File Systems in Operating System
Last Updated : 14 Jan, 2025
A computer file is defined as a medium used for saving and managing data in the computer system. The data stored in the computer system is completely in digital format, although there can be various types of files that help us to store the data.
File systems are a crucial part of any operating system, providing a structured way to store, organize, and manage data on storage devices such as hard drives, SSDs, and USB drives. Essentially, a file system acts as a bridge between the operating system and the physical storage hardware, allowing users and applications to create, read, update, and delete files in an organized and efficient manner.
What is a File System?
A file system is a method an operating system uses to store, organize, and manage files and directories on a storage device. Some common types of file systems include:
- FAT (File Allocation Table): An older file system used by older versions of Windows and other operating systems.
- NTFS (New Technology File System): A modern file system used by Windows. It supports features such as file and folder permissions, compression, and encryption.
- ext (Extended File System): A file system commonly used on Linux and Unix-based operating systems.
- HFS (Hierarchical File System): A file system used by macOS.
- APFS (Apple File System): A new file system introduced by Apple for their Macs and iOS devices.
A file is a collection of related information that is recorded on secondary storage. Or file is a collection of logically related entities. From the user’s perspective, a file is the smallest allotment of logical secondary storage.
The name of the file is divided into two parts as shown below:
- Name
- Extension, separated by a period.
Issues Handled By File System
We've seen a variety of data structures where the file could be kept. The file system's job is to keep the files organized in the best way possible.
A free space is created on the hard drive whenever a file is deleted from it. To reallocate them to other files, many of these spaces may need to be recovered. Choosing where to store the files on the hard disc is the main issue with files one block may or may not be used to store a file. It may be kept in the disk's non-contiguous blocks. We must keep track of all the blocks where the files are partially located.
Files Attributes And Their Operations

File Types and Their Content

File Directories
The collection of files is a file directory. The directory contains information about the files, including attributes, location, and ownership. Much of this information, especially that is concerned with storage, is managed by the operating system. The directory is itself a file, accessible by various file management routines.
Below are information contained in a device directory.
- Name
- Type
- Address
- Current length
- Maximum length
- Date last accessed
- Date last updated
- Owner id
- Protection information
The operation performed on the directory are:
- Search for a file
- Create a file
- Delete a file
- List a directory
- Rename a file
- Traverse the file system
Advantages of Maintaining Directories
- Efficiency: A file can be located more quickly.
- Naming: It becomes convenient for users as two users can have same name for different files or may have different name for same file.
- Grouping: Logical grouping of files can be done by properties e.g. all java programs, all games etc.
Single-Level Directory
In this, a single directory is maintained for all the users.
- Naming Problem: Users cannot have the same name for two files.
- Grouping Problem: Users cannot group files according to their needs.
 Two-Level Directory
Two-Level Directory
In this separate directories for each user is maintained.
- Path Name: Due to two levels there is a path name for every file to locate that file.
- Now, we can have the same file name for different users.
- Searching is efficient in this method.
 Tree-Structured Directory
Tree-Structured Directory
The directory is maintained in the form of a tree. Searching is efficient and also there is grouping capability. We have absolute or relative path name for a file.
 File Allocation Methods
File Allocation Methods
There are several types of file allocation methods. These are mentioned below.
- Continuous Allocation
- Linked Allocation(Non-contiguous allocation)
- Indexed Allocation
Continuous Allocation
A single continuous set of blocks is allocated to a file at the time of file creation. Thus, this is a pre-allocation strategy, using variable size portions. The file allocation table needs just a single entry for each file, showing the starting block and the length of the file. This method is best from the point of view of the individual sequential file. Multiple blocks can be read in at a time to improve I/O performance for sequential processing. It is also easy to retrieve a single block. For example, if a file starts at block b, and the ith block of the file is wanted, its location on secondary storage is simply b+i-1.

Disadvantages of Continuous Allocation
- External fragmentation will occur, making it difficult to find contiguous blocks of space of sufficient length. A compaction algorithm will be necessary to free up additional space on the disk.
- Also, with pre-allocation, it is necessary to declare the size of the file at the time of creation.
Linked Allocation(Non-Contiguous Allocation)
Allocation is on an individual block basis. Each block contains a pointer to the next block in the chain. Again the file table needs just a single entry for each file, showing the starting block and the length of the file. Although pre-allocation is possible, it is more common simply to allocate blocks as needed. Any free block can be added to the chain. The blocks need not be continuous. An increase in file size is always possible if a free disk block is available. There is no external fragmentation because only one block at a time is needed but there can be internal fragmentation but it exists only in the last disk block of the file.

Disadvantage Linked Allocation(Non-contiguous allocation)
- Internal fragmentation exists in the last disk block of the file.
- There is an overhead of maintaining the pointer in every disk block.
- If the pointer of any disk block is lost, the file will be truncated.
- It supports only the sequential access of files.
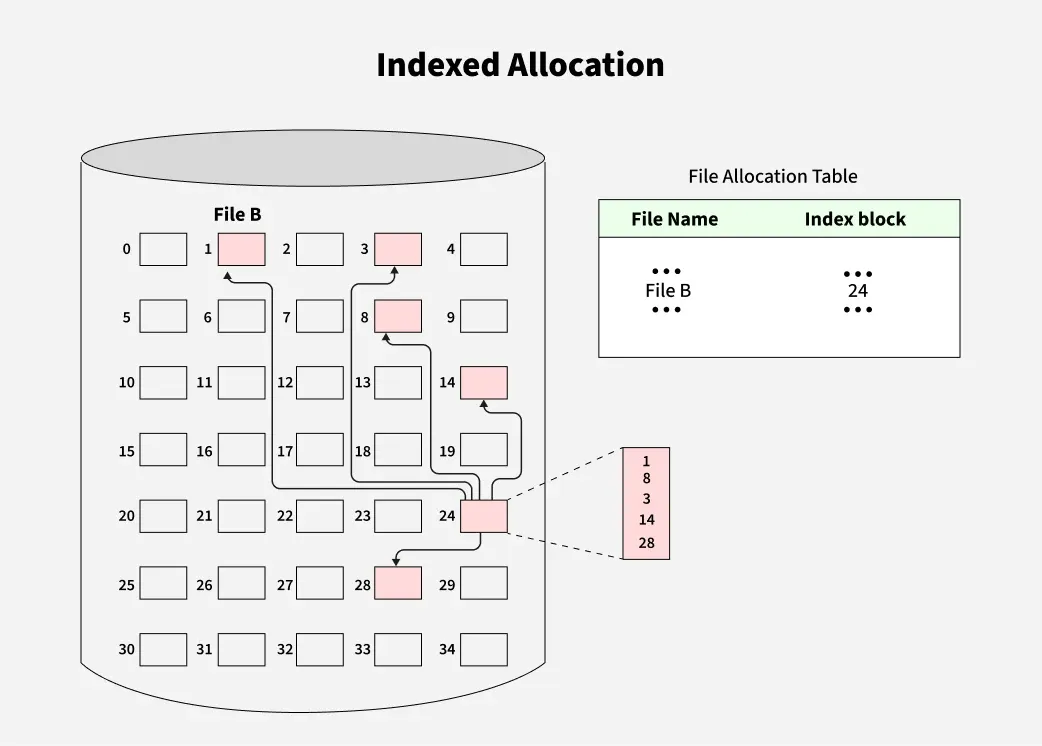
Indexed Allocation
It addresses many of the problems of contiguous and chained allocation. In this case, the file allocation table contains a separate one-level index for each file: The index has one entry for each block allocated to the file. The allocation may be on the basis of fixed-size blocks or variable-sized blocks. Allocation by blocks eliminates external fragmentation, whereas allocation by variable-size blocks improves locality. This allocation technique supports both sequential and direct access to the file and thus is the most popular form of file allocation.
Disk Free Space Management
Just as the space that is allocated to files must be managed, so the space that is not currently allocated to any file must be managed. To perform any of the file allocation techniques, it is necessary to know what blocks on the disk are available. Thus we need a disk allocation table in addition to a file allocation table. The following are the approaches used for free space management.
- Bit Tables: This method uses a vector containing one bit for each block on the disk. Each entry for a 0 corresponds to a free block and each 1 corresponds to a block in use.
For example 00011010111100110001
In this vector every bit corresponds to a particular block and 0 implies that that particular block is free and 1 implies that the block is already occupied. A bit table has the advantage that it is relatively easy to find one or a contiguous group of free blocks. Thus, a bit table works well with any of the file allocation methods. Another advantage is that it is as small as possible.
- Free Block List: In this method, each block is assigned a number sequentially and the list of the numbers of all free blocks is maintained in a reserved block of the disk.

Advantages of File System
- Organization: A file system allows files to be organized into directories and subdirectories, making it easier to manage and locate files.
- Data Protection: File systems often include features such as file and folder permissions, backup and restore, and error detection and correction, to protect data from loss or corruption.
- Improved Performance: A well-designed file system can improve the performance of reading and writing data by organizing it efficiently on disk.
Disadvantages of File System
- Compatibility Issues: Different file systems may not be compatible with each other, making it difficult to transfer data between different operating systems.
- Disk Space Overhead: File systems may use some disk space to store metadata and other overhead information, reducing the amount of space available for user data.
- Vulnerability: File systems can be vulnerable to data corruption, malware, and other security threats, which can compromise the stability and security of the system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, file systems are essential components of operating systems that manage how data is stored, organized, and accessed on storage devices. They provide the structure and rules necessary for creating, managing, and protecting files and directories. By ensuring efficient storage management, easy file navigation, and robust security measures, file systems contribute to the overall functionality, performance, and reliability of computer systems.
Similar Reads
Operating System Tutorial An Operating System(OS) is a software that manages and handles hardware and software resources of a computing device. Responsible for managing and controlling all the activities and sharing of computer resources among different running applications.A low-level Software that includes all the basic fu
4 min read
OS Basics
Structure of Operating System
Types of OS
Batch Processing Operating SystemIn the beginning, computers were very large types of machinery that ran from a console table. In all-purpose, card readers or tape drivers were used for input, and punch cards, tape drives, and line printers were used for output. Operators had no direct interface with the system, and job implementat
6 min read
Multiprogramming in Operating SystemAs the name suggests, Multiprogramming means more than one program can be active at the same time. Before the operating system concept, only one program was to be loaded at a time and run. These systems were not efficient as the CPU was not used efficiently. For example, in a single-tasking system,
5 min read
Time Sharing Operating SystemMultiprogrammed, batched systems provide an environment where various system resources were used effectively, but it did not provide for user interaction with computer systems. Time-sharing is a logical extension of multiprogramming. The CPU performs many tasks by switches that are so frequent that
5 min read
What is a Network Operating System?The basic definition of an operating system is that the operating system is the interface between the computer hardware and the user. In daily life, we use the operating system on our devices which provides a good GUI, and many more features. Similarly, a network operating system(NOS) is software th
2 min read
Real Time Operating System (RTOS)Real-time operating systems (RTOS) are used in environments where a large number of events, mostly external to the computer system, must be accepted and processed in a short time or within certain deadlines. such applications are industrial control, telephone switching equipment, flight control, and
6 min read
Process Management
Introduction of Process ManagementProcess Management for a single tasking or batch processing system is easy as only one process is active at a time. With multiple processes (multiprogramming or multitasking) being active, the process management becomes complex as a CPU needs to be efficiently utilized by multiple processes. Multipl
8 min read
Process Table and Process Control Block (PCB)While creating a process, the operating system performs several operations. To identify the processes, it assigns a process identification number (PID) to each process. As the operating system supports multi-programming, it needs to keep track of all the processes. For this task, the process control
6 min read
Operations on ProcessesProcess operations refer to the actions or activities performed on processes in an operating system. These operations include creating, terminating, suspending, resuming, and communicating between processes. Operations on processes are crucial for managing and controlling the execution of programs i
5 min read
Process Schedulers in Operating SystemA process is the instance of a computer program in execution. Scheduling is important in operating systems with multiprogramming as multiple processes might be eligible for running at a time.One of the key responsibilities of an Operating System (OS) is to decide which programs will execute on the C
7 min read
Inter Process Communication (IPC)Processes need to communicate with each other in many situations. Inter-Process Communication or IPC is a mechanism that allows processes to communicate. It helps processes synchronize their activities, share information, and avoid conflicts while accessing shared resources.Types of Process Let us f
5 min read
Context Switching in Operating SystemContext Switching in an operating system is a critical function that allows the CPU to efficiently manage multiple processes. By saving the state of a currently active process and loading the state of another, the system can handle various tasks simultaneously without losing progress. This switching
4 min read
Preemptive and Non-Preemptive SchedulingIn operating systems, scheduling is the method by which processes are given access the CPU. Efficient scheduling is essential for optimal system performance and user experience. There are two primary types of CPU scheduling: preemptive and non-preemptive. Understanding the differences between preemp
5 min read
CPU Scheduling in OS
Threads in OS
Process Synchronization
Critical Section Problem Solution
Peterson's Algorithm in Process SynchronizationPeterson's Algorithm is a classic solution to the critical section problem in process synchronization. It ensures mutual exclusion meaning only one process can access the critical section at a time and avoids race conditions. The algorithm uses two shared variables to manage the turn-taking mechanis
15+ min read
Semaphores in Process SynchronizationSemaphores are a tool used in operating systems to help manage how different processes (or programs) share resources, like memory or data, without causing conflicts. A semaphore is a special kind of synchronization data that can be used only through specific synchronization primitives. Semaphores ar
15+ min read
Semaphores and its typesA semaphore is a tool used in computer science to manage how multiple programs or processes access shared resources, like memory or files, without causing conflicts. Semaphores are compound data types with two fields one is a Non-negative integer S.V(Semaphore Value) and the second is a set of proce
6 min read
Producer Consumer Problem using Semaphores | Set 1The Producer-Consumer problem is a classic synchronization issue in operating systems. It involves two types of processes: producers, which generate data, and consumers, which process that data. Both share a common buffer. The challenge is to ensure that the producer doesn't add data to a full buffe
4 min read
Readers-Writers Problem | Set 1 (Introduction and Readers Preference Solution)The readers-writer problem in operating systems is about managing access to shared data. It allows multiple readers to read data at the same time without issues but ensures that only one writer can write at a time, and no one can read while writing is happening. This helps prevent data corruption an
7 min read
Dining Philosopher Problem Using SemaphoresThe Dining Philosopher Problem states that K philosophers are seated around a circular table with one chopstick between each pair of philosophers. There is one chopstick between each philosopher. A philosopher may eat if he can pick up the two chopsticks adjacent to him. One chopstick may be picked
11 min read
Hardware Synchronization Algorithms : Unlock and Lock, Test and Set, SwapProcess Synchronization problems occur when two processes running concurrently share the same data or same variable. The value of that variable may not be updated correctly before its being used by a second process. Such a condition is known as Race Around Condition. There are a software as well as
4 min read
Deadlocks & Deadlock Handling Methods
Introduction of Deadlock in Operating SystemA deadlock is a situation where a set of processes is blocked because each process is holding a resource and waiting for another resource acquired by some other process. In this article, we will discuss deadlock, its necessary conditions, etc. in detail.Deadlock is a situation in computing where two
11 min read
Conditions for Deadlock in Operating SystemA deadlock is a situation where a set of processes is blocked because each process is holding a resource and waiting for another resource acquired by some other process. In this article, we will discuss what deadlock is and the necessary conditions required for deadlock.What is Deadlock?Deadlock is
8 min read
Banker's Algorithm in Operating SystemBanker's Algorithm is a resource allocation and deadlock avoidance algorithm used in operating systems. It ensures that a system remains in a safe state by carefully allocating resources to processes while avoiding unsafe states that could lead to deadlocks.The Banker's Algorithm is a smart way for
8 min read
Wait For Graph Deadlock Detection in Distributed SystemDeadlocks are a fundamental problem in distributed systems. A process may request resources in any order and a process can request resources while holding others. A Deadlock is a situation where a set of processes are blocked as each process in a Distributed system is holding some resources and that
5 min read
Handling DeadlocksDeadlock is a situation where a process or a set of processes is blocked, waiting for some other resource that is held by some other waiting process. It is an undesirable state of the system. In other words, Deadlock is a critical situation in computing where a process, or a group of processes, beco
8 min read
Deadlock Prevention And AvoidanceDeadlock prevention and avoidance are strategies used in computer systems to ensure that different processes can run smoothly without getting stuck waiting for each other forever. Think of it like a traffic system where cars (processes) must move through intersections (resources) without getting int
5 min read
Deadlock Detection And RecoveryDeadlock Detection and Recovery is the mechanism of detecting and resolving deadlocks in an operating system. In operating systems, deadlock recovery is important to keep everything running smoothly. A deadlock occurs when two or more processes are blocked, waiting for each other to release the reso
6 min read
Deadlock Ignorance in Operating SystemIn this article we will study in brief about what is Deadlock followed by Deadlock Ignorance in Operating System. What is Deadlock? If each process in the set of processes is waiting for an event that only another process in the set can cause it is actually referred as called Deadlock. In other word
5 min read
Recovery from Deadlock in Operating SystemIn today's world of computer systems and multitasking environments, deadlock is an undesirable situation that can bring operations to a halt. When multiple processes compete for exclusive access to resources and end up in a circular waiting pattern, a deadlock occurs. To maintain the smooth function
8 min read