How to Connect MongoDB with Spring Boot?
Last Updated : 04 Jan, 2025
In recent times MongoDB has been the most used database in the software industry. It's easy to use and learn This database stands on top of document databases it provides the scalability and flexibility that you want with the querying and indexing that you need. In this, we will explain how we connect MongoDB with Spring Boot.
Prerequisites:
Before starting the below software must be installed in your system.
- Java
- Any Spring Boot Supported IDE like STS (Spring Tool Suite), IntelliJ IDE, etc.
- MongoDB
Adding Dependencies
Add the below dependencies in the pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Below is the above dependency in pom.xml file for your reference.

Purpose of this Dependencies:
- spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb: This dependency brings in all the necessary components to work with MongoDB in a Spring Boot application. As name mention it is a starter which means if we don't include this than we have to do so many configuration to work with mongoDb which this package can give us before. Importantly this package gives us so many things including Repositories support, Mapping and Querying with databases.
- spring-boot-starter-web: This dependency sets up the foundation for building web applications, including RESTful services, using Spring MVC (Model-View-Controller) and embedded web servers. This will give us the paradigm for working with APIs.
MongoDB Connection Properties:
There is some important parameter we need to know to connect the MongoDB server with Spring Boot.
- Port (By Default Port - 27017)
- Host (By Default Host - localhost)
- Database Name
- Credential (Optional)
To connect to the MongoDB server, configure the following parameters in your application.properties file:
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.data.mongodb.database=demo
spring.data.mongodb.username=username_value (optional)
spring.data.mongodb.password=password_value (optional)
Note: If there is no username and password set in your MongoDB, you can use the default URI format.
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://your_username:your_password@localhost:27017/demo
Note:
- demo (Database Name)
- By default, you can use like this (if there is no username and password set in your MongoDB) => "spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost:27017/demo"
- By default, we do not need a user and password.
Connect MongoDB with Spring Boot Example Project
For Example, we are using STS (Spring Tool Suite) IDE, and we have created a new Project and added these Spring Data MongoDB, and Spring web dependencies to our project.
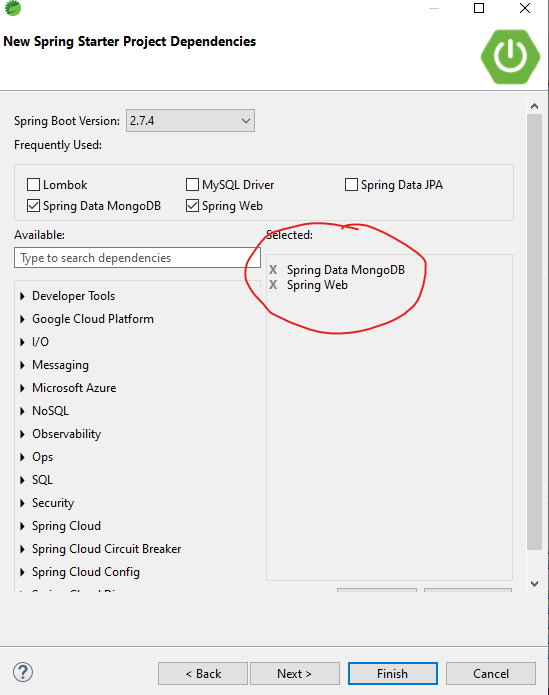
Step 1: Create the "User" Class
Create a User class and annotate it with @Document. This class will represent your MongoDB document.
Java import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document; @Document public class User { @Id private String userId; private String name; private String rollNumber; public User(String name, String rollNumber) { super(); this.name = name; this.rollNumber = rollNumber; } public String getUserId() { return userId; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getRollNumber() { return rollNumber; } public void setRollNumber(String rollNumber) { this.rollNumber = rollNumber; } }
Step 2: Create the Repository Interface
We will create an Interface that will extend MongoRepository with the help of this interface we will perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operation in our database.
Note:
- Please keep in mind if you want to create one or more document (Table) for that every document (Table) you need to define a new interface that will extend MongoRepository.
- MongoRepository<User,String> here "User" is my class name and "String" is my ID data type that we already defined in the User class and annotated with "@Id".
Java import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository; public interface UserRepository extends MongoRepository<User,String>{ }
Step 3: Define MongoDB Connection Parameters
We will define important connection parameters for the MongoDB server. In the application.properties file, define the connection parameters:
Note: # means that line of code is commented.
#spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost
#spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
#spring.data.mongodb.database=userDatabase
server.port=8081
spring.data.mongodb.uri=mongodb://localhost:27017/userDatabase
Step 4: Create the Controller Class
Now this is the final step in this step we will create the controller class from there we will perform CRUD operation in our database.
- We annotate the controller class with @RestController.
- We create an object of our repository and annotate it with @Autowired.
Java import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepo; // Save method is predefine method in Mongo Repository // with this method we will save user in our database @PostMapping("/addUser") public User addUser(@RequestBody User user) { return userRepo.save(user); } // findAll method is predefine method in Mongo Repository // with this method we will all user that is save in our database @GetMapping("/getAllUser") public List<User> getAllUser(){ return userRepo.findAll(); } }
Step 5: Testing with Postman
To test the endpoints, you can use Postman:
Note:
- MongoDB automatically generates a unique ID for each document.
- The JSON keys in the request body must match the variable names in the
User class.
Output:
After executing the above steps, you should be able to add and retrieve user documents from your MongoDB database.
- Add User: Send a POST request to
http://localhost:8081/addUser with a JSON body containing name and rollNumber.

- Get All Users: Send a GET request to
http://localhost:8081/getAllUsers.

Conclusion
Connecting MongoDB with Spring Boot is straightforward and provides a robust way to manage your data. By following these steps, you can easily integrate MongoDB into your Spring Boot application and perform CRUD operations efficiently.
Similar Reads
Spring Boot - Map Entity to DTO using ModelMapper In enterprise applications, we use RESTful services to establish the communication between client and server. The general idea is that the client sends the request to the server and the server responds to that request with some response. Generally, we have three different layers in most of the appli
8 min read
Spring Boot | How to consume JSON messages using Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a stream processing system that lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to publish JSON messages on the console of a Spring boot application using Apache Kafka. In order to learn how to create a Spring Boot project, refer
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to consume string messages using Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging queue used for real-time streams of data. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article we will see how to send string messages from apache kafka to the console of a spring boot application. Appro
3 min read
Spring Boot | How to publish String messages on Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to send string messages to Apache Kafka in a spring boot application. In order to learn how to create a spring boot project, r
2 min read
Spring Boot | How to publish JSON messages on Apache Kafka Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging queue lets you send messages between processes, applications, and servers. In this article, we will see how to send JSON messages to Apache Kafka in a spring boot application. In order to learn how to create a spring boot project, ref
4 min read
Spring Boot - Consume JSON Object From Kafka Topics Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging system. A messaging system lets someone is sending messages between processes, applications, and servers. Broadly Speaking, Apache Kafka is software where topics (A topic might be a category) can be defined and further processed. Applications may connect
4 min read
Spring Boot Kafka Producer Example Spring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Spring Boot Kafka Consumer Example Spring Boot is one of the most popular and most used frameworks of Java Programming Language. It is a microservice-based framework and to make a production-ready application using Spring Boot takes very less time. Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applica
3 min read
Message Compression in Apache Kafka using Spring Boot Generally, producers send text-based data, such as JSON data. It is essential to apply compression to the producer in this situation. Producer messages are transmitted uncompressed by default. There are two types of Kafka compression. 1. Producer-Level Kafka Compression When compression is enabled o
4 min read
Spring Boot - Create and Configure Topics in Apache Kafka Topics are a special and essential component of Apache Kafka that are used to organize events or messages. In other words, Kafka Topics enable simple data transmission and reception across Kafka Servers by acting as Virtual Groups or Logs that store messages and events in a logical sequence. In this
2 min read