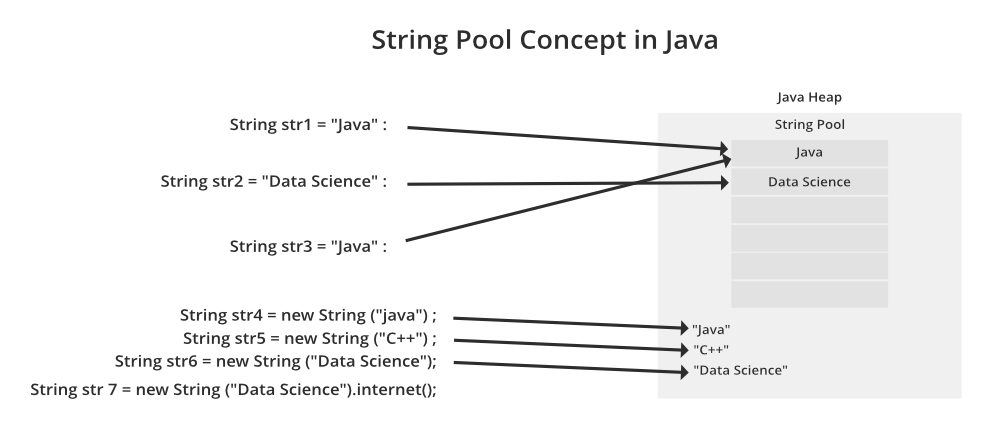
Initialize String using Literals
Direct Initialization(String Constant):
In this method, a String constant object will be created in String pooled area which is inside the heap area in memory. As it is a constant, we can't modify it, i.e. String class is immutable.
Syntax:
String var= "string_to_be_assigned_to_variable_var";
Example:
String str = "GeeksForGeeks";
Illustration:
String str = "GeeksForGeeks"; str = "geeks"; // This statement will make str // point to new String constant "geeks" // rather than modifying the previous // String constant.
Below is the diagram of this approach.

Explanation of the Diagram:
From the left media,
String str = "GeeksForGeeks";
From the right media above,
str = "geeks";
Note: If we again write str = "GeeksForGeeks" as next line, then it first check that if given String constant is present in String pooled area or not. If it present then str will point to it, otherwise creates a new String constant.
Initialize String using "new" keyword
Object Initialization (Dynamic):
In this method, a String object will be created in the heap area (not inside String pooled area as in the upper case). We can't modify it(like in the upper case). Also with the same value, a String constant is also created in the String pooled area, but the variable will point to the String object in the heap area only.
Syntax:
String var = new String("string_to_be_assigned_to_variable_var");
Example:
String str = new String("GeeksForGeeks");
Illustration:
String str = new String("very"); str = "good"; // This creates a string constant "good" in the string pool and 'str' points to it.Below is the diagrammatic explanation of this approach.

Explanation of the Diagram:
In left from the below media,
String str = new String("very"); In right from the below media as follows:
str = "good"
Now, this is a direct assignment, so a String constant with the value "good" is created in the String pooled area and str will point to that.
Note: If we again write str = new String(“very”), then it will create a new object with value “very”, rather than pointing to the available objects in heap area with same value.But if we write str = "very", then it will point to String constant object with value "very", present in String pooled area.
Initialize String using NULL Values
Here, we are going to initialize a string to a NULL value, and it means that it doesn't referencing any object. Which can be done as follows:
Syntax:
String str = null;
Example:
We assign a string to a NULL value and checking whether the variable has a NULL string as value.
Java public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = null; if (str == null) { System.out.println("The string is null."); } else { System.out.println("The string is not null."); } } } OutputThe string is null.
Methods to Compare Strings and their References
1. equals() method: It compares values of string for equality. Return type is boolean. In almost all the situation you can use Objects.equals().
Example:
String s1 = "Ram";
String s2 = "Ram";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
2. == operator: It compares references not values. Return type is boolean. == is used in rare situations where you know you're dealing with interned strings.
Example:
String s1 = "Ram";
String s2 = new String("Ram");
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
3. compareTo() method: It compares values lexicographically and returns an integer value that describes if first string is less than, equal to, or greater than the second string. For example, if str1 and str2 are two string variables then refer below as follows:
- str1 == str2 : return 0
- str1 > str2 : return a positive value
- str1 < str2 : return a negative value
Note: The positive and negative values returned by compareTo method is the difference of first unmatched character in the two strings.
Example:
String s1 = "Ram";
String s2 = "Shyam";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // negative value because "Ram" is lexicographically less than "Shyam"
Implementation: We will be discussing how to compare to strings to justify the above said via below example.
Here is a complete example illustrating different ways to initialize and compare strings:
Java // Java program to Illustrate Comparison of Two Strings // Main class public class GFG { // Main driver method public static void main(String[] args) { // Custom input strings to compare String s1 = "Ram"; String s2 = "Ram"; String s5 = "Shyam"; String s3 = new String("Ram"); String s4 = new String("Ram"); // Checking whether strings are equal or not // with help of equals() method System.out.println( " Comparing strings with equals:"); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); System.out.println(s1.equals(s5)); String nulls1 = null; String nulls2 = null; // NullPointerException will be throws if // we try to compare nulls strings // System.out.println(nulls1.equals(nulls2)); // Comparing strings using == operator System.out.println(" Comparing strings with ==:"); System.out.println(s1 == s2); System.out.println(s1 == s3); System.out.println(s3 == s4); System.out.println(nulls1 == nulls2); // Comparing strings via compareTo() method System.out.println( " Comparing strings via compareTo() Method :"); System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s5)); // NullPointerException if we try to compare strings // with usage of compareTo() method // System.out.println(nulls1.compareTo(nulls2)); } } Output Comparing strings with equals: true true false Comparing strings with ==: true false false true Comparing strings via compareTo() Method : 0 -1
Similar Reads
Compare two Strings in Java String in Java are immutable sequences of characters. Comparing strings is the most common task in different scenarios such as input validation or searching algorithms. In this article, we will learn multiple ways to compare two strings in Java with simple examples.Example:To compare two strings in
4 min read
String in Switch Case in Java The switch statement is a multi-way branch statement. It provides an easy way to dispatch execution to different parts of code based on the value of the expression. Basically, the expression can be a byte, short, char, and int primitive data types. Beginning with JDK7, it also works with enumerated
3 min read
How to Optimize String Creation in Java? In Java, strings are frequently used, and optimizing their creation can help improve performance, especially when creating many strings in a program. In this article, we will explore simple ways to optimize string creation in Java.Example:Using the new keyword creates a new string object. This is st
2 min read
Java String compareTo() Method with Examples Strings in Java are objects that are supported internally by an array only which means contiguous allocation of memory for characters. Please note that strings are immutable in Java which means once we create a String object and assign some values to it, we cannot change the content. However, we can
7 min read
Compare two strings lexicographically in Java In this article, we will discuss how we can compare two strings lexicographically in Java. One solution is to use Java compareTo() method. The method compareTo() is used for comparing two strings lexicographically in Java. Each character of both the strings is converted into a Unicode value for comp
3 min read