Euler's Totient function for all numbers smaller than or equal to n
Last Updated : 27 Dec, 2023
Euler's Totient function ?(n) for an input n is the count of numbers in {1, 2, 3, ..., n} that are relatively prime to n, i.e., the numbers whose GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) with n is 1.
For example, ?(4) = 2, ?(3) = 2 and ?(5) = 4. There are 2 numbers smaller or equal to 4 that are relatively prime to 4, 2 numbers smaller or equal to 3 that are relatively prime to 3. And 4 numbers smaller than or equal to 5 that are relatively prime to 5.
We have discussed different methods for the computation of ?(n) in the previous post.
How to compute ? for all numbers smaller than or equal to n?
Example:
Input: n = 5
Output: Totient of 1 is 1
Totient of 2 is 1
Totient of 3 is 2
Totient of 4 is 2
Totient of 5 is 4
We strongly recommend you to minimize your browser and try this yourself first.
A Simple Solution is to call ?(i) for i = 1 to n.
An Efficient Solution is to use an idea similar to the Sieve of Eratosthenes to precompute all values. The method is based on below product formula.
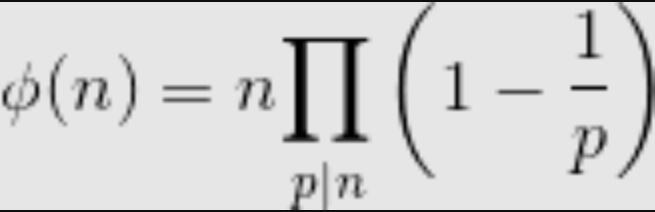
The formula basically says that the value of ?(n) is equal to n multiplied by-product of (1 - 1/p) for all prime factors p of n. For example value of ?(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 - 1/3) = 2.
Below is the complete algorithm:
1) Create an array phi[1..n] to store ? values of all numbers
from 1 to n.
2) Initialize all values such that phi[i] stores i. This
initialization serves two purposes.
a) To check if phi[i] is already evaluated or not. Note that
the maximum possible phi value of a number i is i-1.
b) To initialize phi[i] as i is multiple in the above product
formula.
3) Run a loop for p = 2 to n
a) If phi[p] is p, means p is not evaluated yet and p is a
prime number (similar to Sieve), otherwise phi[p] must
have been updated in step 3.b
b) Traverse through all multiples of p and update all
multiples of p by multiplying with (1-1/p).
4) Run a loop from i = 1 to n and print all Ph[i] values.
Below is the implementation of above algorithm.
C++ // C++ program to compute Totient function for // all numbers smaller than or equal to n. #include<iostream> using namespace std; // Computes and prints totient of all numbers // smaller than or equal to n. void computeTotient(int n) { // Create and initialize an array to store // phi or totient values long long phi[n+1]; for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) phi[i] = i; // indicates not evaluated yet // and initializes for product // formula. // Compute other Phi values for (int p=2; p<=n; p++) { // If phi[p] is not computed already, // then number p is prime if (phi[p] == p) { // Phi of a prime number p is // always equal to p-1. phi[p] = p-1; // Update phi values of all // multiples of p for (int i = 2*p; i<=n; i += p) { // Add contribution of p to its // multiple i by multiplying with // (1 - 1/p) phi[i] = (phi[i]/p) * (p-1); } } } // Print precomputed phi values for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) cout << "Totient of " << i << " is " << phi[i] << endl; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n = 12; computeTotient(n); return 0; } // Java program to compute Totient // function for all numbers smaller // than or equal to n. import java.util.*; class GFG { // Computes and prints totient of all numbers // smaller than or equal to n. static void computeTotient(int n) { // Create and initialize an array to store // phi or totient values long phi[] = new long[n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) phi[i] = i; // indicates not evaluated yet // and initializes for product // formula. // Compute other Phi values for (int p = 2; p <= n; p++) { // If phi[p] is not computed already, // then number p is prime if (phi[p] == p) { // Phi of a prime number p is // always equal to p-1. phi[p] = p - 1; // Update phi values of all // multiples of p for (int i = 2 * p; i <= n; i += p) { // Add contribution of p to its // multiple i by multiplying with // (1 - 1/p) phi[i] = (phi[i] / p) * (p - 1); } } } // Print precomputed phi values for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) System.out.println("Totient of " + i + " is " + phi[i]); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 12; computeTotient(n); } } // This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal. # Python program to compute # Totient function for # all numbers smaller than # or equal to n. # Computes and prints # totient of all numbers # smaller than or equal to n. def computeTotient(n): # Create and initialize # an array to store # phi or totient values phi=[] for i in range(n + 2): phi.append(0) for i in range(1, n+1): phi[i] = i # indicates not evaluated yet # and initializes for product # formula. # Compute other Phi values for p in range(2,n+1): # If phi[p] is not computed already, # then number p is prime if (phi[p] == p): # Phi of a prime number p is # always equal to p-1. phi[p] = p-1 # Update phi values of all # multiples of p for i in range(2*p,n+1,p): # Add contribution of p to its # multiple i by multiplying with # (1 - 1/p) phi[i] = (phi[i]//p) * (p-1) # Print precomputed phi values for i in range(1,n+1): print("Totient of ", i ," is ", phi[i]) # Driver code n = 12 computeTotient(n) # This code is contributed # by Anant Agarwal // C# program to check if given two // strings are at distance one. using System; class GFG { // Computes and prints totient of all // numbers smaller than or equal to n static void computeTotient(int n) { // Create and initialize an array to // store phi or totient values long []phi = new long[n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) // indicates not evaluated yet // and initializes for product // formula. phi[i] = i; // Compute other Phi values for (int p = 2; p <= n; p++) { // If phi[p] is not computed already, // then number p is prime if (phi[p] == p) { // Phi of a prime number p is // always equal to p-1. phi[p] = p - 1; // Update phi values of all // multiples of p for (int i = 2 * p; i <= n; i += p) { // Add contribution of p to its // multiple i by multiplying with // (1 - 1/p) phi[i] = (phi[i] / p) * (p - 1); } } } // Print precomputed phi values for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) Console.WriteLine("Totient of " + i +" is " + phi[i]); } // Driver code public static void Main() { int n = 12; computeTotient(n); } } // This code is contributed by Sam007. <script> // Javascript program to check if given two // strings are at distance one. // Computes and prints totient of all // numbers smaller than or equal to n function computeTotient(n) { // Create and initialize an array to // store phi or totient values let phi = new Array(n + 1); for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) // indicates not evaluated yet // and initializes for product // formula. phi[i] = i; // Compute other Phi values for (let p = 2; p <= n; p++) { // If phi[p] is not computed already, // then number p is prime if (phi[p] == p) { // Phi of a prime number p is // always equal to p-1. phi[p] = p - 1; // Update phi values of all // multiples of p for (let i = 2 * p; i <= n; i += p) { // Add contribution of p to its // multiple i by multiplying with // (1 - 1/p) phi[i] = parseInt(phi[i] / p, 10) * (p - 1); } } } // Print precomputed phi values for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) document.write("Totient of " + i +" is " + phi[i] + "</br>"); } let n = 12; computeTotient(n); </script> <?php // PHP program to compute Totient // function for all numbers smaller // than or equal to n. // Computes and prints totient // of all numbers smaller than // or equal to n. function computeTotient($n) { // Create and initialize // an array to store // phi or totient values for($i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++) // indicates not evaluated yet // and initializes for product // formula. $phi[$i] = $i; // Compute other Phi values for($p = 2; $p <= $n; $p++) { // If phi[p] is not computed already, // then number p is prime if ($phi[$p] == $p) { // Phi of a prime number p is // always equal to p-1. $phi[$p] = $p - 1; // Update phi values of all // multiples of p for($i = 2 * $p; $i <= $n; $i += $p) { // Add contribution of p to its // multiple i by multiplying with // (1 - 1/$p) $phi[$i] = ($phi[$i] / $p) * ($p - 1); } } } // Print precomputed phi values for($i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++) echo "Totient of " , $i , " is ", $phi[$i] ,"\n"; } // Driver Code $n = 12; computeTotient($n); // This code is contributed by ajit ?> OutputTotient of 1 is 1 Totient of 2 is 1 Totient of 3 is 2 Totient of 4 is 2 Totient of 5 is 4 Totient of 6 is 2 Totient of 7 is 6 Totient of 8 is 4 Totient of 9 is 6 Totient of 10 is 4 Totient of 11 is 10 Totient of 12 is 4
Time Complexity: O(n log(log n))
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
The same solution can be used when we have a large number of queries for computing the totient function.
Another way to compute Euler’s totient function can also be done by using the below formula:
 Euler’s totient function
Euler’s totient functionLet us see an example to understand the above function, basically, it does the same job but in a different way:
For example, ?(12) = { (2^(2-1)) x (2-1) } x { (3^(1-1)) x (3-1) } =4
Note that ?(n) = n?1 if n is prime.
Below is the implementation of the above formula:
C++ // C++ program for the above approach #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long ll Euler_totient_function(ll n) { ll result = 1; for (ll i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) { ll c = 0; if (n % i == 0) { while (n % i == 0) { c++; n /= i; } } if (c > 0) { ll power = (ll)pow(i, c - 1); ll sm = (ll)pow(i, c - 1) * (i - 1); result *= sm; } } if (n > 1) { result *= (n - 1); } return result; } // driver code int main() { for (ll i = 1; i < 13; i++) { cout << "Euler_totient_function(" << i << "): "; cout << Euler_totient_function(i) << endl; } } #praveeny182 // Java program for the above approach import java.io.*; class GFG{ static long Euler_totient_function(long n) { long result = 1; for(long i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) { long c = 0; if (n % i == 0) { while (n % i == 0) { c++; n /= i; } } if (c > 0) { long power = (long)Math.pow(i, c - 1); long sm = (long)Math.pow(i, c - 1) * (i - 1); result *= sm; } } if (n > 1) { result *= (n - 1); } return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { for(long i = 1; i < 13; i++) { System.out.print("Euler_totient_function(" + i + "): "); System.out.println(Euler_totient_function(i)); } } } // This code is contributed by rishavmahato348 # python program for the above approach import math def Euler_totient_function(n): result = 1 for i in range(2,n+1): c = 0 if n % i == 0: while (n % i == 0): c+=1 n //= i if (c > 0): power = math.pow(i,c-1) m = math.pow(i,c-1)*(i-1) result*=m if (n > 1): result *= (n - 1) return int(result) for i in range(1,13): print("Euler_totient_function(" , i , "): ",end="") print(Euler_totient_function(i)) // C# program for the above approach using System; class GFG { static long Euler_totient_function(long n) { long result = 1; for (long i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) { long c = 0; if (n % i == 0) { while (n % i == 0) { c++; n /= i; } } if (c > 0) { long sm = (long)Math.Pow(i, c - 1) * (i - 1); result *= sm; } } if (n > 1) { result *= (n - 1); } return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (long i = 1; i < 13; i++) { Console.Write("Euler_totient_function(" + i + "): "); Console.WriteLine(Euler_totient_function(i)); } } } // This code is contributed by rishavmahato348 <script> // Javascript program for the above approach function Euler_totient_function(n) { let result = 1; for (let i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) { let c = 0; if (n % i == 0) { while (n % i == 0) { c++; n = parseInt(n / i); } } if (c > 0) { let power = Math.pow(i, c - 1); let sm = Math.pow(i, c - 1) * (i - 1); result *= sm; } } if (n > 1) { result *= (n - 1); } return result; } // driver code for (let i = 1; i < 13; i++) { document.write("Euler_totient_function(" + i + "): "); document.write(Euler_totient_function(i) + "<br>"); } // This code is contributed by subham348. </script> OutputEuler_totient_function(1): 1 Euler_totient_function(2): 1 Euler_totient_function(3): 2 Euler_totient_function(4): 2 Euler_totient_function(5): 4 Euler_totient_function(6): 2 Euler_totient_function(7): 6 Euler_totient_function(8): 4 Euler_totient_function(9): 6 Euler_totient_function(10): 4 Euler_totient_function(11): 10 Euler_totient_function(12): 4
Time Complexity: O(sqrt(n)*log(n))
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Similar Reads
Euler Totient for Competitive Programming What is Euler Totient function(ETF)?Euler Totient Function or Phi-function for 'n', gives the count of integers in range '1' to 'n' that are co-prime to 'n'. It is denoted by \phi(n) .For example the below table shows the ETF value of first 15 positive integers: 3 Important Properties of Euler Totie
8 min read
Euler's Totient Function Given an integer n, find the value of Euler's Totient Function, denoted as Φ(n). The function Φ(n) represents the count of positive integers less than or equal to n that are relatively prime to n. Euler's Totient function Φ(n) for an input n is the count of numbers in {1, 2, 3, ..., n-1} that are re
10 min read
Count of non co-prime pairs from the range [1, arr[i]] for every array element Given an array arr[] consisting of N integers, the task for every ith element of the array is to find the number of non co-prime pairs from the range [1, arr[i]]. Examples: Input: N = 2, arr[] = {3, 4}Output: 2 4Explanation: All non-co-prime pairs from the range [1, 3] are (2, 2) and (3, 3).All non-
13 min read
Generate an array having sum of Euler Totient Function of all elements equal to N Given a positive integer N, the task is to generate an array such that the sum of the Euler Totient Function of each element is equal to N. Examples: Input: N = 6Output: 1 6 2 3 Input: N = 12Output: 1 12 2 6 3 4 Approach: The given problem can be solved based on the divisor sum property of the Euler
5 min read
Count all possible values of K less than Y such that GCD(X, Y) = GCD(X+K, Y) Given two integers X and Y, the task is to find the number of integers, K, such that gcd(X, Y) is equal to gcd(X+K, Y), where 0 < K <Y. Examples: Input: X = 3, Y = 15Output: 4Explanation: All possible values of K are {0, 3, 6, 9} for which GCD(X, Y) = GCD(X + K, Y). Input: X = 2, Y = 12Output:
8 min read
Count of integers up to N which are non divisors and non coprime with N Given an integer N, the task is to find the count of all possible integers less than N satisfying the following properties: The number is not coprime with N i.e their GCD is greater than 1.The number is not a divisor of N. Examples: Input: N = 10 Output: 3 Explanation: All possible integers which ar
5 min read
Find the number of primitive roots modulo prime Given a prime p . The task is to count all the primitive roots of p .A primitive root is an integer x (1 <= x < p) such that none of the integers x - 1, x2 - 1, ...., xp - 2 - 1 are divisible by p but xp - 1 - 1 is divisible by p . Examples: Input: P = 3 Output: 1 The only primitive root modul
5 min read
Compute power of power k times % m Given x, k and m. Compute (xxxx...k)%m, x is in power k times. Given x is always prime and m is greater than x. Examples: Input : 2 3 3 Output : 1 Explanation : ((2 ^ 2) ^ 2) % 3 = (4 ^ 2) % 3 = 1 Input : 3 2 3 Output : 0 Explanation : (3^3)%3 = 0 A naive approach is to compute the power of x k time
15+ min read
Primitive root of a prime number n modulo n Given a prime number n, the task is to find its primitive root under modulo n. The primitive root of a prime number n is an integer r between[1, n-1] such that the values of r^x(mod n) where x is in the range[0, n-2] are different. Return -1 if n is a non-prime number. Examples: Input : 7 Output : S
15 min read
Euler's Totient function for all numbers smaller than or equal to n Euler's Totient function ?(n) for an input n is the count of numbers in {1, 2, 3, ..., n} that are relatively prime to n, i.e., the numbers whose GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) with n is 1. For example, ?(4) = 2, ?(3) = 2 and ?(5) = 4. There are 2 numbers smaller or equal to 4 that are relatively pri
13 min read