Evolution is a biological process in which inherited traits of any individual or population start transforming or shifting from one generation to another. Evolution occurs through genetic drift and natural selection which causes evolutionary changes. These evolutionary changes can be prevalent in populations. To explain why organisms are suited to their physical and biological surroundings, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace separately developed the idea of evolution by natural selection in the middle of the 19th century.
What is Evolution?
Evolution is the process by which the population inherits genetic changes that lead to the formation of new traits, and new species. Evolution is the sign of environmental adaptation by an individual. Evolution is frequently perceived as a gradual alteration. On the other hand, evolutionary changes don't aim for perfection or a specific objective.
Evolution Theory
There are 5 theories of evolution that include:
- Perpetual Change: According to this view, organisms undergo transformations throughout time and the universe is not static, freshly created, or eternally revolving. Instead, it is changing slowly.
- Common Descent: According to this hypothesis, all kinds of organisms including plants, animals, and microorganisms descended from a single common ancestor and may be traced back to a "single origin of life on earth.
- Multiplication of Species: According to this theory, organisms multiply by binary fission, budding to evolve into new species.
- Gradualism: According to this theory, evolution occurs gradually instead of suddenly to form new local species.
- Natural Selection: According to this theory, evolution only occur when there are large number of genetic variation, which get passed to new generation. Those individual who survive will show these changes.
Evolution Examples
The following are some of the examples of evolution:
- Evolution in bacteria: E.coli evolves to use citric acid as a nutrient for growth. Flavobacterium start synthesizing noval enzymes by which it can culivate on nylon by products. Sphingobium bacterium develops new metabolic pathways through it can able to degrade pentchlorophenol.
- Evolution of horse: It has been discovered that horse was originated from dawn horse which used be present around 50 million year ago. The dawn horse was the size of dog and had multiple toes.
Types of Evolutions
There are different types of evolutionary methods through which different changes occur in different species or within the species. These different evolutionary changes include:
Divergent Evolution
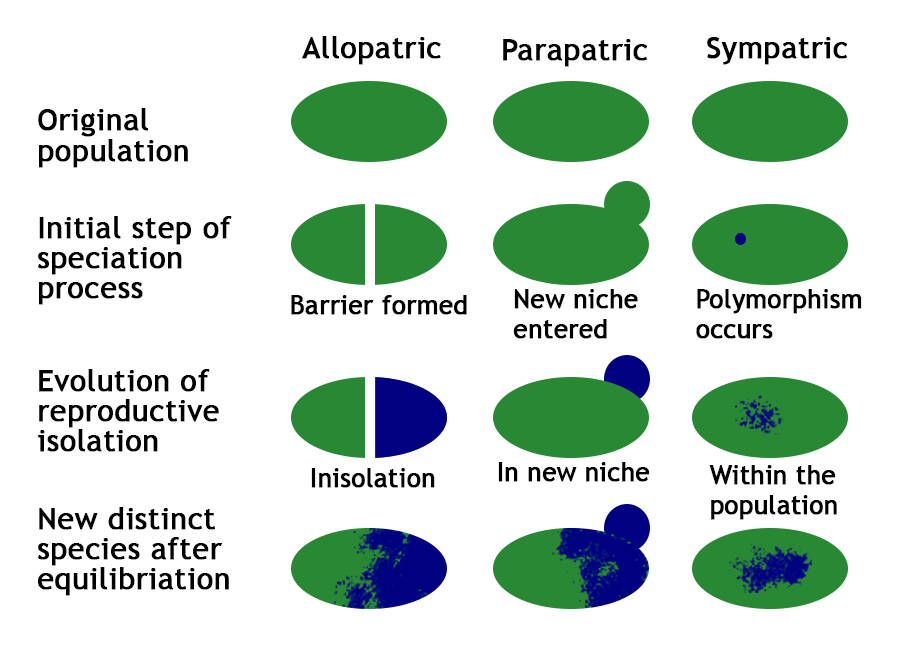
When our ancestral species disperse in different regions of geographic area, niches this is known as divergent evolution. Food sources or any environment sometimes requires special characteristics for survival are known as niches. Divergent evolution in one species known as speciation, which are of two types:
- Sympatric speciation: This process occurs in same geographical area in which an ancestor species gives rise to a new species while remaining unhindered. For example, group of organisms belonging to the same original species may experience reproductive isolation even when they are in the same geographic area.
- Allopatric speciation: When two or more species of same population got seprated geographically that why it is also known as geographical speciation. For example separation can be via mountain range. This speciation can inhibit gene flow between populations.
Also Read: Difference between Sympatric and Allopatric Speciation
Coevolution
Natural selection acts as the driving force behind coevolution, which happens when two or more species that are evolutionary isolated from one another affect one other's evolutionary trajectory. A mutualistic interaction between two species might occasionally result from this kind of development. For instance, certain insects helps in pollination beacuse they get attracted to blooming plants to eat on their nectar, which unintentionally transfers pollen to the blooms. This encourages the flower to reproduce successfully.
Parallel Evolution
When species which are geographically separate and independent undergo similar evolutionary pressure or adapt to comparable environments, they acquire and preserve similar ancestral features. This process is known as parallel evolution. For example, development of mebrane in squirrel to flyor to reach easily.
Convergent Evolution
When two highly separated species acquire equivalent or similar features as a result of similar surroundings, this phenomenon is known as convergent evolution. In other words, two species that have similar features but might have had unrelated origins. For example, Sharks and dolphins. Ancestor dolphin was four legged animal cetaceans because of that dolphin require oxygen from air.
Variation and Adaptation
Organisms undergo variations and adaptations as a result of sexual reproduction, which generates variation, and as a result of their attempts to survive and procreate in order to interface with their surroundings. Once more, Darwin's finches serve as an excellent illustration of how adaptations and variances contribute to natural selection.
Importance of Evolution
There are various importance of evolution which are mentioned below:
- The origin of the planet is explained by the process of evolution.
- Evolution has led to the emergence of biodiversity.
- Genetic drift and shift and natural seclection leads to process of evolution.
- The origins of life on Earth and the relationships between various species is explained by evolution.
- The relationships between evolution and variety of life support each other in tackling biological problems.
- Evolution is important for many fields including anthropology and molecular genetics, environmental disasters, public health and politics.
Branches of Evolution
There are various branches of evolution in which phylogenetic tree is very important.
1. Phylogenetic Tree
It is an evolutionary tree which shows the relationship between biological species with other species on the bsis of genetic and physical charactaristics. There are some types or properties of phylogenetic tree.
Types of Phylogenetic Tree
The following are the types of phylogenic tree:
- Rooted tree: Rooted tree is composed of unique nodes (taxanomic unit) or rootes which are connected to their ancestors thus shows relationship between them.
- Unrooted tree: These type of trees does not show any relationship between ancestor and species as their roots are not connected to ancestors.
- Birfurcating tree: Rooted and unrooted tree can be of bifurcating or multifurcating types.
- Labeled and unlabeled: Rooted and unrooted tree can be labeled as well as unlabeled. Labeled trees have specific values while unlabeled has not.
- Enumerating tree: Every tree leaf node has assigned with specific number which depends upon type of tree.

2. Dendogram
These are common phylogentic trees. Any phylogentic tree can be called as dendogram.
3. Cladogram
Cladogram are the branching tree which do not represents any time or any character.
4. Phylogram
Phylograms are also branching trees but they do represents time and character relationship.
5. Dahlgranogram
It is the cross section of any phylogentic tree.
6. Spindle diagram
This type of diagram represents taxa on horizontal axis with time on verticle axis to describe the variation between taxas.
Also Read:
Similar Reads
What is Divergent Evolution? Evolution is the process that we can observe in every living object. Evolution is a continuous process. It does not get stuck at any point in time. Since, from the very first ancestor, the earth witnessed a number of evolutions. A unicell gradually generates multicell living elements. This is also a
7 min read
What is the Process of Evolution? The process of evolution refers to the change in heritable traits within a population over successive generations. This process is driven by several key mechanisms, including natural selection, mutation, genetic drift and gene flow. The process involved in evolution is: What is the Process of Evolut
3 min read
What is Adaptation? Adaptation refers to a change in an organism's structure and function as a result of a natural process that makes the organism more suited to endure and proliferate in a given environment. Adaptation occurs in plants and animals, allowing them to adjust well within a given environment. E.g. Dessert
9 min read
What do you Mean by Evolution? Evolution is the process by which species change over time through genetic variation and natural selection. It is characterized by genetic variations, heredity, and reproductive success over time. Some mechanisms that drive evolution are as follows: Natural Selection: Due to the selective pressures
2 min read
What is Reproduction? Reproduction is a biological process where living things create new individuals that inherit the same biological traits. Interestingly, humans and animals share this incredible ability. As evolution unfolded, more complex cells emerged, and it became crucial for them to have this ability to replicat
6 min read