Difference Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
Last Updated : 21 Aug, 2024
Sequential circuits are fundamental components in digital systems, and they are categorized into two types: synchronous and asynchronous sequential circuits. Both types have distinct characteristics based on how they manage timing and respond to inputs.
Synchronous Sequential Circuits are easier to design, more predictable, and better suited for applications where precise timing is crucial whereas Asynchronous Sequential Circuits offer faster operation and are better suited for dynamic environments but require more careful design due to their susceptibility to timing-related issues.
What is a Synchronous Sequential Circuit?
The Synchronous Sequential Circuit is a type of circuit where all state variables that represent the internal state of the circuit change synchronously with a given input clock signal for the next state to be achieved. Such synchronization with a universal clock signal helps to ensure that all internal state changes happen at once thus making it more reliable and less likely to experience problems such as race problems.
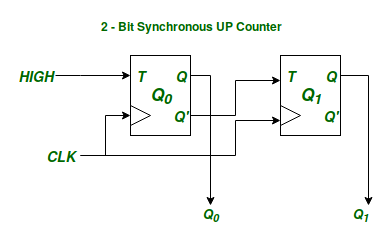
What is an Asynchronous Sequential Circuit?
In an Asynchronous Sequential Circuit, it is impossible for the state variables to synchronize with a universal clock signal and may not all change their state at once so as to arrive at the next stable internal state. Any shift in input results in a change in the internal state causing race conditions among other problems.
Now let's illustrate the difference between that of Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits with the example of a Synchronous and Asynchronous 2-bit binary UP Counter using T-Flip-Flops.
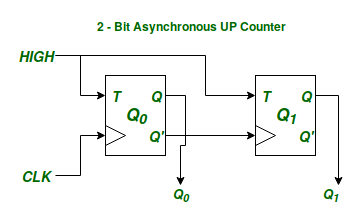 2-bit Binary Asynchronous UP Counter using T-Flip-Flops.
2-bit Binary Asynchronous UP Counter using T-Flip-Flops.In both the above circuits Q_0, Q_1 are the State Variables denoting the Internal State of each of the above circuits. Since there are 2 state variable the above sequential circuits can be in 4 possible states, and the function of a counter is to cycle through these 4 states in a particular order. Now the difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous
Circuits is in how the circuit goes for one Internal State to the Next Internal State. In a Synchronous Sequential Circuit all the State Variables representing the internal state of the circuit change their state simultaneously with a given input clock signal to achieve the next state. On the other hand in case of an Asynchronous Circuit all the State Variables may not change their state simultaneously to achieve the next steady internal state. In other words the state variables are not synchronized with any universal clock signal.
Difference Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
| Synchronous Circuit | Asynchronous Circuit |
|---|
| All the State Variable changes are synchronized with a universal clock signal. | The State Variables are not synchronized to change simultaneously and may change at anytime irrespective of each other to achieve the next Steady Internal State |
| Since all the Internal State changes are in the strict control of a master clock source they are less prone to failure or to a race condition and hence are more reliable. | Since there is no such universal clock source, the internal state changes as soon as any of the inputs change and hence are more prone to a race condition. |
| Timings of the internal state changes are in our control. | The changes in the internal state of an asynchronous circuit are not in our control. |
Conclusion
Synchronous sequential circuits and asynchronous sequential circuits differ mainly in the way they manage transition from one internal state to another.Synchronous circuits use common clock signal while as a consequence they become very reliable and hence predictable.A clock signal is not needed by asynchronous circuit that can result in timing problems and race conditions.The choice between these two depends on specific application requirements like timing control,reliability and complexity.I’m operating at maximum capacity at this point.