The genotype refers to the genetic makeup or combination of alleles possessed by an organism. Studying the genotype meaning and genotype ratio helps in understanding the inheritance patterns of traits.
In this article, we will cover the genotype meaning, genotype examples and genotype ratio in detail.
Genotype Meaning
Genotype refers to the genetic constitution or combination of alleles present within an organism's DNA. It includes the specific alleles inherited from parental genes and determines the genetic potential for phenotype expression. In biology, the term "genotype" includes all of the organism's genetic makeup, including the specific alleles present at each genetic locus. It represents the genetic blueprint inherited from an organism's parents, comprising the DNA sequences that encode various traits and characteristics.
The genotype determines the potential range of phenotypic traits that an organism can exhibit, laying the foundation for its observable characteristics. Alleles may be dominant, recessive, or co-dominant, influencing the expression of traits in different ways.
Genotype Examples
Some of the genotype examples are given below:
- Blood Type: In humans, blood type is determined by the genotype of the ABO gene, which encodes for the A, B, and O blood group alleles. Different combinations of these alleles result in blood types A, B, AB, or O.
- Seed Color in Peas: In Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants, seed color was determined by the genotype of the seed color gene (Y = yellow, y = green). Homozygous dominant (YY) individuals have yellow seeds, while homozygous recessive (yy) individuals have green seeds.
- Fur Color in Mice: In laboratory mice, fur color is controlled by multiple genes, including the Agouti gene. Variations in the genotype of the Agouti gene result in different coat colors, such as agouti, black, or albino.
- Genetic Disorders: Genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia, are caused by specific mutations in genes. The genotype of individuals carrying these mutations determines their susceptibility to these disorders and the severity of symptoms.
- Plant Height in Peas: In Mendel's pea plant experiments, plant height was determined by the genotype of the height gene (T = tall, t = short). Homozygous dominant (TT) individuals are tall, while homozygous recessive (tt) individuals are short.
Genotype Ratio in Dihybrid Cross
In a dihybrid cross, which involves the simultaneous consideration of two different traits controlled by separate genes, the genotype ratio among the offspring reflects the possible combinations of alleles inherited from the parental generation. The genotype ratio is determined by Mendelian genetics principles and can be predicted using Punnett squares or probability calculations.
For example, in a dihybrid cross between individuals heterozygous for both traits (AaBb x AaBb), where 'A' and 'a' represent alleles for one trait and 'B' and 'b' represent alleles for the other trait, the expected genotype ratio among the offspring is 9:3:3:1. This ratio represents the proportions of offspring with different combinations of genotypes based on the inheritance of alleles for both traits.
The genotype ratio of a dihybrid cross provides insights into the independent assortment of alleles for each gene during gamete formation and the distribution of genotypic traits among the offspring population.
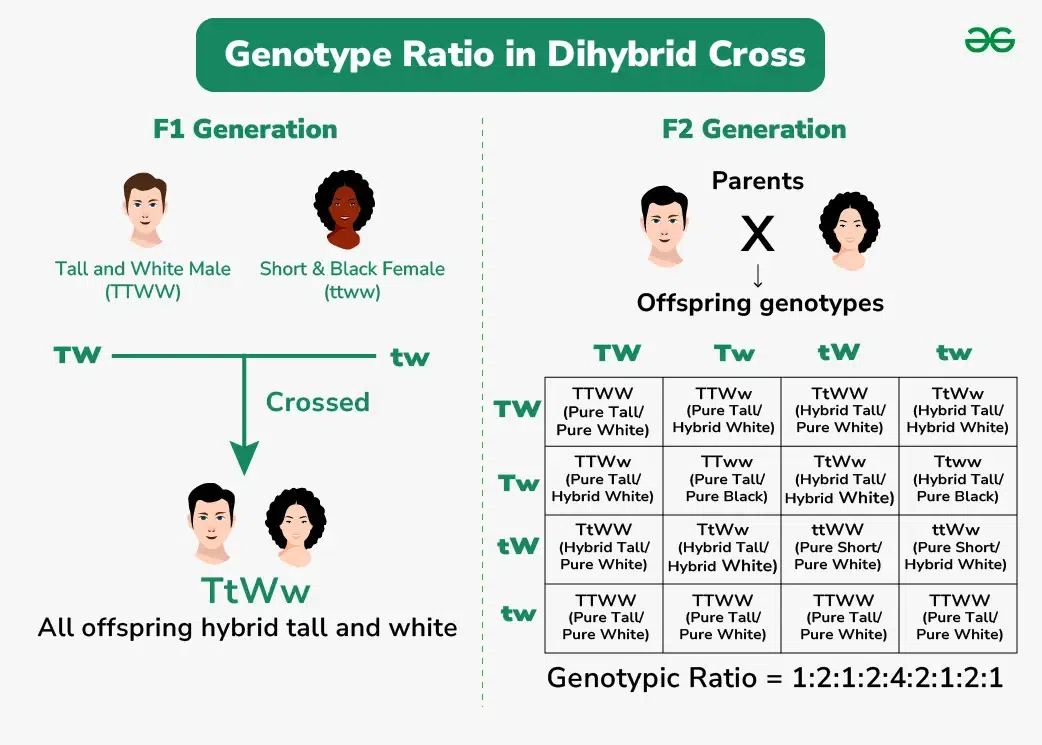 Genotype Ratio in Dihybrid Cross
Genotype Ratio in Dihybrid CrossGenotype Ratio of Monohybrid Cross
In a monohybrid cross, which involves the mating of individuals differing in only one trait, the genotype ratio refers to the proportion of different genetic combinations among the offspring. This ratio is determined by Mendelian genetics principles and can be predicted using Punnett squares or probability calculations.
For example, in a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals (Aa x Aa), where 'A' represents a dominant allele and 'a' represents a recessive allele, the expected genotype ratio among the offspring is 1:2:1. This means that one-fourth of the offspring are expected to be homozygous dominant (AA), half are expected to be heterozygous (Aa), and one-fourth are expected to be homozygous recessive (aa).
The genotype ratio of a monohybrid cross provides valuable insights into the genetic composition of offspring and serves as a foundation for understanding the principles of genetic inheritance.
.webp) Genotype Ratio in Monohybrid Cross
Genotype Ratio in Monohybrid CrossGenotype Test
A genotype test is a genetic analysis used to determine an individual's genetic makeup, specifically the alleles present at particular gene loci. These tests are instrumental in identifying genetic variations that may influence traits, susceptibility to diseases, and responses to treatments. Here are key aspects of genotype testing:
Purpose of Genetic Test
Genotype tests are conducted for various reasons, including diagnosing genetic disorders, predicting disease risk, guiding personalized medical treatments, and understanding genetic contributions to traits and behaviors.
Methods of Genetic Test
Common methods of genotype testing include DNA sequencing, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and microarray analysis. These techniques allow for precise identification of genetic variants and mutations.
Applications of Genetic Test
Genotype tests are widely used in healthcare to screen for genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis, BRCA mutations related to breast cancer, and pharmacogenetic markers that affect drug metabolism. They are also used in ancestry testing to trace genetic heritage.
Benefits of Genetic Test
Genotype testing provides valuable information for personalized medicine, enabling tailored treatment plans based on an individual's genetic profile. It also helpss in early detection and prevention of genetic diseases.
Considerations of Genetic Test
While genotype testing offers significant benefits, it also raises ethical and privacy concerns. It is important to ensure informed consent, protect genetic data, and consider the psychological impact of test results.
Phenotype vs Genotype - Difference Between Phenotype and Genotype
The difference between genotype and phenotype is given below:
| Feature | Phenotype | Genotype |
|---|
| Definition | Observable traits of an organism | Genetic makeup of an organism |
| Expression | Affected by both genetic and environmental factors | Purely determined by genes |
| Examples | Eye color, height, behavior | Allelic combinations, DNA sequences |
| Influence | Influenced by genotype and environment | Determines phenotype |
| Variability | Can vary within individuals of the same genotype | Unique to each individual |
| Observable | Directly observable | Requires genetic testing |
| Role in Inheritance | Not directly passed to offspring | Passed from parent to offspring |
Genotype and Blood Group
The relationship between genotype and blood group is a well-established example of how genetic inheritance determines specific traits. Blood group is determined by the alleles present in the ABO gene, which encodes for antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Here are key points about this relationship:
- ABO Blood Group System: The ABO blood group system is controlled by a single gene with three primary alleles: A, B, and O. The combination of these alleles determines an individual's blood type.
- AA or AO Genotype: Results in blood type A, with A antigens on the red blood cells.
- BB or BO Genotype: Results in blood type B, with B antigens on the red blood cells.
- AB Genotype: Results in blood type AB, with both A and B antigens on the red blood cells.
- OO Genotype: Results in blood type O, with no A or B antigens on the red blood cells.
- Rh Factor: Another important component of blood group is the Rh factor, determined by the presence (Rh+) or absence (Rh-) of the D antigen on red blood cells. The Rh factor is inherited independently of the ABO blood group system.
- Inheritance Pattern: Blood group inheritance follows Mendelian genetics principles. Each parent contributes one allele to their offspring, leading to various possible combinations that determine the child's blood type.
- Importance in Medicine: Understanding the genotype and blood group is crucial for blood transfusions, organ transplants, and pregnancy. Compatibility between donor and recipient blood types is essential to avoid adverse reactions.
- Genotype Testing: Genotype testing can accurately determine an individual's blood group and Rh factor, providing essential information for medical procedures and prenatal care.
 Genotype and Blood Group
Genotype and Blood GroupConclusion - Genotype
In conclusion, the concept of genotype encompasses the genetic blueprint of an organism, determining its potential traits and characteristics. This genetic constitution, inherited from parents, influences the observable traits, or phenotype, of an organism. Examples like blood type, seed color, and fur texture illustrate how genotypes govern specific traits. Genotype ratios in monohybrid and dihybrid crosses help predict the genetic outcomes of offspring, providing insights into inheritance patterns.
Similar Reads
How to use ChatGPT to Create Tutorial Guides Using ChatGPT to create tutorial guides blends AI capabilities with human intelligence in a smooth process. Through the use of ChatGPT's extensive knowledge base and language comprehension, users can create in-depth tutorials on any subject easily. Users first define the topic and create a collectio
8 min read
Gentoo Linux Operating System Gentoo Linux is a highly customizable and source-based Linux distribution known for its flexibility and performance optimization. Users have fine-grained control over system components, allowing them to use the operating system to their specific hardware and preferences. Its Portage package manageme
7 min read
How to Create a Game in Scratch? | Step-by-Step Tutorial For Beginners Scratch is a high-level visual programming language that interacts with users with diagrams and blocks that has the basics of the program inbuilt in it. Scratch is used to make interactive programs, especially for kids using the block kind of interface. In Scratch, we can create games also. Before w
7 min read
Generative AI Projects This tutorial will give you a comprehensive idea about Generative AI Projects like Text generation, Code generation, Music Generation, and Image generation. Generative AI projects, a cornerstone of modern artificial intelligence research, focus on creating models that generate new content, from text
7 min read
How to generate PGP keys using GnuPG on Linux? Linux is a family of open-source operating systems and comes as various distributions or distros. GnuPG or GPG is free software that allows users to encrypt and sign their data and communications. It is based on PGP also called Pretty Good Privacy. It is used to generate PGP keys and can generate pu
3 min read