Difference between Programmable Logic Array and Programming Array Logic
Last Updated : 13 Aug, 2024
Programmable Logic Array (PLA) and Programming Array Logic (PAL) are the categories of programming logic devices. In PLA or Programmable Logic Array, there are massive functions can be implemented. Whereas in PAL or Programmable Array Logic, there is finite functions can be implemented. The distinction between PLA and PAL is that, PAL have programmable AND array and fixed OR array. On the other hand, PLA have a programmable AND array and programming OR array.
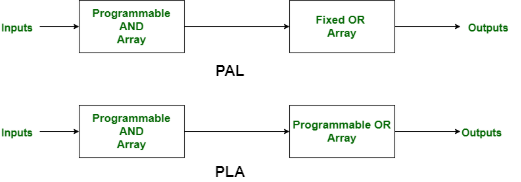
What is Programmable Logic Array or PLA?
A Programmable Rationale Cluster (PLA) is a computerized gadget used to execute combinational rationale circuits. It consists of a programmable AND door cluster and a programmable OR entryway exhibit. The PLA permits clients to arrange its inward associations to understand any Boolean capability by programming the associations between the sources of information, AND entryways, or potentially doors. This adaptability makes PLAs reasonable for custom rationale planning and prototyping. Not at all like fixed-capability rationale gadgets, PLAs can be custom fitted to explicit necessities by programming, making them helpful in applications where custom rationale arrangements are required.
Applications of PLA
- Custom Reasoning Arrangement: PLAs are used to make exceptionally mechanized reasoning circuits for unequivocal capacities, habitually in embedded structures and purchaser devices.
- Prototyping: Draftsmen use PLAs to demonstrate and test reasoning plans before zeroing in on ASIC or FPGA plans.
- Estimation Execution: They can complete complex computations in hardware, such as encoding/unraveling plans or custom data dealing with computations.
- Modernized Circuit Unraveling: PLAs develop the arrangement of puzzling high-level circuits by allowing fashioners to design Boolean capacities directly into gear.
- Control Structures: Used in control systems for programmable state machines and to complete unambiguous control reasoning.
What is Programming Array Logic or PAL?
Programmable Array Logic is a sort of computerized gadget used to carry out combinational rationale circuits with proper engineering, however programmable usefulness. Buddies comprise a fixed OR cluster and a programmable AND exhibit. Clients program the AND cluster to make explicit rationale capabilities, which are then joined utilizing the fixed OR exhibit. This arrangement takes into consideration the production of custom rationale capabilities without the requirement for complex wiring. Buddies offer a less complex, more practical arrangement compared with PLAs for carrying out clear rationale and are generally utilized in computerized circuit plans for undertakings like information directing and control signaling.
Benefits of PAL
- Savvy: Buddies are, for the most part, more affordable than PLAs and FPGAs for their less complex rationale capabilities due to their fixed OR exhibit and less complex engineering.
- Convenience: Buddies are simpler to program and arrange compared with additional mind-boggling gadgets like FPGAs, making them available for a clear rationale.
- Speed: Buddies regularly have quicker speeds for rationale activities in view of their decent engineering, which diminishes the time required for signal steering and handling.
- Unwavering quality: The fixed OR exhibit design adds to higher dependability and consistency in execution.
- Smaller Plan: Buddies give a minimized answer for executing combinational rationale, saving space on circuit sheets.
Difference between PLA and PAL
| S.NO | PLA | PAL |
|---|
| 1. | PLA stands for Programmable Logic Array. | While PAL stands for Programmable Array Logic. |
|---|
| 2. | PLA speed is lower than PAL. | While PAL's speed is higher than PLA. |
|---|
| 3. | The complexity of PLA is high. | While PAL's complexity is less. |
|---|
| 4. | PLA has limited amount of functions implemented. | While PAL has a huge number of functions implemented. |
|---|
| 5. | The cost of PLA is also high. | While the cost of PAL is low. |
|---|
| 6. | Programmable Logic Array is less available. | While Programmable Array Logic is more available than Programmable Logic Array. |
|---|
| 7. | PLA design may be built using a programmable set of AND gates and a programmable set of OR gates. | PAL design may be built using a programmable set of AND and a fix set of OR gates |
|---|
| 8. | The flexibility of PLA is high as compared to PAL. | Flexibility of PAL is less. |
|---|
| 9. | It is less used than PAL. | While it is more used than PLA. |
|---|
Conclusion
Programmable Cluster Rationale (Buddy) gadgets are adaptable and practical apparatuses for carrying out combinational rationale circuits. Their fixed OR exhibit and programmable AND cluster engineering take into consideration productive plans and fast prototyping of custom rationale capabilities. Buddies offer advantages like convenience, speed, unwavering quality, a conservative plan, and low power utilization. They are especially appropriate for direct rationale applications, making them a significant part of computerized circuit planning and control frameworks. While not quite as adaptable as Programmable Rationale Clusters (PLAs) or as strong as FPGAs, Buddies give a down-to-earth answer for some computerized rationale needs.
Similar Reads
Difference Between Functional and Logical Programming Programming paradigm is an approach to solve problems using some programming language or also we can say it is a method to solve a problem using tools and techniques that are available to us following some approach. There are lots of programming languages that are known but all of them need to follo
3 min read
Difference between Structured Programming and Object Oriented Programming 1. Structured Programming :Structured Programming, as name suggests, is a technique that is considered as precursor to OOP and usually consists of well-structured and separated modules. In this programming, user can create its own user-defined functions as well as this methodology tries to resolve i
3 min read
Difference between Array and String in Java An array is a collection of similar type of elements that are stored in a contiguous memory location. Arrays can contain primitives(int, char, etc) as well as object(non-primitives) references of a class depending upon the definition of the array. In the case of primitive data type, the actual value
5 min read
Difference between array_merge() and array_combine() functions in PHP array_merge() Function: The array_merge() function is used to merge two or more arrays into a single array. This function is used to merge the elements or values of two or more arrays together into a single array. The merging occurs in such a manner that the values of one array are appended at the e
3 min read
Difference between Program and File 1. Program : Program, as name suggest, are simple executable files that contain set or collection of instructions used by computer to execute or complete particular tasks as well as produce results you want. 2. File : File, as name suggests, is basic concept in computer that is designed to store dat
2 min read