Height and Depth of a node in a Binary Tree
Last Updated : 03 Apr, 2025
Given a Binary Tree consisting of n nodes and a integer k, the task is to find the depth and height of the node with value k in the Binary Tree.
Note:
- The depth of a node is the number of edges present in path from the root node of a tree to that node.
- The height of a node is the maximum number of edges from that node to a leaf node in its subtree.
Examples:
Input: k = 25,
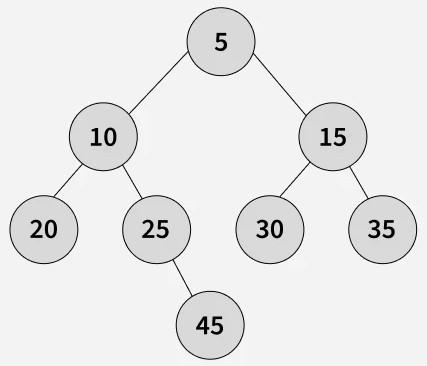
Output: Depth of node 25 = 2
Height of node 25 = 1
Explanation: The number of edges in the path from root node to the node 25 is 2. Therefore, depth of the node 25 is 2.
The number of edges in the longest path connecting the node 25 to any leaf node is 1. Therefore, height of the node 25 is 1.
Input: k = 10,

Output: Depth of node 10 = 1
Height of node 10 = 2
Explanation: The number of edges in the path from root node to the node 10 is 1.
The number of edges in the longest path connecting the node 10 to any leaf node is 2.
[Approach 1] Using Recursion – O(n) time and O(h) space
Depth of a node K (of a Binary Tree) = Number of edges in the path connecting the root to the node K = Number of ancestors of K (excluding K itself).
Follow the steps below to find the depth of the given node:
- If the tree is empty, print -1.
- Otherwise, perform the following steps:
- Initialize a variable, say dist as -1.
- Check if the node K is equal to the given node.
- Otherwise, check if it is present in either of the subtrees, by recursively checking for the left and right subtrees respectively.
- If found to be true, print the value of dist + 1.
- Otherwise, print dist.
Height of a node K (of a Binary Tree) = Maximum number of edges from that node to a leaf node in its subtree.
Follow the steps below to find the height of the given node:
- If the tree is empty, print -1.
- Otherwise, perform the following steps:
- Calculate the height of the left subtree recursively.
- Calculate the height of the right subtree recursively.
- Update height of the current node by adding 1 to the maximum of the two heights obtained in the previous step. Store the height in a variable, say ans.
- If the current node is equal to the given node k, print the value of ans as the required answer.
C++ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Structure of a Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = nullptr; } }; int findDepth(Node* root, int x) { // Base case if (root == nullptr) return -1; int dist = -1; // Check if x is current node= if ((root->data == x) // Otherwise, check if x is // present in the left subtree || (dist = findDepth(root->left, x)) >= 0 // Otherwise, check if x is // present in the right subtree || (dist = findDepth(root->right, x)) >= 0) // Return depth of the node return dist + 1; return dist; } int findHeightUtil(Node* root, int x, int& height) { if (root == nullptr) { return -1; } // Store the maximum height of // the left and right subtree int leftHeight = findHeightUtil( root->left, x, height); int rightHeight = findHeightUtil( root->right, x, height); // Update height of the current node int ans = max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; // If current node is the required node if (root->data == x) height = ans; return ans; } int findHeight(Node* root, int x) { // Store the height of // the given node int h = -1; // Stores height of the Tree int maxHeight = findHeightUtil(root, x, h); // Return the height return h; } int main() { Node* root = new Node(5); root->left = new Node(10); root->right = new Node(15); root->left->left = new Node(20); root->left->right = new Node(25); root->left->right->right = new Node(45); root->right->left = new Node(30); root->right->right = new Node(35); int k = 25; cout << "Depth: " << findDepth(root, k) << "\n"; cout << "Height: " << findHeight(root, k); return 0; } // Structure of a Binary Tree Node class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } public class GfG{ int findDepth(Node root, int x) { // Base case if (root == null) return -1; // Initialize distance as -1 int dist = -1; // Check if x is current node if ((root.data == x) || (dist = findDepth(root.left, x)) >= 0 || (dist = findDepth(root.right, x)) >= 0) // Return depth of the node return dist + 1; return dist; } int findHeightUtil(Node root, int x, int[] height) { // Base Case if (root == null) { return -1; } // Store the maximum height of the left and right subtree int leftHeight = findHeightUtil(root.left, x, height); int rightHeight = findHeightUtil(root.right, x, height); // Update height of the current node int ans = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; // If current node is the required node if (root.data == x) height[0] = ans; return ans; } int findHeight(Node root, int x) { // Store the height of the given node int[] h = {-1}; // Stores height of the Tree findHeightUtil(root, x, h); // Return the height return h[0]; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(10); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(25); root.left.right.right = new Node(45); root.right.left = new Node(30); root.right.right = new Node(35); int k = 25; GfG tree = new GfG(); System.out.println("Depth: " + tree.findDepth(root, k)); System.out.println("Height: " + tree.findHeight(root, k)); } } class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # Function to find depth of a given node def find_depth(root, x): if root is None: return -1 dist = -1 # Check if x is the current node or # if it exists in the left or right subtree if (root.data == x or (dist := find_depth(root.left, x)) >= 0 or (dist := find_depth(root.right, x)) >= 0): return dist + 1 return dist # Utility function to find height of a given node def find_height_util(root, x, height): if root is None: return -1 # Store the maximum height of left and right subtree left_height = find_height_util(root.left, x, height) right_height = find_height_util(root.right, x, height) # Update height of the current node ans = max(left_height, right_height) + 1 # If current node is the required node, update height if root.data == x: height[0] = ans return ans # Function to find height of a given node def find_height(root, x): height = [-1] # Using a list to # store height by reference find_height_util(root, x, height) return height[0] if __name__ == "__main__": # Construct the tree root = Node(5) root.left = Node(10) root.right = Node(15) root.left.left = Node(20) root.left.right = Node(25) root.left.right.right = Node(45) root.right.left = Node(30) root.right.right = Node(35) k = 25 # Print depth and height of the given node print("Depth:", find_depth(root, k)) print("Height:", find_height(root, k)) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Structure of a Binary Tree Node class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GfG{ int FindDepth(Node root, int x) { // Base case if (root == null) return -1; // Initialize distance as -1 int dist = -1; // Check if x is current node if ((root.data == x) || (dist = FindDepth(root.left, x)) >= 0 || (dist = FindDepth(root.right, x)) >= 0) // Return depth of the node return dist + 1; return dist; } int FindHeightUtil(Node root, int x, ref int height) { // Base Case if (root == null) { return -1; } // Store the maximum height of the left and right subtree int leftHeight = FindHeightUtil(root.left, x, ref height); int rightHeight = FindHeightUtil(root.right, x, ref height); // Update height of the current node int ans = Math.Max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; // If current node is the required node if (root.data == x) height = ans; return ans; } int FindHeight(Node root, int x) { // Store the height of the given node int h = -1; // Stores height of the Tree FindHeightUtil(root, x, ref h); // Return the height return h; } public static void Main(string[] args) { Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(10); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(25); root.left.right.right = new Node(45); root.right.left = new Node(30); root.right.right = new Node(35); int k = 25; GfG tree = new GfG(); Console.WriteLine("Depth: " + tree.FindDepth(root, k)); Console.WriteLine("Height: " + tree.FindHeight(root, k)); } } class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function to find depth of a given node function findDepth(root, x) { if (!root) return -1; let dist = -1; // Check if x is the current node or // if it exists in the left or right subtree if (root.data === x || (dist = findDepth(root.left, x)) >= 0 || (dist = findDepth(root.right, x)) >= 0) { return dist + 1; } return dist; } // Utility function to find height of a given node function findHeightUtil(root, x, height) { if (!root) return -1; // Store the maximum height of left and right subtree let leftHeight = findHeightUtil(root.left, x, height); let rightHeight = findHeightUtil(root.right, x, height); // Update height of the current node let ans = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; // If current node is the required node, update height if (root.data === x) height.value = ans; return ans; } // Function to find height of a given node function findHeight(root, x) { let height = { value: -1 }; // Using an object // to store height by reference findHeightUtil(root, x, height); return height.value; } // Construct the tree let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(10); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(25); root.left.right.right = new Node(45); root.right.left = new Node(30); root.right.right = new Node(35); let k = 25; // Print depth and height of the given node console.log("Depth:", findDepth(root, k)); console.log("Height:", findHeight(root, k)); Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
[Approach 2] Using Level Order Traversal – O(n) time and O(n) space
We can calculate the depth of each node using level order traversal by storing the current level as its depth.
To calculate the height of a node k, we find the maximum depth of any leaf node in its subtree.
Then:
Height of node k = (Max depth of leaf in subtree) − (Depth of node k) − 1
Algorithm:
- Initialize height and depth variable with -1;
- Initialize a queue and a level variable with 0 and push the root in the queue.
- When the value of
frontNode is equal to the target k, we stop processing the nodes at that level and clear the queue to only focus on the children of the node k. This ensures that we find the furthest leaf node in the subtree of k. - So the value of depth will be equal to current level.
- After completion we can calculate the value of height using height = level – depth – 1;
- Print the value of height and depth variable.
C++ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = nullptr; } }; void findDepthAndHeight(Node *root, int k) { if (root == nullptr) return; int depth = -1; int height = -1; queue<Node *> q; q.push(root); int level = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int n = q.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Node *frontNode = q.front(); q.pop(); if (frontNode->data == k) { depth = level; // Clear the queue after finding the node while (!q.empty()) { q.pop(); } } // Push left and right children of // the current node to the queue if (frontNode->left) q.push(frontNode->left); if (frontNode->right) q.push(frontNode->right); if (frontNode->data == k) { break; } } // Increment the level after processing // all nodes at the current level level++; } height = level - depth - 1; cout << "Depth : " << depth << endl; cout << "Height : " << height << endl; } int main() { Node *root = new Node(5); root->left = new Node(10); root->right = new Node(15); root->left->left = new Node(20); root->left->right = new Node(25); root->left->right->right = new Node(45); root->right->left = new Node(30); root->right->right = new Node(35); int k = 10; findDepthAndHeight(root, k); return 0; } import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } public class GfG{ static void findDepthAndHeight(Node root, int k) { if (root == null) return; int depth = -1; int height = -1; Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.add(root); int level = 0; while (!q.isEmpty()) { int n = q.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Node frontNode = q.poll(); if (frontNode.data == k) { depth = level; // Clear the queue after finding the node q.clear(); } // Push left and right children of the current node to the queue if (frontNode.left != null) q.add(frontNode.left); if (frontNode.right != null) q.add(frontNode.right); if (frontNode.data == k) { break; } } // Increment the level after processing all nodes at the current level level++; } height = level - depth - 1; System.out.println("Depth : " + depth); System.out.println("Height : " + height); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(10); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(25); root.left.right.right = new Node(45); root.right.left = new Node(30); root.right.right = new Node(35); int k = 10; findDepthAndHeight(root, k); } } class Node: def __init__(self, item): self.data = item self.left = None self.right = None def find_depth_and_height(root, k): if root is None: return depth = -1 height = -1 q = [root] level = 0 while q: n = len(q) for i in range(n): front_node = q.pop(0) if front_node.data == k: depth = level # Clear the queue after finding the node q.clear() # Push left and right children of the current node to the queue if front_node.left: q.append(front_node.left) if front_node.right: q.append(front_node.right) if front_node.data == k: break # Increment the level after processing all nodes at the current level level += 1 height = level - depth - 1 print(f'Depth : {depth}') print(f'Height : {height}') def main(): root = Node(5) root.left = Node(10) root.right = Node(15) root.left.left = Node(20) root.left.right = Node(25) root.left.right.right = Node(45) root.right.left = Node(30) root.right.right = Node(35) k = 10 find_depth_and_height(root, k) if __name__ == '__main__': main() using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GfG{ static void FindDepthAndHeight(Node root, int k) { if (root == null) return; int depth = -1; int height = -1; Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); q.Enqueue(root); int level = 0; while (q.Count > 0) { int n = q.Count; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Node frontNode = q.Dequeue(); if (frontNode.data == k) { depth = level; // Clear the queue after finding the node q.Clear(); } // Push left and right children of the current node to the queue if (frontNode.left != null) q.Enqueue(frontNode.left); if (frontNode.right != null) q.Enqueue(frontNode.right); if (frontNode.data == k) { break; } } // Increment the level after processing all nodes at the current level level++; } height = level - depth - 1; Console.WriteLine("Depth : " + depth); Console.WriteLine("Height : " + height); } static void Main() { Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(10); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(25); root.left.right.right = new Node(45); root.right.left = new Node(30); root.right.right = new Node(35); int k = 10; FindDepthAndHeight(root, k); } } // Node structure class Node { constructor(item) { this.data = item; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function findDepthAndHeight(root, k) { if (root === null) return; let depth = -1; let height = -1; let queue = []; queue.push(root); let level = 0; while (queue.length > 0) { let n = queue.length; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { let frontNode = queue.shift(); if (frontNode.data === k) { depth = level; // Clear the queue after finding the node queue = []; } // Push left and right children of the current node to the queue if (frontNode.left) queue.push(frontNode.left); if (frontNode.right) queue.push(frontNode.right); if (frontNode.data === k) { break; } } // Increment the level after processing all nodes at the current level level++; } height = level - depth - 1; console.log("Depth : " + depth); console.log("Height : " + height); } let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(10); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(25); root.left.right.right = new Node(45); root.right.left = new Node(30); root.right.right = new Node(35); let k = 10; findDepthAndHeight(root, k); OutputDepth : 2 Height : 1
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)due to queue data structure.
Similar Reads
Find the Deepest Node in a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find the deepÂest node in it. Examples: Input : Root of below tree 1 / \ 2 3 / \ / \ 4 5 6 7 \ 8 Output : 8 Input : Root of below tree 1 / \ 2 3 / 6 Output : 6 Method 1: The idea is to do Inorder traversal of a given binary tree. While doing Inorder traversal, we pass level of c
15+ min read
Height of a complete binary tree (or Heap) with N nodes
Consider a Binary Heap of size N. We need to find the height of it. Examples: Input : N = 6 Output : 2 () / \ () () / \ / () () () Input : N = 9 Output : 3 () / \ () () / \ / \ () () () () / \ () ()Recommended PracticeHeight of HeapTry It! Let the size of the heap be N and the height be h. If we tak
3 min read
Count Balanced Binary Trees of Height h
Given a height h, count and return the maximum number of balanced binary trees possible with height h. A balanced binary tree is one in which for every node, the difference between heights of left and right subtree is not more than 1. Examples : Input : h = 3 Output : 15 Input : h = 4 Output : 315Re
9 min read
Introduction to Height Balanced Binary Tree
A height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the height of the left and the right subtree of any node differ by not more than 1. AVL tree, red-black tree are examples of height-balanced trees. Conditions for Height-Balanced Binary Tree: Following are the conditions for a height
5 min read
Sum of nodes at maximum depth of a Binary Tree
Given a root node to a tree, find the sum of all the leaf nodes which are at maximum depth from root node. Example: 1 / \ 2 3 / \ / \ 4 5 6 7 Input : root(of above tree) Output : 22 Explanation: Nodes at maximum depth are: 4, 5, 6, 7. So, sum of these nodes = 22 While traversing the nodes compare th
15+ min read
Find Minimum Depth of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth. The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node. For example, minimum depth of below Binary Tree is 2. Note that the path must end on a leaf node. For example, the minimum depth of below Bi
15 min read
Depth of an N-Ary tree
Given an n-ary tree containing positive node values, the task is to find the depth of the tree.Note: An n-ary tree is a tree where each node can have zero or more children nodes. Unlike a binary tree, which has at most two children per node (left and right), the n-ary tree allows for multiple branch
5 min read
Maximum Depth or Height Of a Binary Tree with python
Binary trees are hierarchical data structures that have widespread applications in computer science, from databases to graphics. One essential property of a binary tree is its depth or height. In this article, we'll discuss how to compute the maximum depth (or height) of a binary tree using Python.
5 min read
Sum of heights of all individual nodes in a binary tree
Given a binary tree, find the sum of heights of all individual nodes in the tree. Example: For this tree: 1). Height of Node 1 - 3 2). Height of Node 2 - 2 3). Height of Node 3 - 1 4). Height of Node 4 - 1 5). Height of Node 5 - 1 Adding all of them = 8 Prerequisites:- Height of binary tree Simple S
11 min read
Replace node with depth in a binary tree
Given a binary tree, replace each node with its depth value. For example, consider the following tree. Root is at depth 0, change its value to 0 and next level nodes are at depth 1 and so on. 3 0 / \ / \ 2 5 == >; 1 1 / \ / \ 1 4 2 2 The idea is to traverse tree starting from root. While traversi
11 min read