Difference between Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD)
Last Updated : 10 May, 2025
Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and Solid State Drives (SSD) are two types of storage devices used to store data on computers,laptops, and other devices. While HDDs have been around for decades, SSDs are a newer, faster, and more advanced technology. The main difference between them lies in how they store and access data. Let's look at the fundamental distinctions between HDD and SSD.
 Difference Between HDD and SSD
Difference Between HDD and SSD
- HDD: Better for large storage at a lower price but slower and less durable.
- SSD: Faster, more durable, and energy-efficient, but more expensive per GB.
What is a Hard Disk Drive(HDD)?
An HDD consists of a spinning disk (platter) coated with a magnetic material and a read/write head that reads and writes data on the disk's surface. The read/write head moves back and forth across the spinning disk to access different parts of the data stored on the disk. HDDs have been around for decades and are the more traditional type of storage device.
 What is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD)?
What is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD)?Also read, Hard Disk Drive.
How do HDDs work?
A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) works by using spinning disks and a moving read/write head to store and retrieve data. Inside the HDD, there are platters coated with a magnetic material that spin at high speeds, usually 5400 or 7200 RPM. A tiny read/write head moves across these spinning platters without touching them, reading and writing data by detecting small magnetic charges. The platters are divided into tracks and sectors, which act like an address system to help locate stored information. When you save a file, the HDD records data by changing the magnetic charges at specific locations. When you open a file, the HDD finds the correct location, and the read head retrieves the data, which is then sent to the computer. An I/O controller manages communication between the HDD and the computer, ensuring data is accessed correctly. Since HDDs have moving parts, they are slower and can wear out over time compared to Solid State Drives (SSDs), which have no moving components. However, HDDs remain popular because they offer large storage capacity at a lower cost.
Features of Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
- Large Storage Capacity: HDDs can store large amounts of data, ranging from a few gigabytes (GB) to several terabytes (TB).
- Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper than SSDs, making them an affordable option for large data storage.
- Size: Typically larger and heavier than SSDs.
- Performance: Slower than SSDs due to mechanical parts.
- Mechanical Parts: Due to its moving parts, HDDs can be less durable than SSDs.
Advantages of HDD
- Cost-Effective: HDD is also cheaper per gigabyte comparing to SSD which is good for cost effective storage of large amounts of data.
- High Storage Capacity: HDDs are available in higher capacities than that of Floppy disks are available making them ideal for application by people who require large storage facilities such as multimedia.
- Availability: HDD has a relatively long history of usage and that is why it is widely supported by the majority of devices.
Disadvantages of HDD
- Slower Speed: Due to the mechanical design of the actuator, have relatively low I/O data rates in comparison to SSDs.
- More Fragile: As compared to SSDs, HDDs have higher chances of getting damaged due to physical shocks or drops this is because they have moving parts.
- Higher Power Consumption: As it is a magnetic disk that continues to spin platters, HDDs have higher power consumption and hence are less energy efficient particularly for portable devices.
What is Solid State Drive(SSD)?
SSDs, on the other hand, use flash memory to store data instead of a spinning disk. SSDs have no moving parts, making them much faster, more durable, and less susceptible to mechanical failure than HDDs.
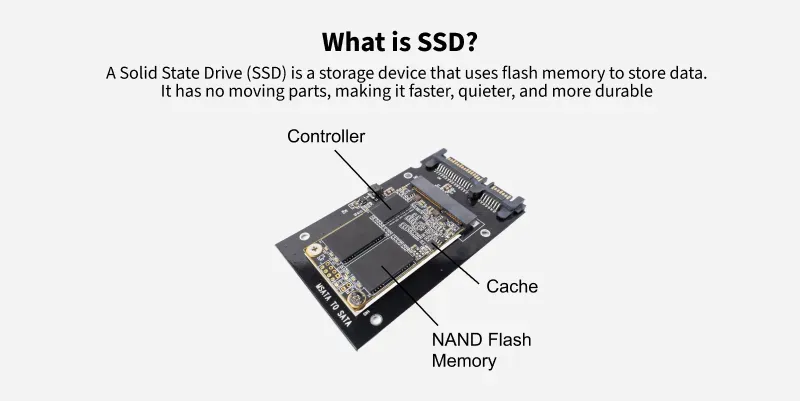
Also read, Solid State Drive(SSD).
How do SSD work?
A Solid State Drive (SSD) stores and retrieves data using flash memory instead of moving parts, making it much faster and more durable than a traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
SSDs use NAND flash memory chips to store data. When you save a file, electrical charges are used to store information in tiny memory cells inside these chips. Each cell retains data even when the power is turned off, allowing the SSD to keep your files permanently. Since SSDs have no spinning disks or moving read/write heads like HDDs, they can access data almost instantly.
When you open a file or program, the SSD's controller quickly finds the required data and sends it to the computer. Because SSDs rely on electronic circuits rather than mechanical parts, they operate silently, use less power, and are more resistant to damage from drops or shocks. Their speed significantly improves computer performance, making tasks like booting up, loading applications, and transferring files much faster compared to HDDs.
Features of Solid State Drive (SSD)
- Fast Performance: SSDs offer much faster data access and transfer speeds than HDDs.
- Compact Size: SSDs are smaller and lighter than HDDs, making them an ideal option for use in portable devices such as laptops and tablets.
- Lower Power Consumption: SSDs consume less power than HDDs, making them more energy-efficient.
- Higher Cost: SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs, making them a less cost-effective option for storing large amounts of data.
- No Mechanical Parts: SSDs have no moving parts, making them more durable and less susceptible to mechanical failure than HDDs.
Advantages of SSD
- Faster Performance: They are also significantly faster than their mechanical counterparts, this in terms of booting up, transmitting files as well as improving on the general performance of any device.
- Durability: Since there is no moving parts, there is low possibility of the SSDDs getting damaged physically and as result are recommendable for use in laptops and other portable devices.
- Lower Power Consumption: Further, SSDs are less power hungry that AT’s, which is important in increasing battery back-up time in laptops and decreasing power consumption in desktops.
Disadvantages of SSD
- Higher Cost: SSDs are still costlier than the HDD per unit of capacity, although the he is reducing every now and then.
- Limited Storage Capacity: While today SSDs exist in larger capacities it should be noted that when it comes to higher storage capacities SSDs are commonly costlier than the HDDs.
Similarities Between HDD and SDD
- HDD and SDD both are used to store data.
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD) are used to boot the system.
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD) Both are I/O devices.
Differences Between Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD)
Here the differentiate table of Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD):
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|
Definition | Uses spinning disks and mechanical parts | Uses electronic components (no moving parts) |
| Storage Technology | Uses spinning magnetic disks for storage. | Uses NAND flash memory with no moving parts. |
| Speed | Slower boot times and file access. | Much faster boot times and file access. |
| Durability | Has moving parts, making it prone to damage. | More durable and shock-resistant. |
| Noise | Produces noise due to spinning disks. | Operates silently. |
| Power Consumption | Consumes more power. | Uses less power, improving battery life. |
| Lifespan | Wears out over time due to mechanical movement. | Lasts longer but has limited write cycles. |
| Cost | More affordable per GB, cost-effective for large storage. | More expensive per GB but offers better performance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for budget-friendly, high-capacity storage. | Best for high-speed computing, gaming, and fast system performance. |
Reliability | Less reliable due to moving parts (e.g., head crash) | More reliable (no moving parts, less risk of failure) |
Data Fragmentation | Performance can suffer from fragmentation | No fragmentation; performance remains consistent |
Conclusion
In Conclusion, both HDDs and SSDs have their advantages and disadvantages. HDDs are a more traditional and cost-effective option for storing large amounts of data, while SSDs offer faster performance, durability, and energy efficiency. The choice between HDD and SSD ultimately depends on the user's specific needs and requirements, such as the amount of data they need to store, their budget, and the device they are using the storage device with.
Similar Reads
Difference between Random Access Memory (RAM) and Hard Disk Drive (HDD) If you’re new to computers, terms like RAM and HDD might sound confusing. Don’t worry! This guide explains what RAM and HDD are, how they differ, and why they matter for your computer’s performance. Whether you’re a high school or college student, this article breaks it down in simple terms to help
5 min read
Difference between OneDrive and Yandex Disk 1. OneDrive : OneDrive or Microsoft OneDrive is a file hosting and synchronization service provided by the Microsoft. It gives the convenience to users for storing files, personal data and for sharing files. It offers 5 GB free storage space. It was launched by Microsoft in 2007. It is mostly used b
2 min read
Difference between Google Drive and Yandex Disk 1. Google Drive : Google Drive is a file storage and synchronization service provided by the Google. It allows the users to store the files and personal data and to share the files. It offers 15 GB free storage space. It was launched by Google in 2012. It is used by almost each and every person whic
4 min read
Difference between Hard Disk and Floppy Disk In computer two prominent types of storage devices that have been widely used are hard disk and floppy disk. A hard disk is a high-capacity, durable storage device that uses magnetic disks to store data, offering faster access and larger storage compared to a floppy disk, Where as Floppy disks are p
5 min read
Difference between Amazon Drive and Yandex Disk 1. Amazon Drive : Amazon Drive is a file hosting service and cloud storage provided by Amazon. It allows cloud storage, file hosting, file sharing and file backup. File and folders on this drive can be transferred from multiple devices like desktop, mobile and tablets. Amazon Drive was initially kno
2 min read