Difference Between MVC, MVP and MVVM Architecture Pattern in Android
Last Updated : 14 Apr, 2025
Developing an android application by applying a software architecture pattern is always preferred by the developers. An architecture pattern gives modularity to the project files and assures that all the codes get covered in Unit testing. It makes the task easy for developers to maintain the software and to expand the features of the application in the future. MVC (Model — View — Controller), MVP (Model — View — Presenter), and MVVM (Model — View — ViewModel) is the most popular and industry-recognized android architecture pattern among developers.
The Model—View—Controller(MVC) Pattern
The MVC pattern suggests splitting the code into 3 components. While creating the class/file of the application, the developer must categorize it into one of the following three layers:
- Model: This component stores the application data. It has no knowledge about the interface. The model is responsible for handling the domain logic(real-world business rules) and communication with the database and network layers.
- View: It is the UI(User Interface) layer that holds components that are visible on the screen. Moreover, it provides the visualization of the data stored in the Model and offers interaction to the user.
- Controller: This component establishes the relationship between the View and the Model. It contains the core application logic and gets informed of the user’s response and updates the Model as per the need.

The Model—View—Presenter(MVP) Pattern
MVP pattern overcomes the challenges of MVC and provides an easy way to structure the project codes. The reason why MVP is widely accepted is that it provides modularity, testability, and a more clean and maintainable codebase. It is composed of the following three components:
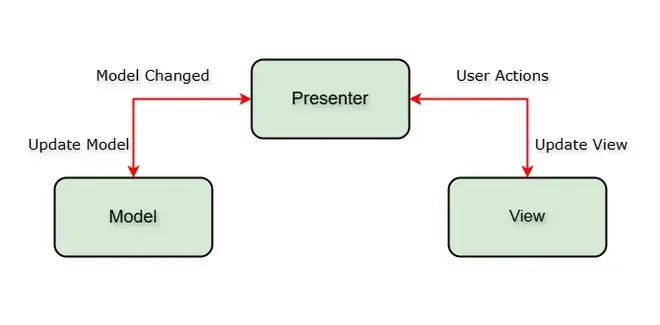
- Model: Layer for storing data. It is responsible for handling the domain logic(real-world business rules) and communication with the database and network layers.
- View: UI(User Interface) layer. It provides the visualization of the data and keep a track of the user’s action in order to notify the Presenter.
- Presenter: Fetch the data from the model and applies the UI logic to decide what to display. It manages the state of the View and takes actions according to the user’s input notification from the View.
The Model — View — ViewModel (MVVM) Pattern
MVVM pattern has some similarities with the MVP(Model — View — Presenter) design pattern as the Presenter role is played by the ViewModel. However, the drawbacks of the MVP pattern has been solved by MVVM. It suggests separating the data presentation logic(Views or UI) from the core business logic part of the application. The separate code layers of MVVM are:
- Model: This layer is responsible for the abstraction of the data sources. Model and ViewModel work together to get and save the data.
- View: The purpose of this layer is to inform the ViewModel about the user’s action. This layer observes the ViewModel and does not contain any kind of application logic.
- ViewModel: It exposes those data streams which are relevant to the View. Moreover, it servers as a link between the Model and the View.

Difference Between MVC, MVP, and MVVM Design Pattern
MVC(MODEL VIEW CONTROLLER) | MVP(MODEL VIEW PRESENTER) | MVVM(MODEL VIEW VIEWMODEL) |
|---|
| One of the oldest software architecture | Developed as the second iteration of software architecture which is advance from MVC. | Industry-recognized architecture pattern for applications. |
| UI(View) and data-access mechanism(Model) are tightly coupled. | It resolves the problem of having a dependent View by using Presenter as a communication channel between Model and View. | This architecture pattern is more event-driven as it uses data binding and thus makes easy separation of core business logic from the View. |
| Controller and View exist with the one-to-many relationship. One Controller can select a different View based upon required operation. | The one-to-one relationship exists between Presenter and View as one Presenter class manages one View at a time. | Multiple View can be mapped with a single ViewModel and thus, the one-to-many relationship exists between View and ViewModel. |
| The View has no knowledge about the Controller. | The View has references to the Presenter. | The View has references to the ViewModel |
| Difficult to make changes and modify the app features as the code layers are tightly coupled. | Code layers are loosely coupled and thus it is easy to carry out modifications/changes in the application code. | Easy to make changes in the application. However, if data binding logic is too complex, it will be a little harder to debug the application. |
| User Inputs are handled by the Controller. | The View is the entry point to the Application | The View takes the input from the user and acts as the entry point of the application. |
| Ideal for small scale projects only. | Ideal for simple and complex applications. | Not ideal for small scale projects. |
| Limited support to Unit testing. | Easy to carry out Unit testing but a tight bond of View and Presenter can make it slightly difficult. | Unit testability is highest in this architecture. |
| This architecture has a high dependency on Android APIs. | It has a low dependency on the Android APIs. | Has low or no dependency on the Android APIs. |
| It does not follow the modular and single responsibility principle. | Follows modular and single responsibility principle. | Follows modular and single responsibility principle. |
The key difference between MVP and MVC is that the Presenter in MVP has a more active role in the communication between the Model and the View, and is responsible for controlling the flow of data between the two. MVVM stands for Model-View-ViewModel. In the MVVM pattern, the "Model" represents the data and logic of the application, the "View" represents the UI of the application, and the "ViewModel" is a layer that sits between the Model and the View and is responsible for exposing the data and logic of the Model to the View in a way that is easier to work with. The ViewModel also handles user input and updates the Model as needed.
Overall, the main difference between these patterns is the role of the mediator component. MVC and MVP both involve a Controller or Presenter that acts as a mediator between the Model and the View, while MVVM involves a ViewModel that serves as the mediator between the Model and the View. MVC is the simplest of these patterns, while MVP and MVVM are more flexible and allow for a cleaner separation of concerns between the different layers of the application.